Archaeologists have uncovered the earliest known case of artificial cranial modification (ACM – deliberate head shaping) on the continent, dating back over 12,000 years.
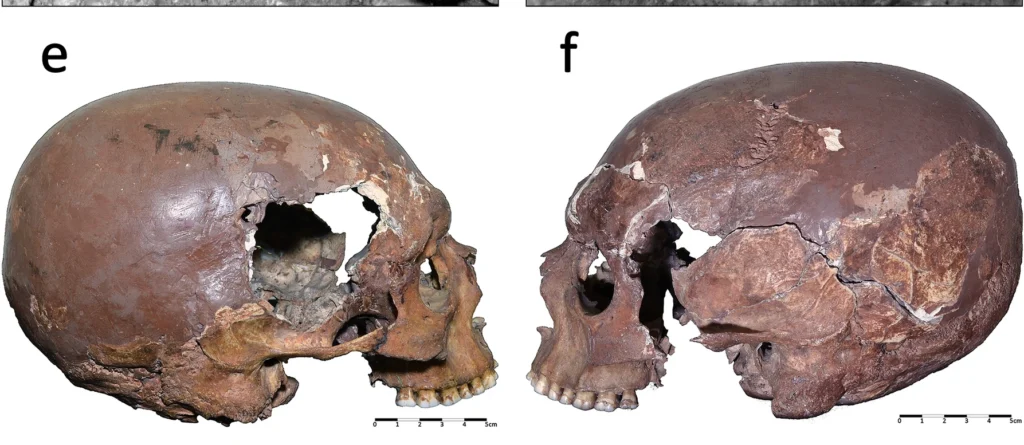
A team of Italian and international researchers has identified what is now considered the oldest example of deliberate head shaping in Europe. The discovery, published in Scientific Reports, centers on a Late Upper Palaeolithic skull known as “Arene Candide 12” (AC12), found in the Arene Candide Cave on the Ligurian coast of northwestern Italy. Radiocarbon dating places the individual’s burial between 12,620 and 12,190 years ago.
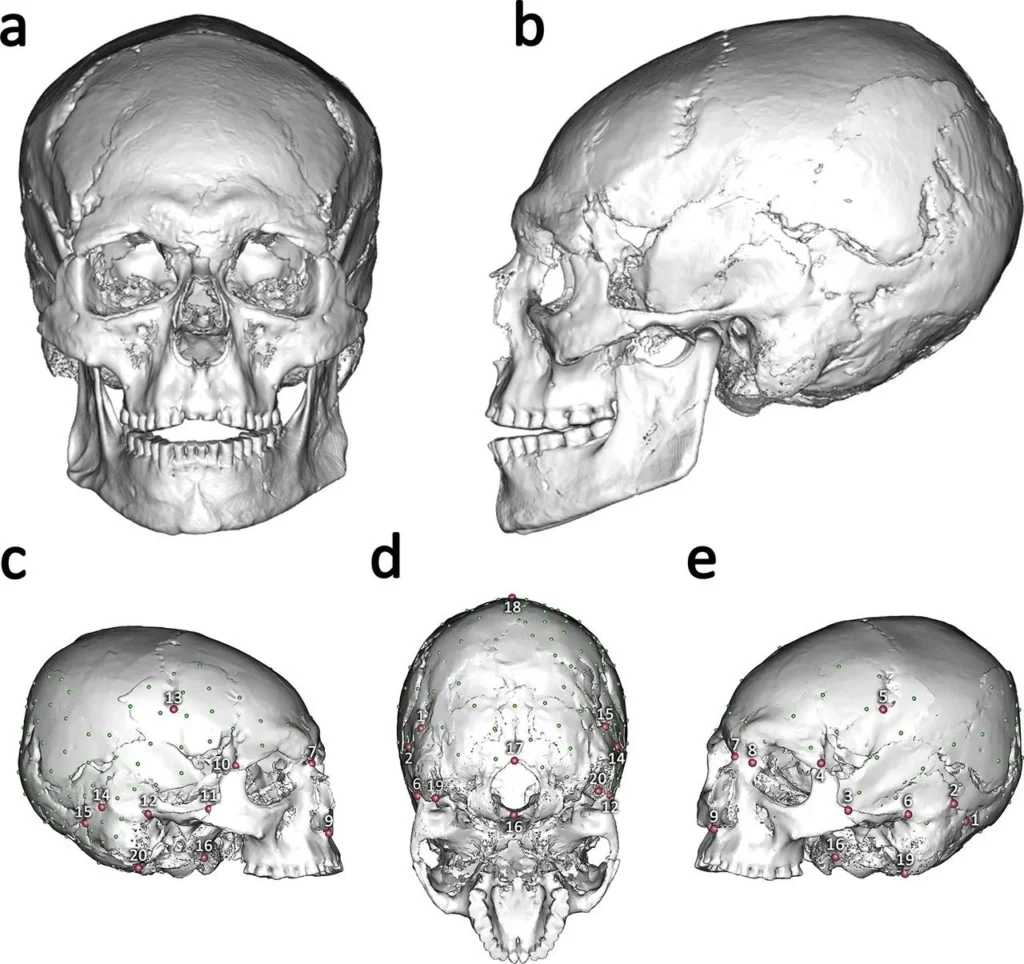
The study used advanced virtual anthropology and geometric morphometrics to reconstruct the skull and compare its form with prehistoric and modern examples. The results confirmed that AC12’s elongated and flattened cranium was not the result of disease or accidental deformation, but of a deliberate cultural practice known as artificial cranial modification (ACM).
ACM involves shaping an infant’s head by applying pressure during early development, often using bandages, boards, or other devices. This results in distinctive cranial profiles that serve as markers of identity, status, or cultural affiliation. AC12’s skull exhibited traits consistent with the “annular” type of modification, achieved through constrictive wrapping.
“This pushes back the known timeline for head shaping in Europe by several millennia,” said lead author Dr. Irene Dori of the University of Florence. “It shows that Late Palaeolithic hunter-gatherers were engaging in complex cultural practices that expressed ascribed identity from birth.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
A Remarkable Archaeological Context
The Arene Candide Cave is one of Europe’s most significant prehistoric sites, with human occupation spanning from the Upper Palaeolithic into historic times. During the Younger Dryas cooling period (about 12,900–11,600 years ago), the cave served as a large necropolis for hunter-gatherer groups.
AC12’s skull was found deliberately placed atop another burial—known as the “Tomb of the Antlers”—within a carefully arranged stone setting. The jaw and other bones were found nearby in a secondary deposit. Such treatment suggests the individual held a special status in life or death.
The site is also known for its complex funerary rituals, including the rearrangement of older skeletal remains around newer burials. Researchers believe these practices reinforced group identity and ancestral connections during a period of environmental stress and resource competition.
Ruling Out Disease
Earlier scholars had debated whether AC12’s cranial shape was caused by pathological conditions such as craniosynostosis, a premature fusion of skull sutures. However, the new study found no evidence to support this diagnosis.
By comparing AC12 with a sample of unmodified Late Upper Palaeolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic skulls, as well as with pathologically deformed crania and known ACM examples from around the world, the team demonstrated that AC12 clustered closely with intentionally modified skulls.
“Our analyses consistently classified AC12 within the artificial cranial modification group, with high statistical confidence,” the authors report.
Global and Cultural Significance
ACM has been documented across the globe for thousands of years—from ancient Peru to Bronze Age Eurasia and the 19th-century French countryside. Reasons for the practice vary, including aesthetic ideals, group identity, social rank, and spiritual beliefs.
The new Italian find now joins a small but growing list of early ACM cases worldwide, including examples from prehistoric China and Australia. Its discovery in a European Late Palaeolithic context suggests that the roots of head shaping lie deeper in human history than previously confirmed.
The fact that only one out of five complete crania from the Arene Candide necropolis shows this modification indicates it was likely reserved for a select subset of individuals—perhaps those with inherited status or special roles within their group.
A Window Into Palaeolithic Identity
As a permanent body modification imposed in infancy, cranial shaping is considered a powerful symbol of ascribed identity, physically embodying cultural values across generations.
For the people of Arene Candide, AC12’s distinctive head may have been a visible sign of belonging, prestige, or spiritual significance. While the exact meaning remains unknown, the find underscores that Europe’s Late Palaeolithic societies engaged in elaborate social traditions, extending beyond hunting and toolmaking into the realm of symbolic expression.
Future genetic studies on AC12 and other individuals from the site may reveal kinship links and shed further light on how social identity was constructed more than 12,000 years ago.
Mori, T., Sparacello, V.S., Riga, A. et al. Early European evidence of artificial cranial modification from the Italian Late Upper Palaeolithic Arene Candide Cave. Sci Rep 15, 27792 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-13561-8
Cover ımage Credit: Illustrative image – AI-generated depiction of artificial cranial modification (head shaping).
















