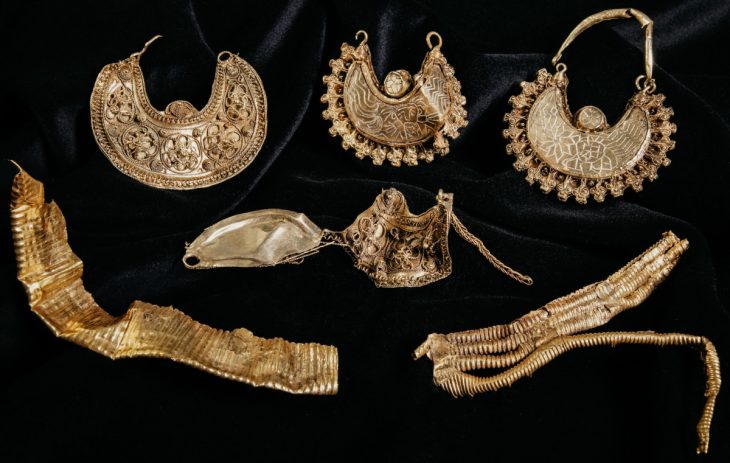
Illyrian Queen Teuta is one of the most extraordinary figures of Illyrian antiquity and of Albanian heritage. She was also called the pirate queen, and folklore says that she was wiser than a snake, braver than a lion, and more beautiful than fairies.
Bordered by the Adriatic Sea to the west and the Morava River to the east, Illyria corresponds to parts of modern-day Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Slovenia, Montenegro, Kosovo, Serbia, and Albania.
Teuta was the first child of a noble Illyrian family and was born around 268 BC. She received a traditional education but was also trained as she was a boy, learning the art of war, hunting, horse riding, etc.
The ancient Illyrians, like the Spartans, encouraged their women to learn the arts of war and fighting skills. Teuta rose to fame as a rare beauty, and the heir to the throne chose her as his wife and queen.
Teuta, who was married to King Agron, was a good warrior first and foremost: aggressive and hotheaded, with a strong sense of justice. Teuta’s marriage with King Agron lasted for 18 years, which was a time of great political, economic, and military advancement for the Illyrian kingdom.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Teuta ascended the throne in 231 BC.. After the death of her husband Agron, she ruled in the name of her minor stepson Pinnes, and at that time the powerful Illyrian state stretched from the left bank of the Neretva to Epirus, encompassing all the islands except Vis.
Within a short time Teuta managed to strengthen and consolidate her power, made powerful allies, and continued further the reforms of her husband. She stimulated the economy, promoted the development of Illyrian cities, strengthened the army, and created her own navy, through the creation of Liburnian ships.
Teuta managed to expand the borders of her kingdom, after defeating the Greek army and taking Phoenicia, the richest and most important city of Epirus. Not only she controlled the Adriatic Sea, but after her military success, she gained control of Ionian Sea. The people started calling Teuta the “Queen of Seas”.
However, perhaps more so even than her powerful navy, Teuta’s most feared forces were the Illyrian pirates that roamed the nearby seas. Interestingly, piracy was completely legal in Illyria and even considered a viable if not respectable profession. Teuta gave her ships free reign in the Mediterranean Sea.
Her political and military empowerment in such a short time, in the region was disturbing to Rome. The Senate found unacceptable the rivalry of such a powerful woman, who had great ambitions.

Rome had already turned its attention to its eastern neighbors following the historic victory at Cartagena. Illyria and its possessions at sea were among Rome’s main objectives due to their strategic importance. The senators used the attacks on Roman merchant ships by Illyrian pirates as an excuse to launch the next military campaign.
At first, the Romans tried the diplomatic route. They sent two ambassadors to Illyria to convince Teuta. But when they got there, Teuta refused, informing them that piracy was not illegal in the Ardiaean Kingdom.
Teuta was apparently so offended by the Roman envoys that she commandeered their ships. What’s more, she held one ambassador captive and killed the other one. This action of hers was enough for Rome to use as a pretext to start the war.
The queen fought heroically and blocked the entire coast. She also won numerous battles against the Roman army, which in number was twice as large as the Illyrian army. To defeat the warrior queen, Romans used different tricks. Teuta was betrayed by one of her most powerful and trustful commanders, Demetrius of Pharos, who had claims upon the thrones.
Although betrayed and in unequal conditions, Teuta and her army continued fighting for another 6 months against the Romans. Unable to continue her resistance, Teuta was forced to accept a peace treaty with the Roman ambassadors, retreating to the Illyrian city of Rizan, fearing that Scutari (today Shkodra), the capital of the Ardian kingdom, might fall to the Romans.
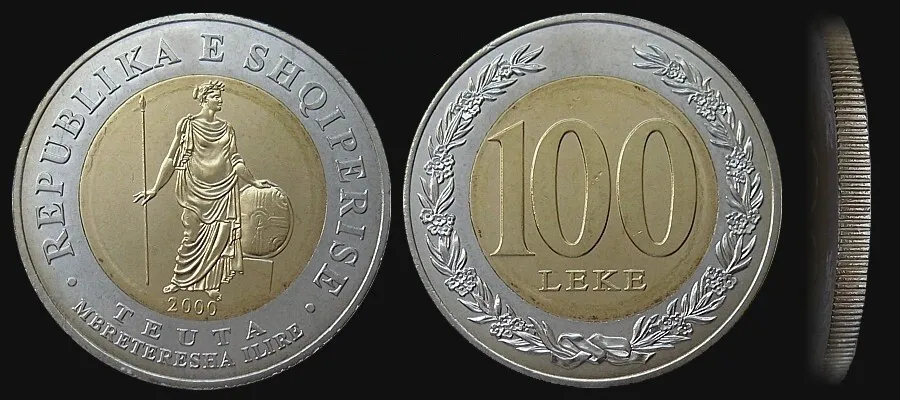

Despite being defeated, Teuta was able to negotiate with Roman delegates to improve the terms of peace for the Illyrians. The queen’s negotiations later provided the Illyrians with the opportunity to recover economically and militarily, giving impetus to a second war against Roman occupation. However, Teuta did not return to the throne and the historical data for what happened to her after this period are a few and uncertain.
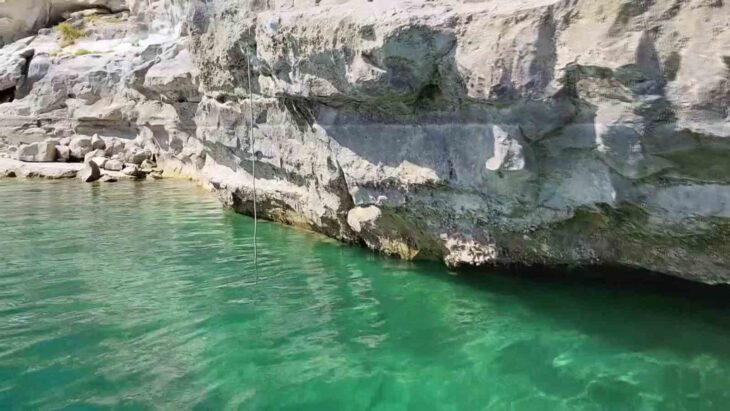
The most popular account tells that Teuta eventually ended his life by jumping off a cliff in the Bay of Kotor, in modern-day Risan, Montenegro.
According to legend, Risan was cursed by the queen’s passing and is now the only town in the area without a maritime heritage. However, the exact circumstances surrounding Teuta’s death have never been confirmed.
Despite her tragic end, Teuta made an indelible mark on history. Indeed, even after her fall from grace, Illyria defied Rome for decades. It would not be until the Third Illyrian War in 168 B.C.
















