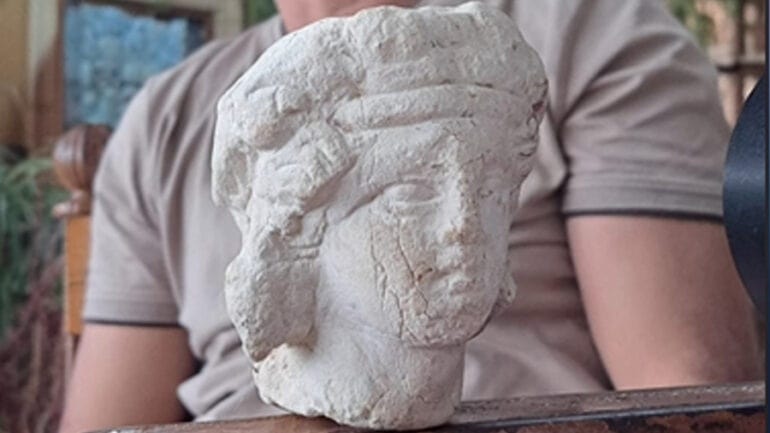
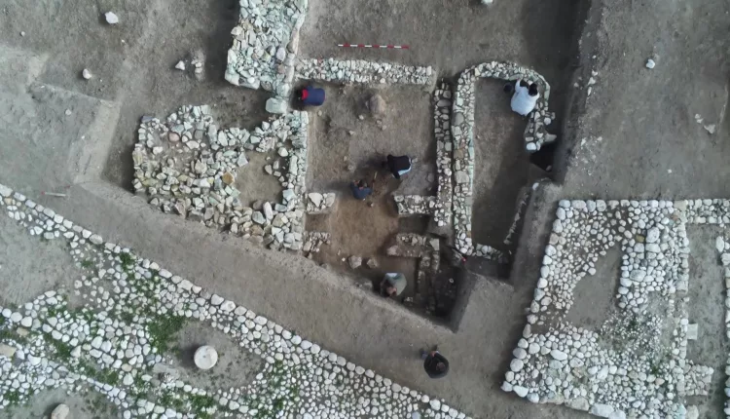
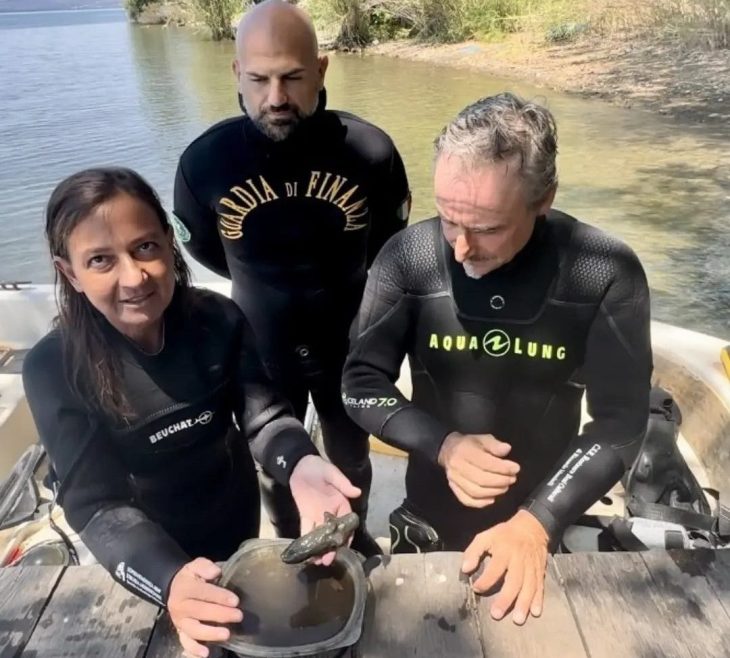
Libyan Archeology researcher, Issam Menfi found the head of the statue of Bacchus, which dates back to the Greek era, inside a water channel near the ancient city of Cyrene.
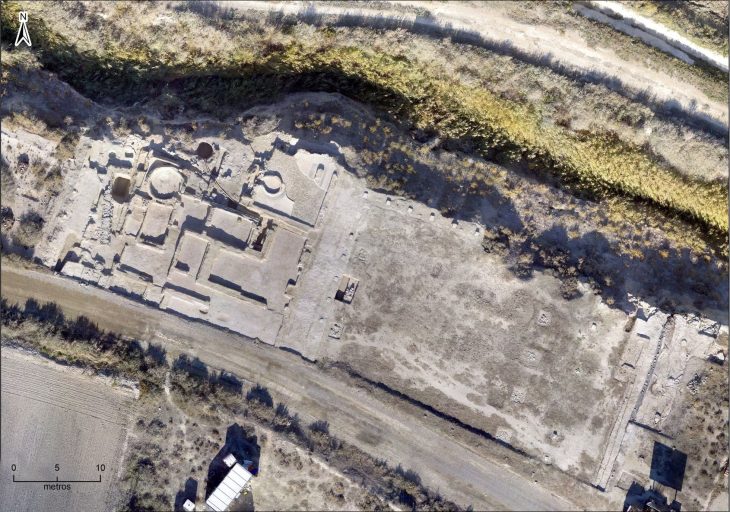
Set back from the Meditteranean shore in the foothills of the al-Jabal al-Akhdar region, the ancient city of Cyrene. Located today in Shahhat in eastern Libya, Cyrene was founded in 631 BC by a group of emigrants from the Greek island of Thera located in the Aegean Sea.
Battus, their first king, founded the dynasty of the Battiads, which ruled Cyrene for eight generations (until 440 BC). Under the rule of the Battiads, the city prospered economically and expanded to include several ports known today as Marsa Susah, al-Marj, and Benghazi.
However, with the rise of Ptolemaic Egypt in 323 BC, Cyrene became one of the classical world’s most intellectually influential centers. With a medical school and great philosophers, Cyrene eventually piqued the Romans’ interest and came under their control in 96 BC. The province of Cyrenaica was united with Crete in 67 BC, making Cyrene the local capital.

Cyrene experienced two centuries of relative peace and prosperity under Roman rule, which was interrupted by a revolt by Cyrene Jews in 115 AD, resulting in the city’s steady decline. Cyrene’s ongoing decline was exacerbated by a significant earthquake in 365 AD. The Arab conquest of 642 AD sealed the city’s fate, leaving it in ruins that can still be found today.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The third artifact discovered as a result of storm “Daniel” that hit the eastern region last September, according to the Libyan News Agency, was saved by Menfi for scientific purposes.
The agency further stated that the head of the statue is that of the figure “Bacchus,” also known as “Dionysus” and “Bacchus” in the Roman era, who is their god of wine. It was given to the Cyrene Antiquities Control Authority.
Bacchus was the god of agriculture and wine, but he was also linked to fertility, drama, and revelry. In regards to agriculture, he was depicted as a god of trees and forest, and was often sought ought to help the orchards grow.
Cover Photo: Libyan News Agency