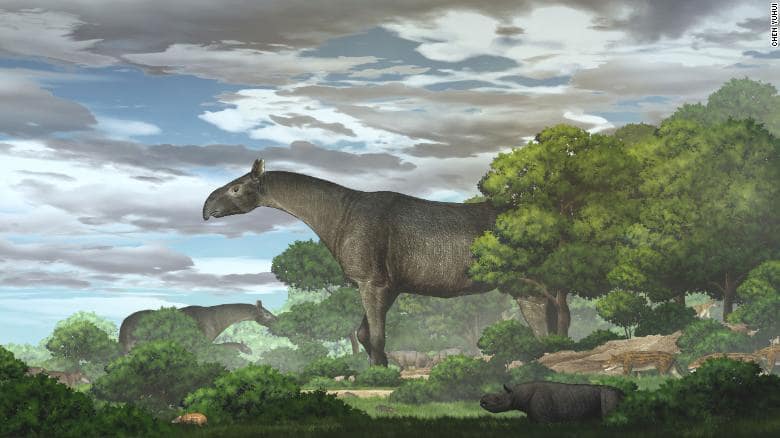
Paleontologists studying in China have found a new species of gigantic rhinoceros, the world’s biggest land animal.
According to a press release issued by the Chinese Academy of Sciences on Friday, giant rhinos, known as Paraceratherium, were mostly located in Asia.
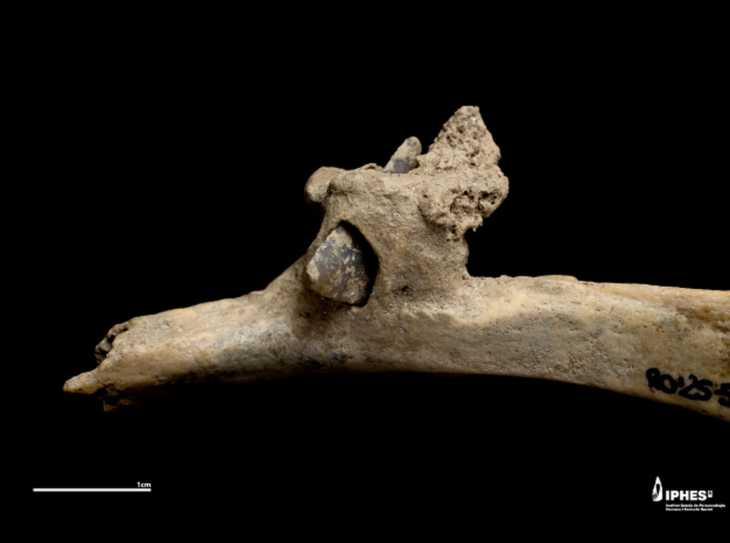
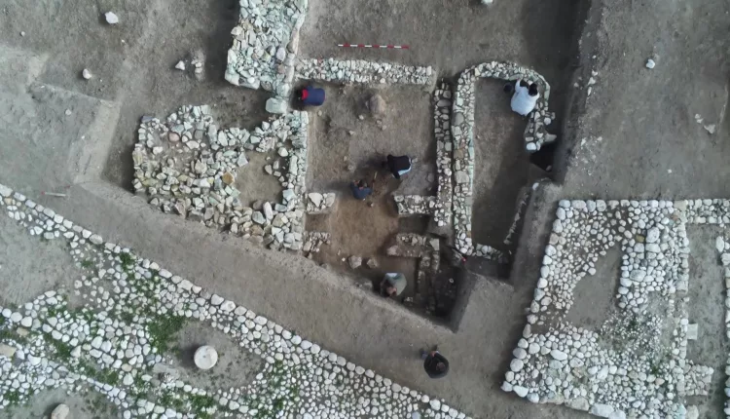
A Chinese and US team led by Deng Tao of the academy’s Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) examined remains discovered in 2015 and called the new species, Paraceratherium linxiaense, or Linxia Giant Rhino.
“Usually fossils come in pieces, but this one is complete, with a very complete skull and a very complete jaw, which is rare,” Deng told CNN.
“The skull was more than a meter (three feet) long, and it was very rare for a skull of that size to be preserved. We also found the cervical spine,” he said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
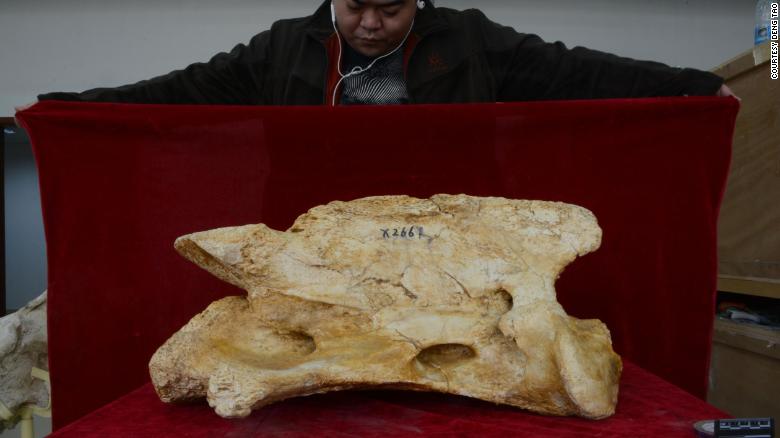
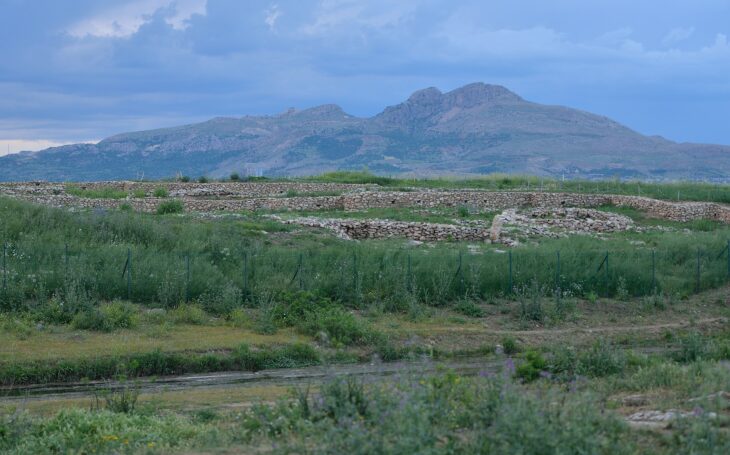
The bones were discovered in Gansu Province, northern China, and genetic research revealed that they belonged to a new species of gigantic rhino.
Deng told CNN that the huge animal weighed 24 tons and was the size of six elephants. He stated that its shoulders were more than 16 feet from the ground, its head was 23 feet, and its body was 26 feet long.
“This is the largest mammal ever to have lived on land,” Deng said.
It mainly lived in China, Mongolia, Kazakhstan and Pakistan, with a few in Eastern Europe, he added.
Around 31 million years ago, giant rhinos lived in the northern part of the Tibetan plateau before migrating southwest to Kazakhstan and then Pakistan. The Linxia Giant Rhino is descended from Pakistani rhinos. They would have had to cross the Tibetan plateau on their way north to Linxia, which means the plateau would have been lower than it is now, according to Deng.
“In addition, animal migration is linked to climate change. So 31 million years ago, when the Mongolian plateau dried up, they moved south. Then the weather got wet and they went back to the north. Therefore, this discovery is of great significance to the study of the whole plateau uplift process, climate, and environment,” he said.
The study was published in the journal Communications Biology.