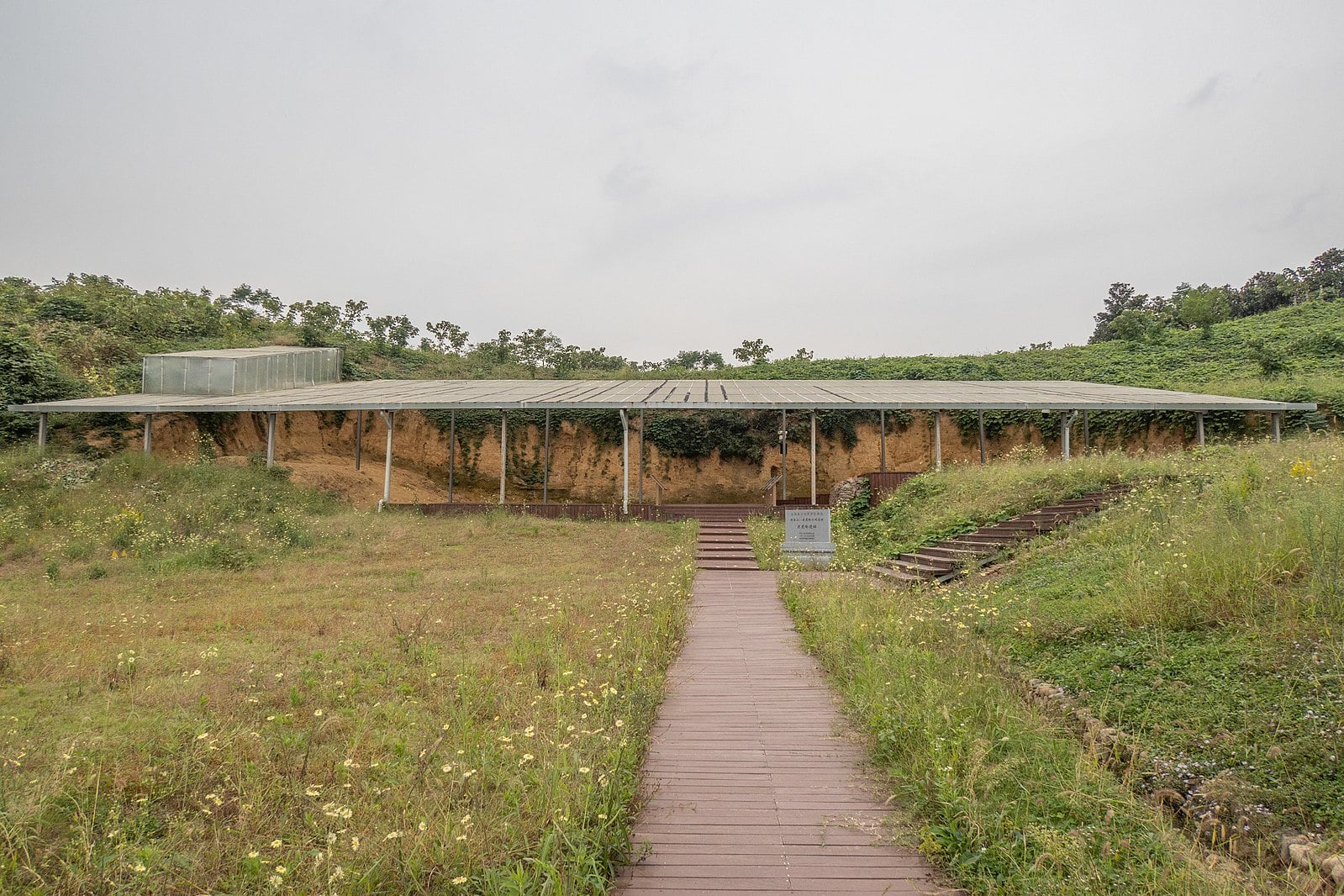
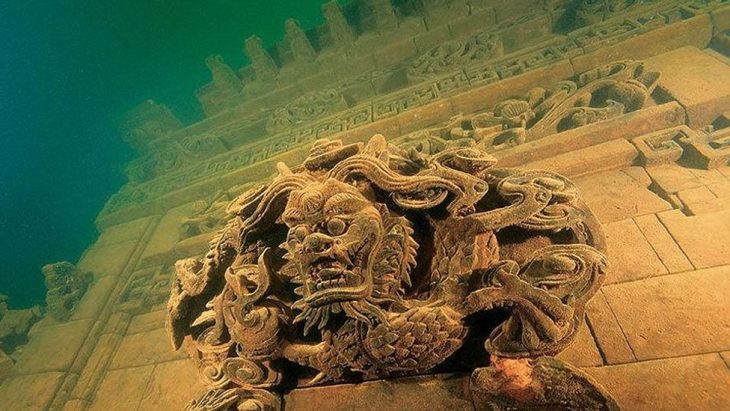
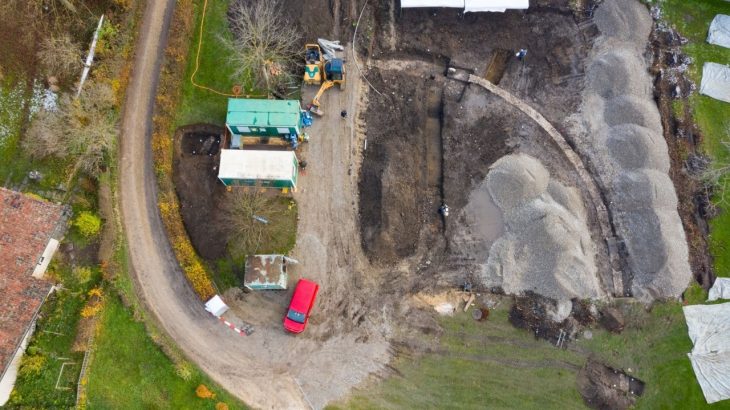
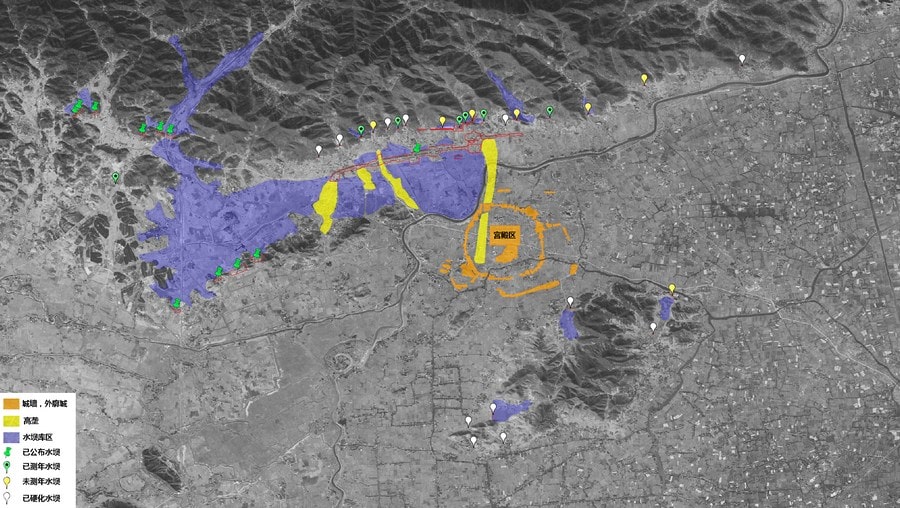
In recent excavations around the Liangzhu Ruins in east China’s Zhejiang Province, researchers have discovered about 20 ancient dams. Seven of these newly found dams can be dated around 5,000 years ago and are part of the same local water conservancy system.
Located in the Yangtze River Basin the archaeological ruins of Liangzhu (about 3,300-2,300 BCE) reveal an early regional state with a unified belief system based on rice cultivation in Late Neolithic China.
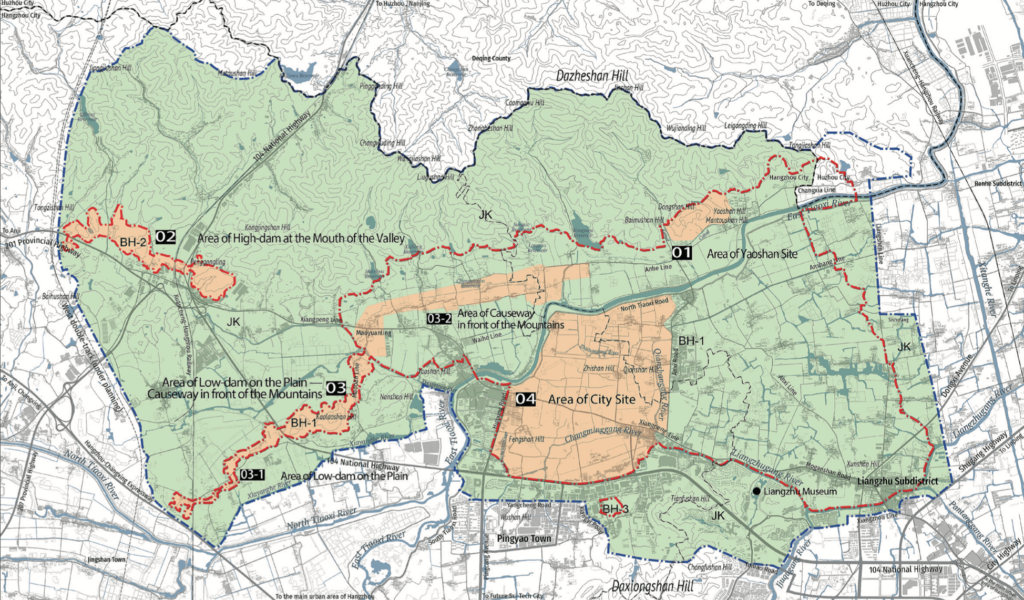
Four areas make up the property: the Yaoshan Site Area, the High-dam Area at the Valley Mouth, the Low-dam Area on the Plain, and the City Site Area. With their earthen monuments, urban planning, water conservation system, and distinct burials in the property’s cemeteries, these ruins are a superb illustration of early urban civilization.
Previous studies have found China’s hitherto earliest large-scale water conservancy system in the northwest of the Liangzhu ancient city.
“Following the confirmation of 11 dams around the outer water conservancy systems of the Liangzhu Ruins in earlier studies, archaeologists have recently discovered more than 20 additional dams by making use of technology such as remote sensing, geographic information systems, and artificial intelligence. This discovery has essentially revealed the complete layout of the Liangzhu water system,” said Chen Guangsheng, director of the Culture, Radio, Television, and Tourism Department of Zhejiang Province, at a press conference for the second Liangzhu Forum.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The construction of dams can be seen as one of the hallmarks of the Liangzhu civilization’s advanced development 5,000 years ago. Only early forms of state-level societies could have undertaken such monumental engineering projects,” Liu Zheng, a member of the China Cultural Relics Academy, told the Global Times.
“Discovering hydraulic engineering sites is one of the challenges in archaeological work. However, the use of advanced technology has introduced innovation into the field of archaeology, making it easier to advance research,” he said.
“Surprisingly, one of the dams had stones built on its side slope facing the water, supposedly a specific measure to cope with the impact of the transient floods,” said Wang Ningyuan from the provincial institute of cultural relics and archaeology, who is also in charge of the archaeology project on the Liangzhu ancient city and its water conservancy system.
The recent findings have provided a preliminary understanding of the Liangzhu ruins’ three development phases, which began with scattered settlements and progressed to the construction of a water conservancy system and, eventually, the erection of the Liangzhu ancient city.
Early Liangzhu settlements demonstrated distinct social stratification, with smaller villages making use of the mountainous terrain to grow. The site, however, exhibited a scattered, multi-centered pattern and lacked a cohesive plan.
Large ceremonial areas were built in the middle of the site by the middle phase, showing a centralized planning concept and keeping a constant distance of roughly three kilometers from the neighboring mountains. A well-structured ancient urban system was formed in the latter stages as the building of city walls and external defenses proceeded.
The research findings confirm the revolutionary changes in the structure of the Liangzhu site in different periods and show the clear process of social organization and evolution at the early state level, the press conference said.
Archaeological findings have revealed the evolution of the concept of settlement management and urban construction, as well as the belief system of the Liangzhu people.
Cover Image: Liangzhu High Dams.