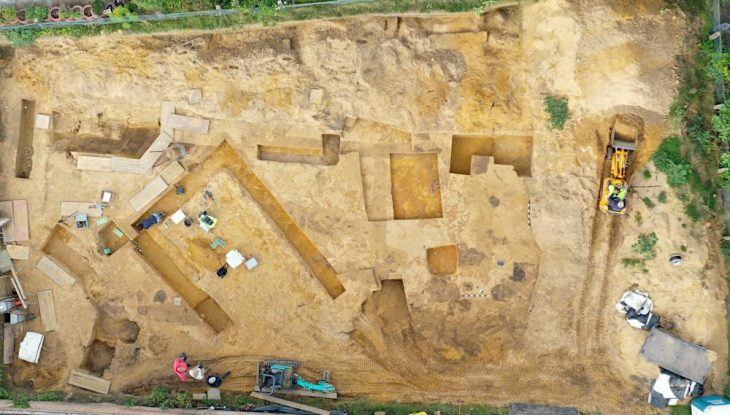
Archaeologists have located a boat grave from the Viking Age near Øyesletta in Norway during a ground-penetrating radar (GPR) survey.
This archaeological discovery was the result of research conducted by the Norwegian Institute for Cultural Heritage Research (NIKU) was undertaken on behalf of Nye Veier and the National Heritage Board.
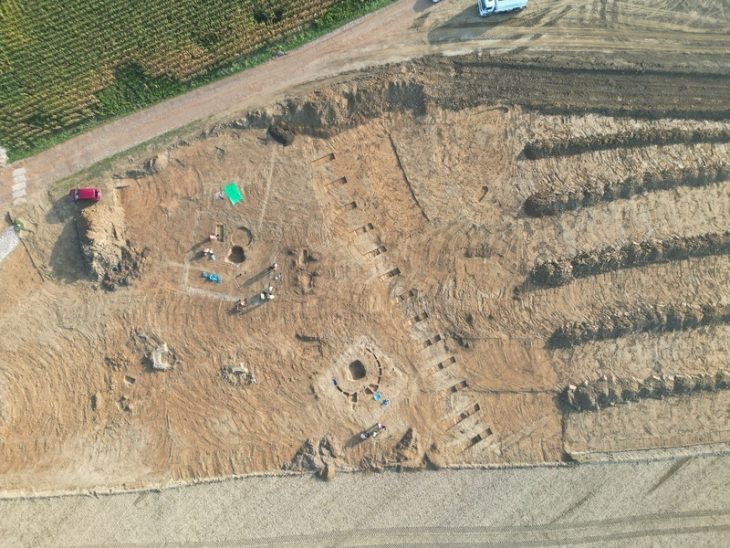
The discovery is highly significant not only because Viking ship burials are rarely found, but also due to the fact that Kvinesdal was once the home to one of Southern Norway’s largest known burial sites from the Iron and Viking Ages (AD 200 – 1000).
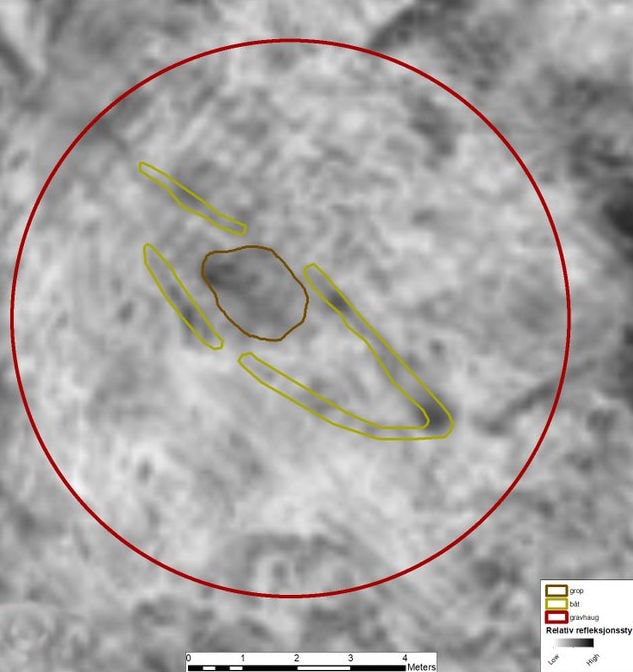
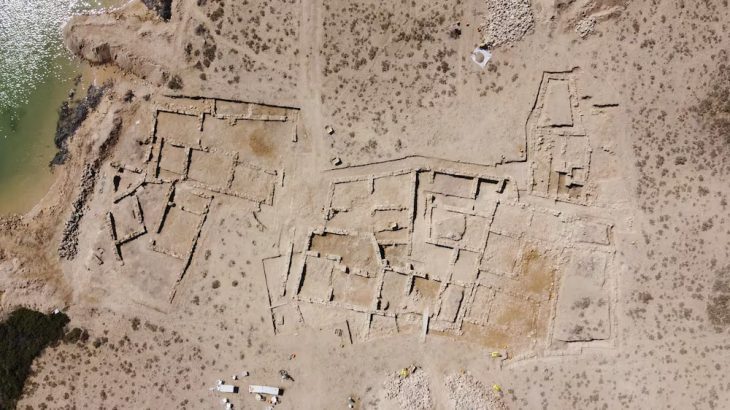
The study area was already known for being one of Øyesletta’s largest burial grounds which was active between 1500 and 2000 years ago.
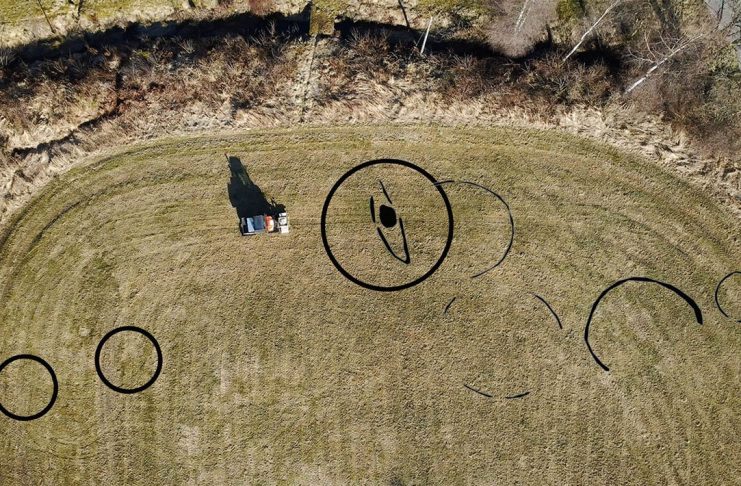
The survey has now revealed a boat grave in addition to several burial mounds. The boat measures between 8 to 9 meters and was placed in the ground beneath a burial mound. The discovery is the first boat burial to be uncovered in the region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
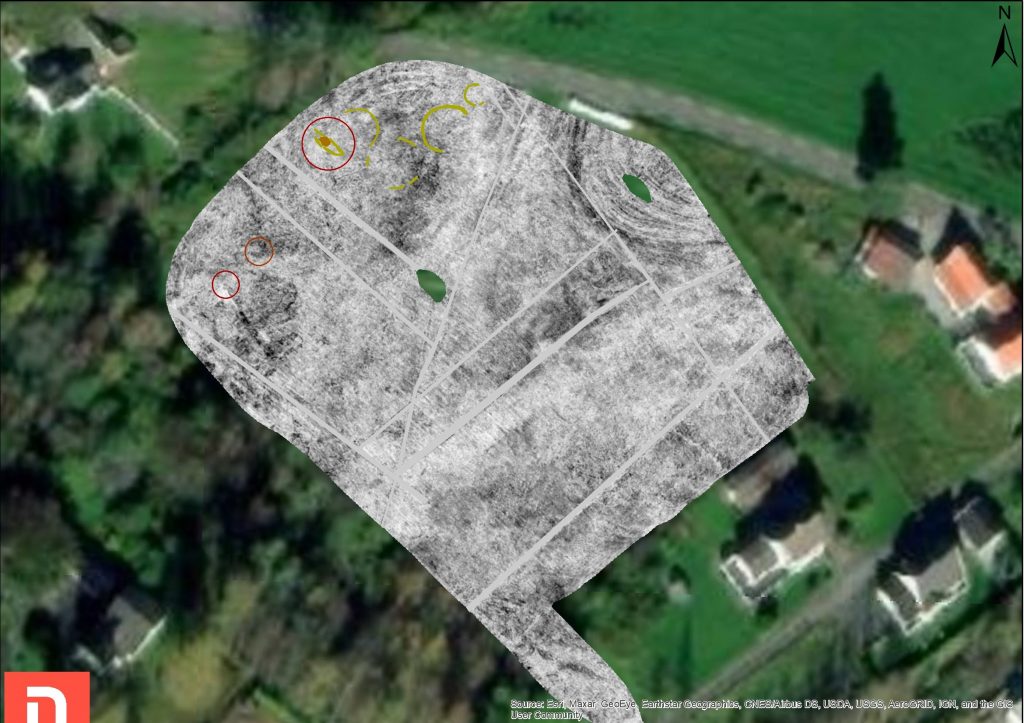
Niku researchers inform that in addition to the boat burial there are traces of several other burial mounds.
Jani Causevic, an archaeologist at NIKU, used the georadar and was the one who discovered the boat grave in the georadar data.
Jani Causevic said: “This is incredibly exciting. Both in finding such a discovery, but also to see how the use of georadar gives us the opportunity to explore and document cultural history through new and exciting methods.”

Ground-penetrating radar is a geophysical method that uses radar pulses to image the subsurface. It is a non-intrusive method that allows data to be plotted as profiles, plan view maps isolating specific depths, or as three-dimensional models.
At present, it is still unknown how much of the Viking boat remains. We’re waiting for great news. Because Based on discovered archaeological evidence it is known that the funeral boat or wagon was a practice reserved for the wealthy.
Header Image Credit : Jani Causevic, NIKU
















