Hundreds of human remains unearthed from a burial site point to a warfare between Stone Age people long before the formation of powerful states in Europe, according to a new study.
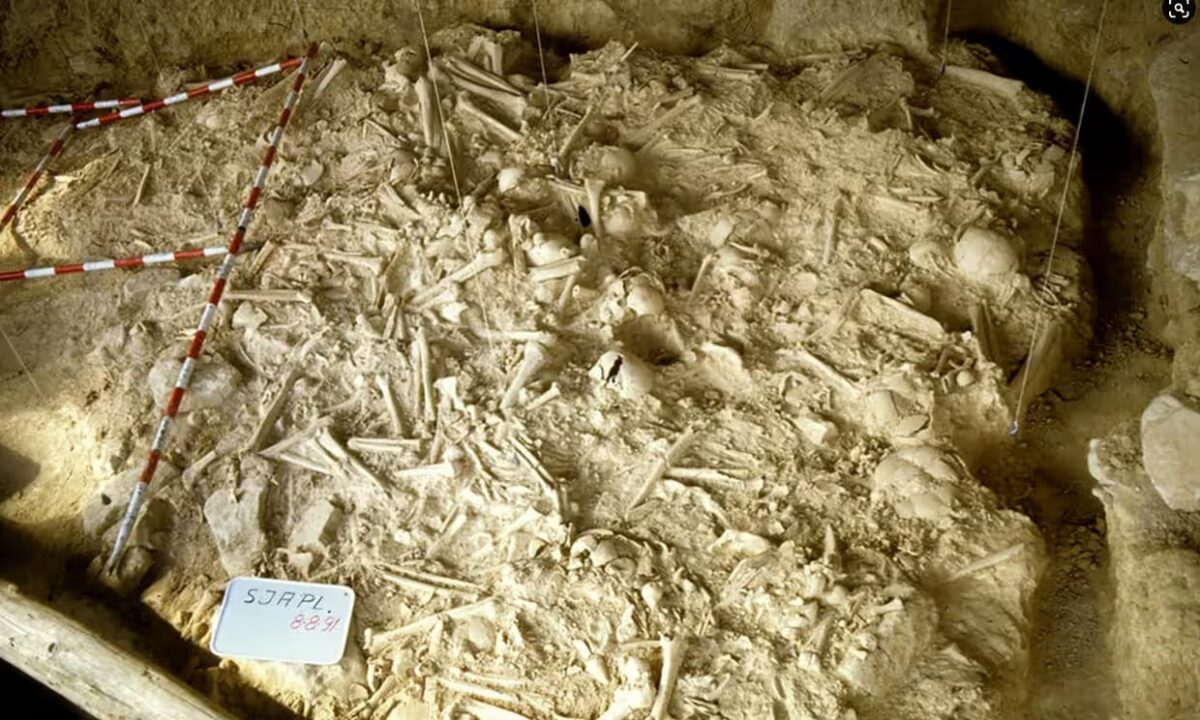
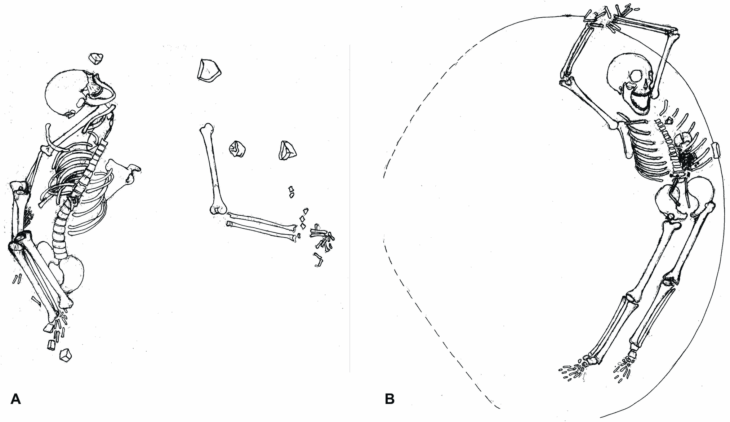
The evidence comes from a re-analysis of more than 300 sets of skeletal remains uncovered in northern Spain (radiocarbon dated to between 5,400 and 5,000 years ago).
The bones are predominantly male and many have evidence of injuries from stabbing and blunt-force trauma – suggesting they belonged to a warrior class.
The study pushes the first evidence of large-scale warfare back more than 1,000 years, and indicates that periods of conflict lasted for months on end.
Previous research has suggested that conflicts during this period, known as the Late Neolithic, consisted of short raids lasting no more than a few days and involved small groups of 20-30 individuals. The assumption, therefore, was that early societies lacked the logistical capabilities to support longer, larger-scale conflicts.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
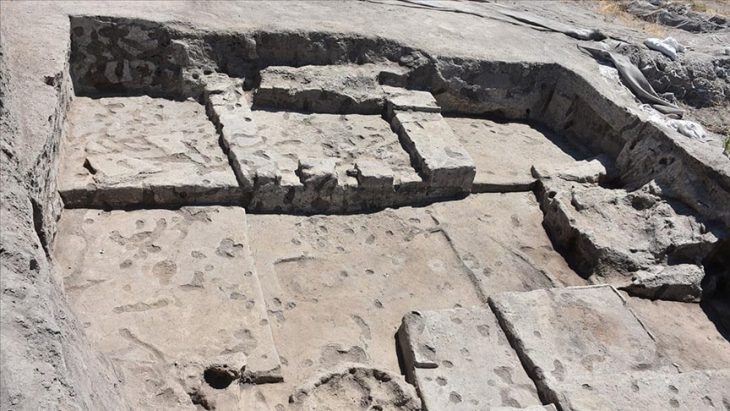
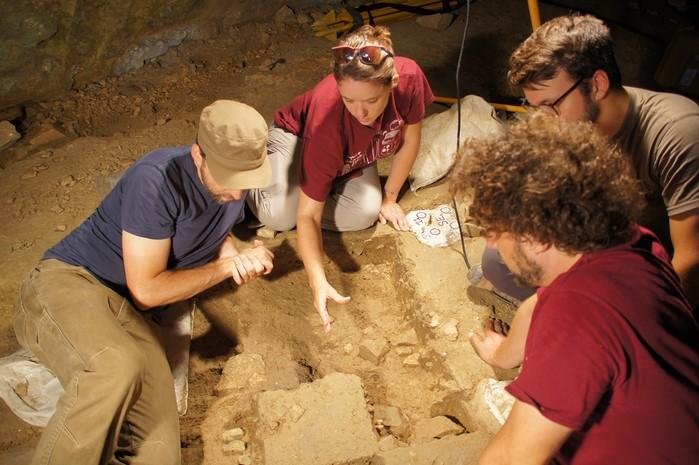
In the new study, researchers re-examined the skeletal remains of 338 people recovered from a mass grave site in a shallow cave in the Rioja Alavesa region of northern Spain. The site in question is San Juan ante Portam Latinam, a rock shelter in a valley in northern Spain.
San Juan ante Portam Latinam is about 20 square meters in area. In that small space, researchers found densely packed human bones. They include 90 complete skeletons, over 200 partial skeletons and thousands of seemingly isolated bones. There were also many stone weapons, including blades, arrowheads, and axes.
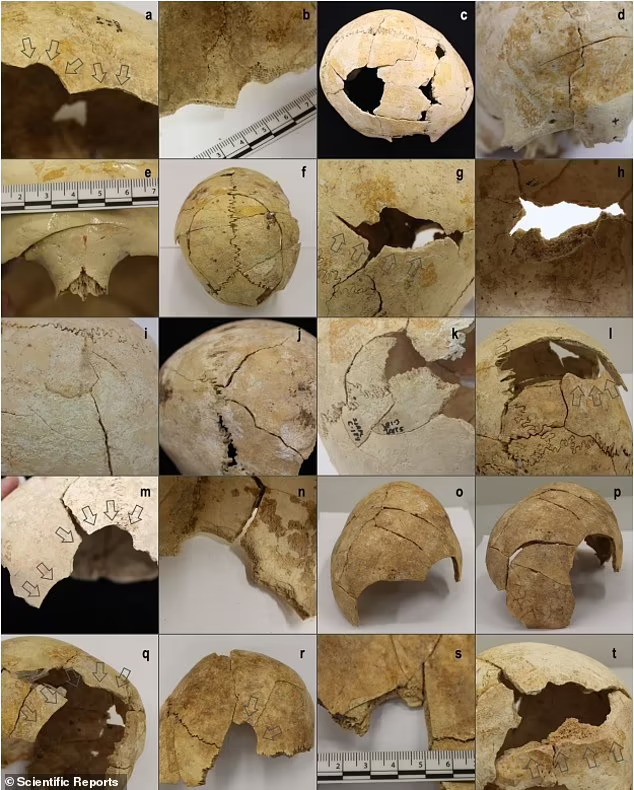

Teresa Fernández‑Crespo and colleagues from the University of Oxford re-examined the skeletal remains of 338 individuals for evidence of healed and unhealed injuries.
Some 52 flint arrowheads had also been discovered at the same site, with previous research finding that 36 of these had minor damage associated with hitting a target.
The authors found that 23.1% of the individuals had skeletal injuries, with 10.1% having unhealed injuries, substantially higher than estimated injury rates for the time (7–17% and 2–5%, respectively).
Most of the head injuries could be attributed to blunt-force trauma, which may have been caused by axes, wooden clubs, slingshots or thrown stones.
The researchers also found that the majority of injuries had occurred in adolescent or adult males – a significantly higher rate than in females. The findings suggest many of the individuals at the burial site were exposed to violence and may have been casualties of conflict.
The earliest such conflict in Europe was previously thought to have occurred during the bronze age, approximately 4,000 to 2,800 years ago.
The authors speculate that the conflict persisted over several months based on the comparatively high rate of healed injuries. Although the authors offer a number of theories, including conflict between various cultural groups in the area during the Late Neolithic, the reasons for the conflict remain unclear.
The study was published in Scientific Reports.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-43026-9
Cover Photo: Scientific Reports