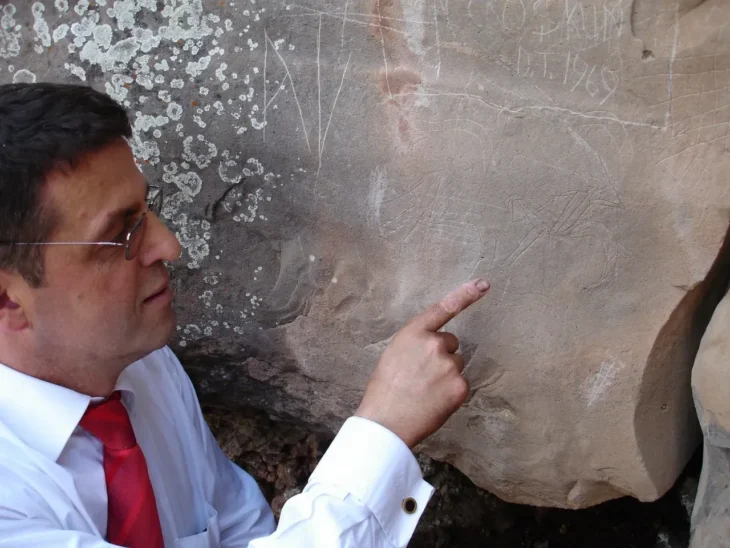
A research team at the University of Cologne’s Department of Linguistics deciphered a writing system belonging to the Kushan Empire, one of the influential states in the history of Central Asia.
The unknown Kushan script has puzzled academics for over seventy years, and now a team of early career researchers at the University of Cologne has managed to decipher it.
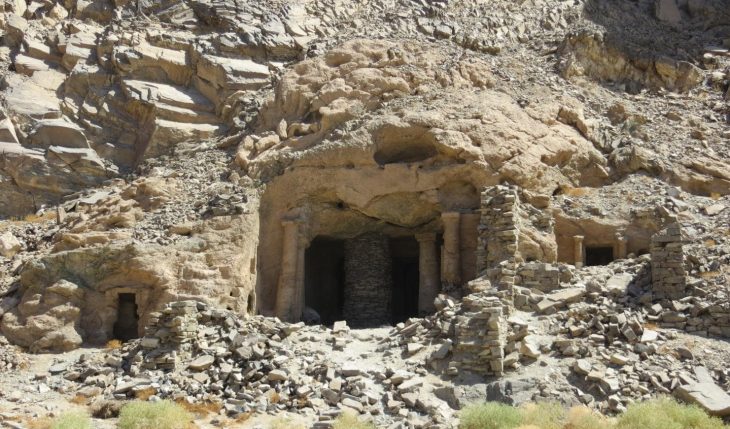
Over a period of several years, Svenja Bonmann, Jakob Halfmann, and Natalie Korobzow examined photographs of inscriptions found in caves as well as characters on bowls and clay pots from various Central Asian countries in order to put the pieces of the puzzle together.
On 1 March 2023, they first announced their partial decipherment of the unknown Kushan script at an online conference of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Tajikistan. Currently, about 60 percent of the characters can be read, and the group is working to decipher the remaining characters. A detailed description of the decipherment has now been published in the journal Transactions of the Philological Society under the title ‘A Partial Decipherment of the Unknown Kushan Script’.
New discovery led to breakthrough
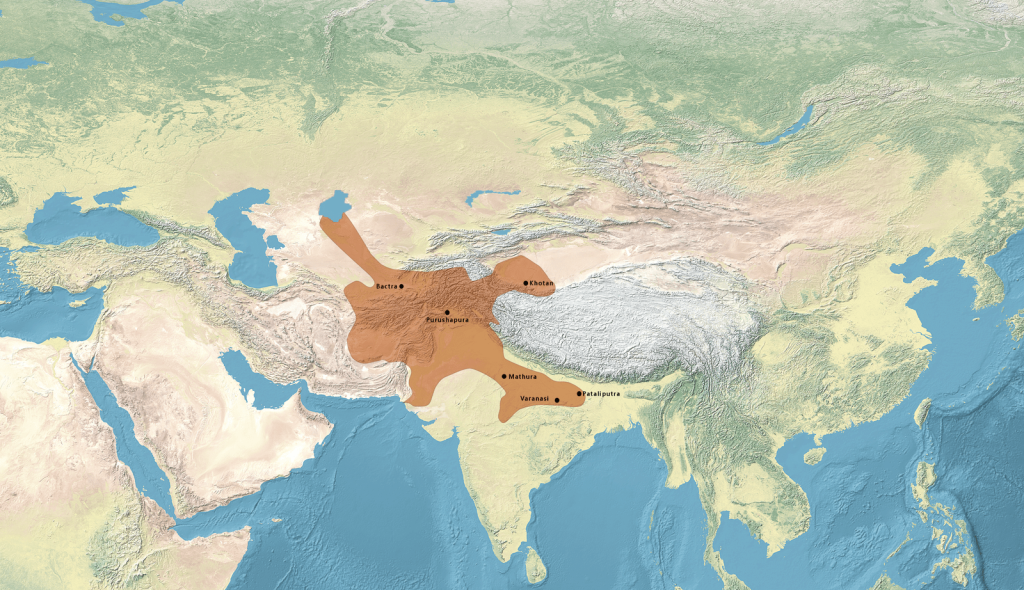
The ‘unknown Kushan script’ is a writing system that was in use in parts of Central Asia between about 200 BCE and 700 CE. It can be associated with both the early nomadic peoples of the Eurasian steppe, such as the Yuèzhī, and the ruling dynasty of the Kushans. The Kushans founded an empire which, among other things, was responsible for the spread of Buddhism to East Asia. They also created monumental architecture and artworks.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
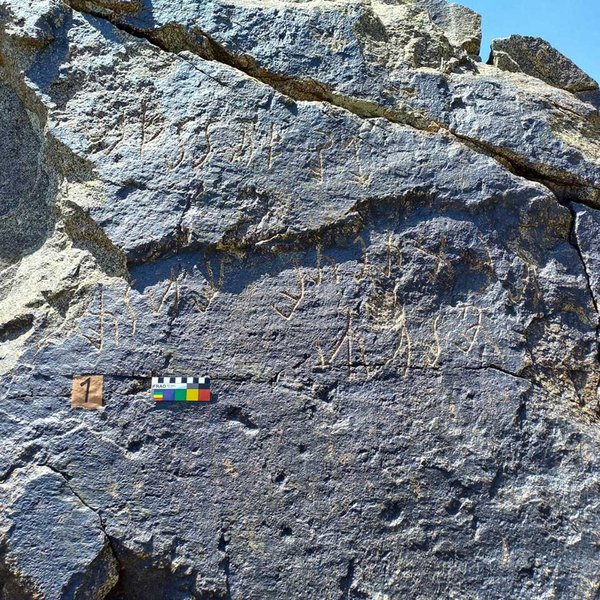

So far, several dozen mostly short inscriptions are known, most of them originating from the territory of the present-day states of Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Uzbekistan. There is also a longer trilingual that was found by French archaeologists in the 1960s at Dašt-i Nāwur in Afghanistan: on a boulder at 4,320 m altitude on Mount Qarabayu, approximately 100 km southwest of Kabul.
The writing system was has been known since the 1950s, but had never been successfully deciphered. In 2022, a short bilingual was found carved into a rock face in the Almosi Gorge in northwestern Tajikistan, approximately 30 km from the capital Dushanbe. In addition to the unknown Kushan script, it also contains a section in the already known Bactrian language. This discovery led to renewed attempts by several researchers to decode the script – independently of one another. In the end, the linguists at the University of Cologne succeeded in partially deciphering the writing system in collaboration with the Tajik archaeologist Dr. Bobomullo Bobomulloev, who was instrumental in the discovery and documentation of the bilingual.
Success 200 years after the deciphering of the Egyptian hieroglyphs
The team applied a methodology based on the way unknown scripts have been deciphered in the past, i.e. the Egyptian hieroglyphs using the Rosetta Stone, ancient Persian cuneiform script or Greek Linear B script: Thanks to the known content of the bilingual inscription found in Tajikistan (Bactrian and unknown Kushan script) and the trilingual inscription from Afghanistan (Gandhari or Middle Indo-Aryan, Bactrian and unknown Kushan script), Bonmann, Halfmann and Korobzow were able to gradually draw conclusions about the type of writing and language.
The breakthrough was finally made possible by the royal name Vema Takhtu, which appeared in both Bactrian parallel texts, and the title ‘King of Kings’, which could be identified in the corresponding sections in the unknown Kushan script. The title especially proved to be a good indicator of the underlying language. Step by step, using the Bactrian parallel text, the linguists were able to analyse further character sequences and determine the phonetic values of individual characters.
Key to a better understanding of Kushan culture
According to the research group, the Kushan script recorded a completely unknown Middle Iranian language, which is neither identical to Bactrian nor to the language known as Khotanese Saka, which was once spoken in western China. The language probably occupies a middle position in the development between these languages. It could be either the language of the settled population of northern Bactria (on a part of the territory of today’s Tajikistan) or the language of certain nomadic peoples of Inner Asia (the Yuèzhī), who originally lived in northwestern China. For a certain period of time, it apparently served as one of the official languages of the Kushan Empire alongside Bactrian, Gandhari/Middle Indo-Aryan and Sanskrit. As a preliminary name, the researchers propose the term ‘Eteo-Tocharian’ to describe the newly identified Iranian language.
The group is planning future research trips to Central Asia in close cooperation with Tajik archaeologists, as new finds of further inscriptions are to be expected and promising potential sites have already been located. First author Svenja Bonmann remarked, “Our decipherment of this script can help enhance our understanding of the language and cultural history of Central Asia and the Kushan Empire, similar to the deciphering of the Egyptian hieroglyphs or Mayan glyphs for our understanding of ancient Egypt or Mayan civilization.”
















