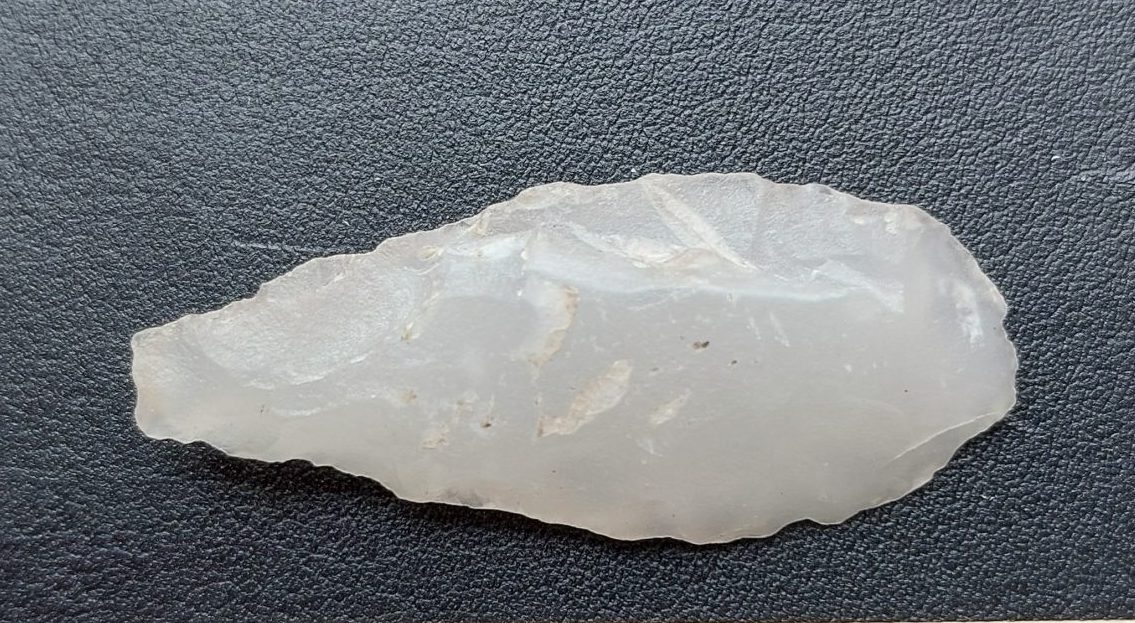
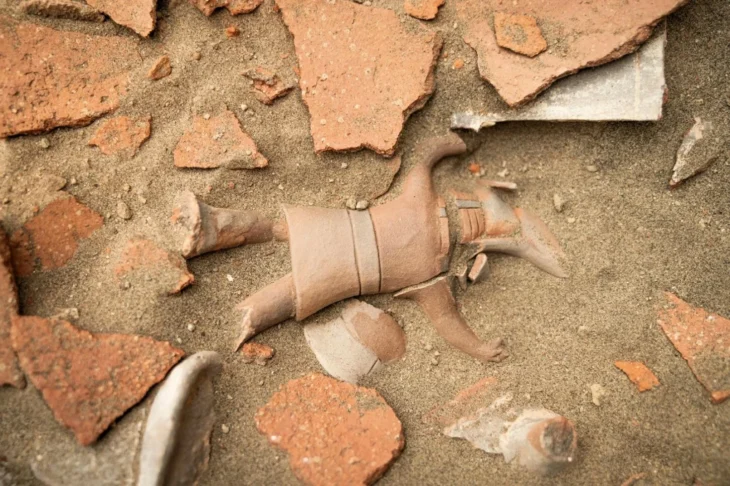
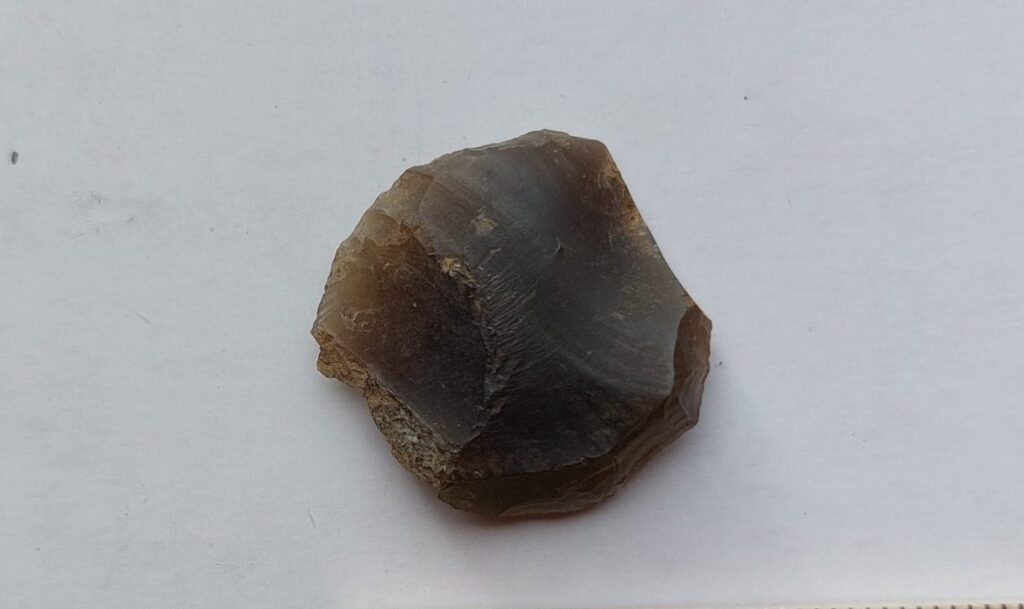
A bifacially crafted arrowhead made of white quartzite has become the most remarkable discovery at an archaeological excavation in northern Sweden. Unearthed at the Hedkammen ridge, just south of Bureå, this rare artifact reveals exceptional skill and craftsmanship, pointing to advanced prehistoric technology and long-distance material exchange networks over 2,500 years ago.
A Unique Artifact in the North
The arrowhead is not only finely made but also carved from white quartzite, a material rarely used for such tools in this region. Its symmetrical form, sharp edges, and bifacial pressure-flaking technique suggest it was not just a utilitarian object, but potentially a high-status item or used in ceremonial contexts. Given the precision required to shape quartzite, the find showcases the technological capabilities of prehistoric communities in northern Scandinavia during the Late Bronze Age or Early Iron Age.
“This is prehistoric craftsmanship at its finest,” says Olof Östlund of Skellefteå Museum, who is documenting the excavation.
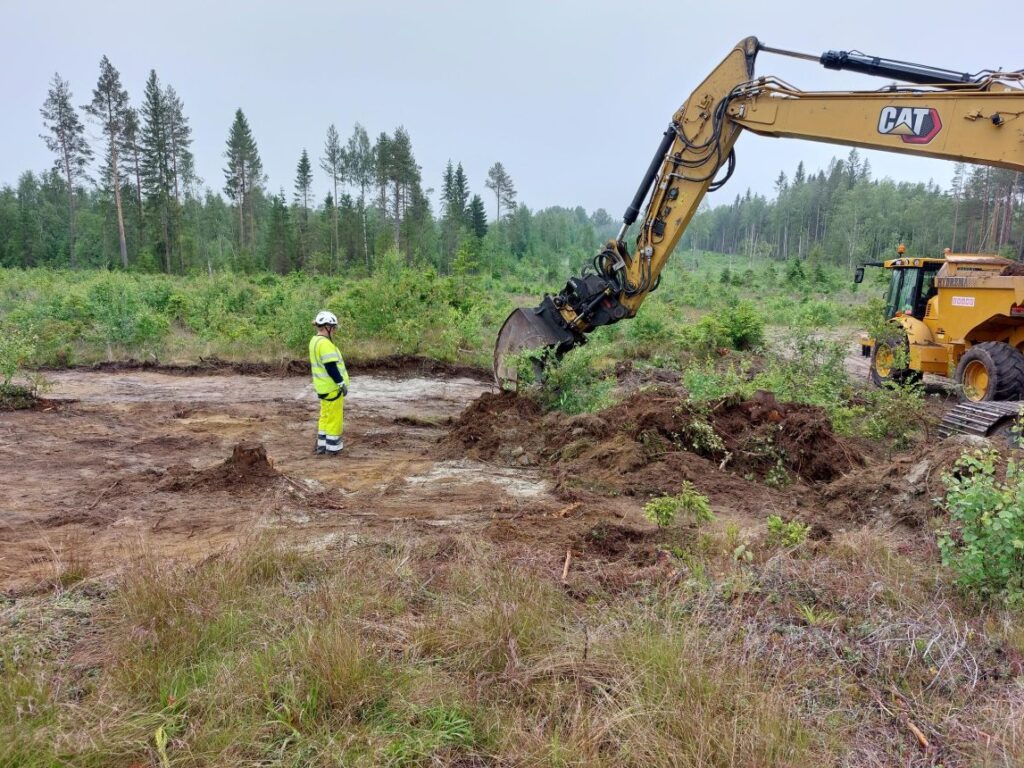

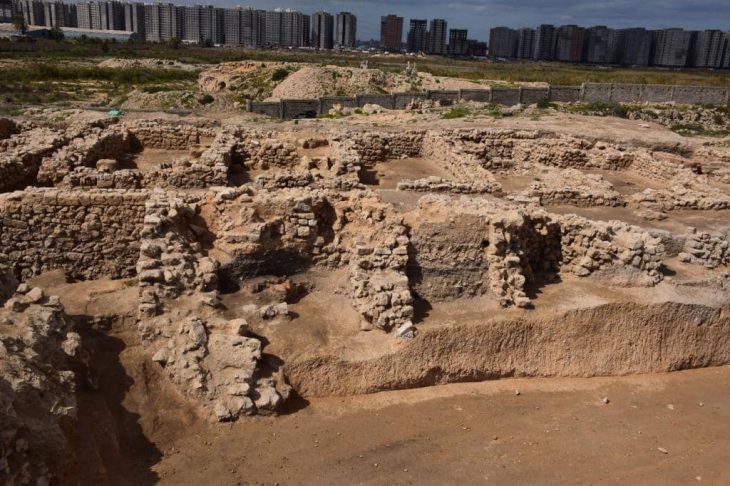
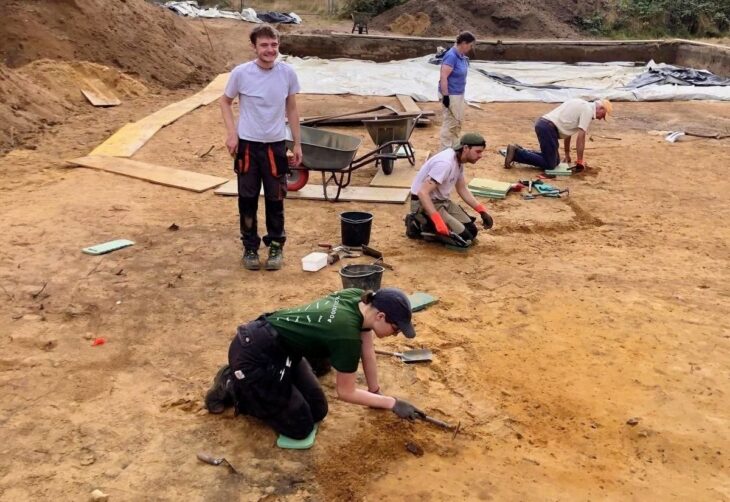
Large-Scale Excavation Reveals Over 300 Features
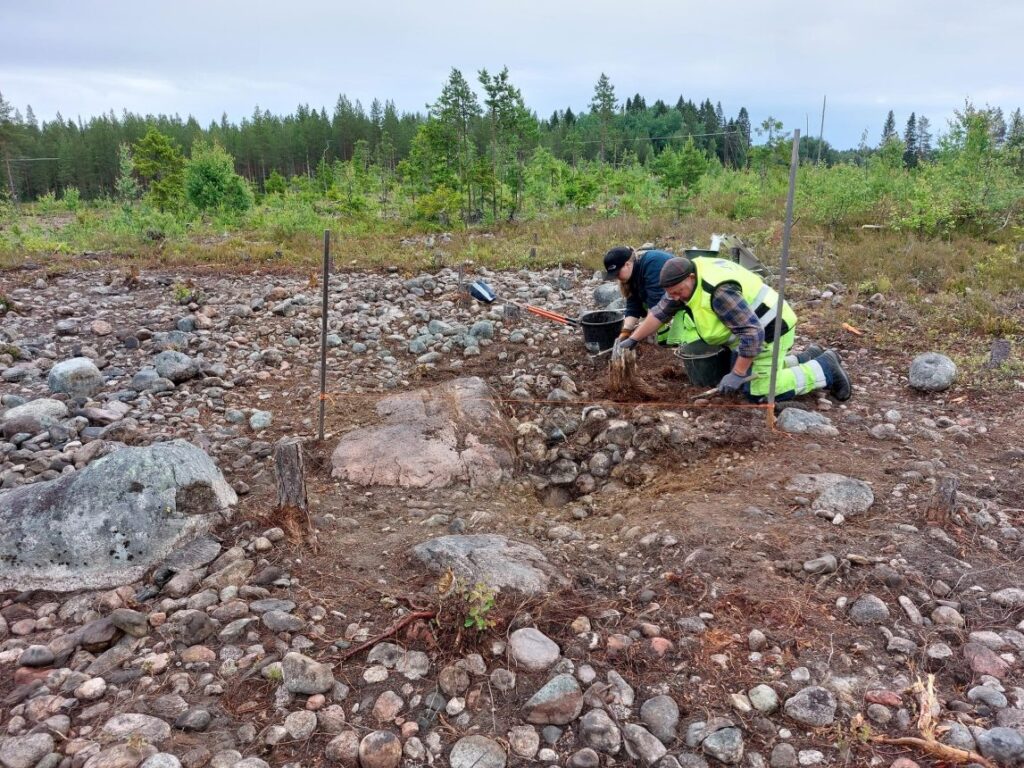
The arrowhead is part of a broader excavation project at Hedkammen, where archaeologists have cleared 16,000 square meters across two main areas on either side of the ridge. So far, the team has registered about 300 archaeological features, including:
Hearths
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Cooking pits
Fire-cracked stone clusters
Red-burnt sand features
Stone alignments likely linked to ancient boat landings or storage structures
Many of these features are located near natural harbors that were likely in use around 500 BCE, reinforcing the idea of Hedkammen as a coastal activity center during prehistoric times.

Traces of Life from 500 BCE to the Middle Ages
The excavation has revealed signs of continuous human presence from around 500 BCE to the late medieval period. Alongside the arrowhead, archaeologists have uncovered:
Burnt bones
Asbestos-tempered and mica-tempered ceramics
Stone tools and flakes in quartz, quartzite, flint, and slate
Flint scraper tools—rare in the region
One flint flake shows a polished surface, suggesting it may have originated from a reworked axe, possibly imported from Denmark, as previous chemical studies of similar flint tools in northern Västerbotten have shown. This points to trade or contact routes between Scandinavia’s southern and northern regions during the prehistoric era.
In addition, archaeologists discovered foundation stones (syllstenar) once used for timber buildings, possibly from a later settlement phase, adding another layer to the site’s historical significance.

Burial Monuments and Public Engagement
The site also contains four stone cairns (burial mounds)—two of which were previously excavated in the 1990s. Work has already begun on the remaining two, which may offer further insight into prehistoric burial practices.
To engage the public, guided tours are being held every Wednesday in July, from 1:00 PM to 2:00 PM. The first event attracted around 75 participants, demonstrating strong local interest in archaeology and cultural heritage.
Collaboration Driving Discovery
The excavation is a joint effort between Arkeologerna, Västerbottens Museum, and Skellefteå Museum. The collaboration has been praised for its smooth execution and knowledge-sharing among professionals.
“It’s incredibly valuable to learn from one another and to uncover history together,” says Östlund.
Cover Image Credit: Bifacially flaked arrowhead made of white quartzite. Arkeologerna