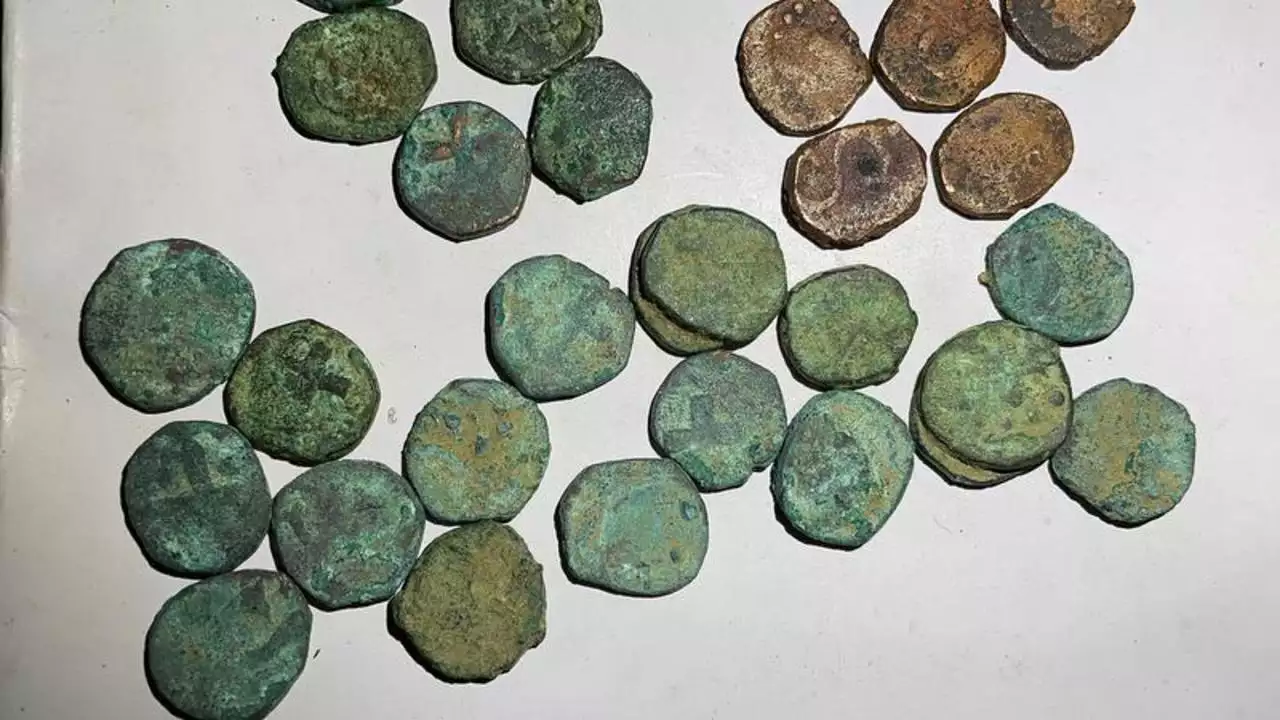
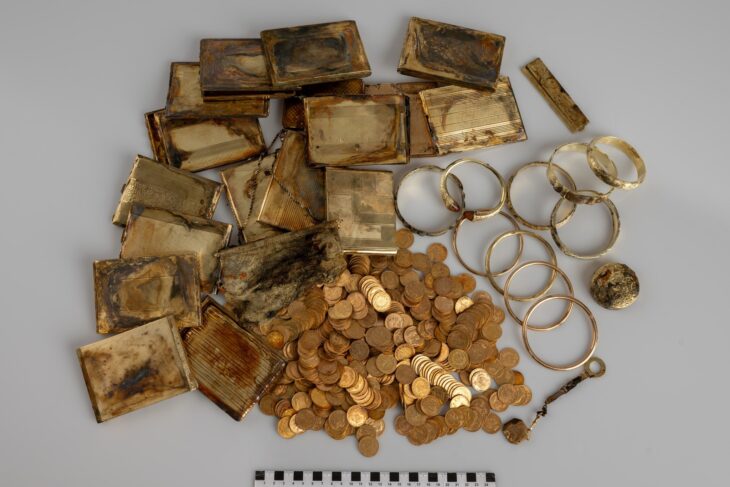
In Sattari, Nanoda, in the state of Goa on the west coast of India, 832 copper coins that are believed to be from the 16th or 17th-century Portuguese era were found at a cashew farm.
Vishnu Shridhar Joshi, a farmer in Nanoda Bamber village, was clearing weeds at his cashew plantation a fortnight ago when he noticed a pot buried in the soil. After a little digging, Joshi discovered a vessel containing coins from a bygone era.
He handed over the coins to a team of state archaeologists. The Goa archaeology department, headed by Minister Subhash Phal Dessai, is preparing to carbon-date the coins to determine their exact age and historical context.
“A treasure has been discovered,” said director of archaeology Nilesh Fal Desai. “The coins are connected to the history of Goa’s erstwhile kingdoms and the people of the time. Prima facie, the coins are from the 16th or 17th century.”
Joshi had unknowingly discovered a “treasure” from centuries ago — 832 copper coins believed to have been minted in Goa around the 16th or 17th century when it was under Portuguese rule.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Goa was a Portuguese colony from 1510 to 1961. The small coastal area was conquered by Afonso de Albuquerque (c. 1453-1515) and became an important trade hub for the Eastern spice trade. For 450 years, Goa was the capital of the entire Portuguese Empire east of the Cape of Good Hope.
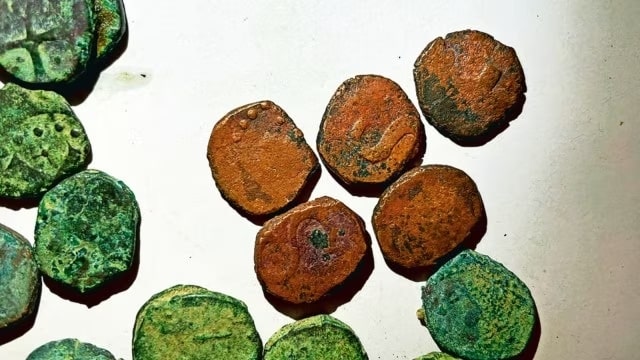
The rare discovery is now part of a study that will be undertaken by the state’s Department of Archaeology, which could offer insights into trade relations, commerce, and the economic history of Goa during the early years of Portuguese rule.
Officials said the “buried treasure” could offer insights into Goa’s numismatic history.
“Prima facie, from the alphabets and symbols, it appears that the coins were issued in the 16th-17th Century during the early years of Portuguese rule. On some coins, one side has a cross and an alphabet, which could be interpreted as the initials of a king, under whose kingdom the coins may have been circulated,” said Dr Nilesh Fal Dessai.
Joshi said the earthen pot was found at Haddiche Bharad situated on a hillock about 1km from the Kalasa nullah site.
The coins are expected to offer historical riches because they were found on the Ghat pathway connecting British India with Portuguese India.
Under Indian law, a treasure trove (buried treasure that has been lost or forgotten) is considered the government’s property. The law requires anyone who discovers such treasure to report to the authorities.