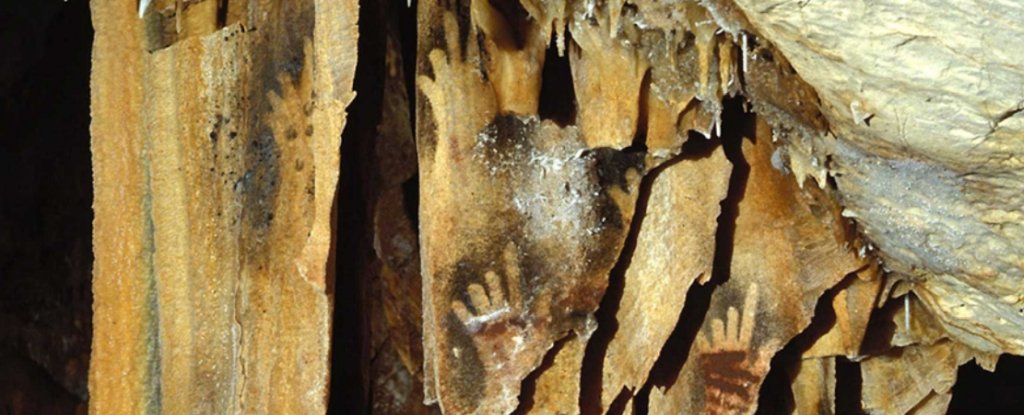
Researchers who examined prehistoric cave art in France and Spain, a new interpretation of Paleolithic cave art proposes that prehistoric people cut off their fingers for religious rituals.
Professor Mark Collard and PhD candidate Brea McCauley of Simon Fraser University’s (SFU) Department of Archaeology have considered over 200 hand images with one or more missing fingertips from caves in France and Spain attributed to the Gravettian people — an Upper Paleolithic hunter-gatherer population that lived on the European landmass.
In some cases, only a segment of the finger is missing, while in others several fingers have been lost. For many years, this peculiarity has been the subject of intense debate. How did they get that way? Since we humans rely heavily on our hands, it seems like it would be exceptionally careless for so many individuals to lose so many fingers accidentally.
That’s why many archaeologists have concluded that the missing fingers are deliberate. But how, and why, has proven trickier to pin down. Some archaeologists argue that the artists merely folded their fingers down, painted over parts of the stencil, or resulted from medical issues such as frostbite.
Collard and McCauley have argued since 2018 that the lost phalanges were intentional body modifications by cross-referencing examples present in other cultures.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Because finger amputation was not an uncommon practice in certain cultures and societies, the researchers wondered if there was any link that could be made to explain the Upper Paleolithic hand images.
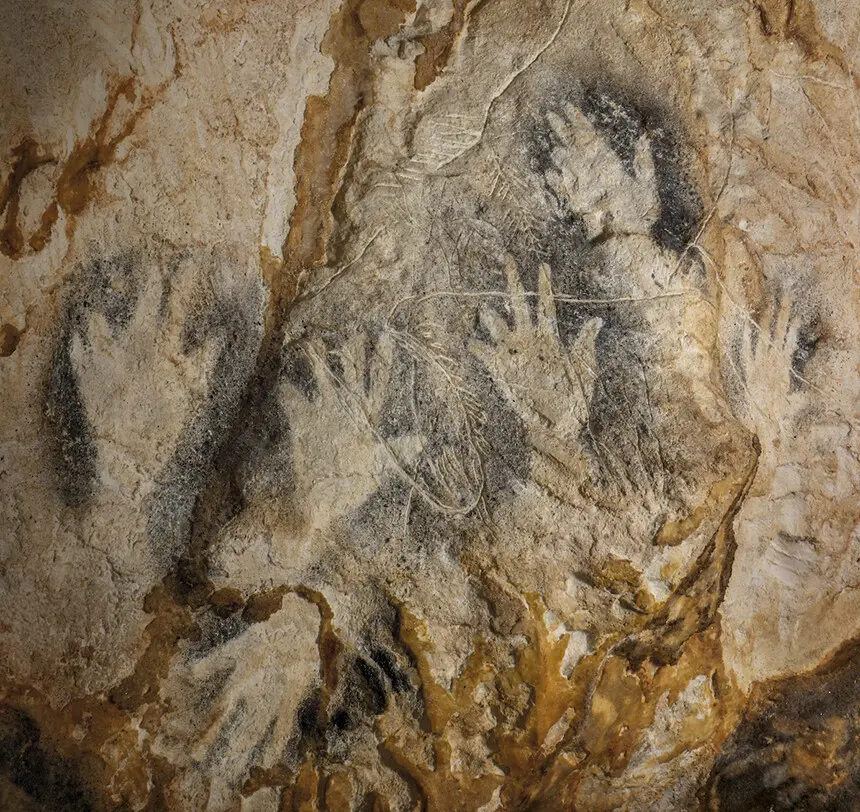

Looking into existing research of 10 documented motivations for finger amputation from a over 100 cultures across all continents, Collard and McCauley concluded that the presentation of shortened fingers in Gravettian hand images was most likely evidence of a religious sacrificial ritual to elicit help from a higher power, or a social survival ritual that strengthened bonds and loyalty within the group and fostered hostility toward outsiders.
In response to criticisms of their 2018 conclusion, particularly the “catastrophic” impact of amputations to the middle and ring fingers during the late Ice Age versus that of the little finger which is most commonly cut across cultures, the SFU researchers conducted further research to back their claim and presented additional evidence this year at a European Society for the Study of Human Evolution meeting.
The researchers reviewed many different historical texts including travel journals, expedition archives, and ethnographic documents to find evidence of societies that engaged in “phalangeal amputation” or the intentional removal of fingers and created a taxonomy of amputation practices around the world.
At Grotte de Gargas in Hautes-Pyrénées in France, 231 hand stencils have been recorded, made by around 45-50 individuals. Of these, 114 are missing one or more digits.
At Cosquer Cave, also in France, 28 of 49 hands are missing digits. And at Maltravieso in western Spain, 61 of 71 hand images are missing digits.

There’s also evidence to suggest that there were people with missing fingers making the art. At Grotte de Gargas, archaeologist C. Barrière reported in 1976, there are impressions of human limbs found in hardened mud – some of which are distinctly missing digits. These impressions are thought to be the same age as the hand stencils.
The reasons for finger amputation ranged from sacrificial, to a type of punishment, to a sign of mourning.
Collard told New Scientist that he and his team hypothesize that the Upper Paleolithic hand images were the result of a religious sacrifice or mourning.
“The idea that the hand images reflect sacrifice is consistent with the way that cave art has been interpreted by many researchers over the years,” said Collard. “Cave art is often in dark, hard-to-access parts of caves, which is consistent with them being part of some sort of dysphoric ritual.”
Cover Photo: Jean Clottes/McCauley et al./Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology