The importance of what is written in the scriptures in the development of archeology is really great. It is possible to follow many historical facts from the scriptures.
One notable event that is described on the pages of the Bible is the Babylonian conquest of ancient Judah. The conquest led to the downfall of Jerusalem, which is believed to have been besieged in the sixth century BC by King Nebuchadnezzar II.
The Sunday Express quoted Tom Meyer of the Shasta Bible College in the United States as saying that archaeological discoveries in the Middle East may have confirmed the accuracy of the predictions made by the Old Testament prophet Zephaniah.
Combining many archaeological discoveries since the beginning of the 20th century, experts such as Tom Meyer of the Shasta Bible College in the United States are convinced that the Bible can withstand historical review.
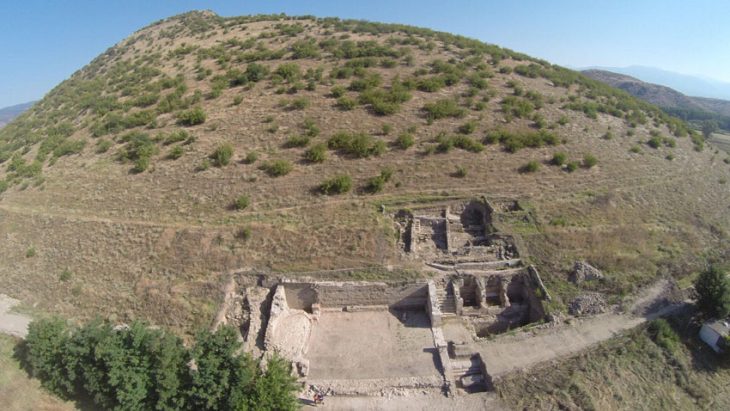
The prophecy in question predicted the destruction of the Philistine city of Ekron in the 7th century BC.at the hands of the Babylonian who beginning to destroy Jerusalem, as described in the Bible.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In 1996, Meyer said an Israeli archaeologist named Trude Dothan “was excavating what she thought to be the famous Philistine city of Ekron but still couldn’t prove it”.

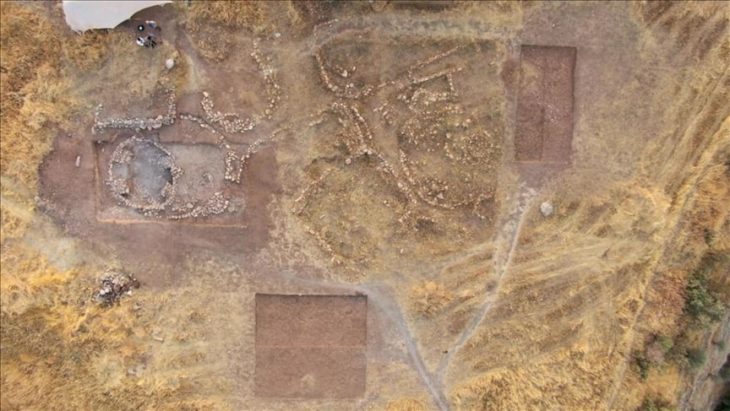
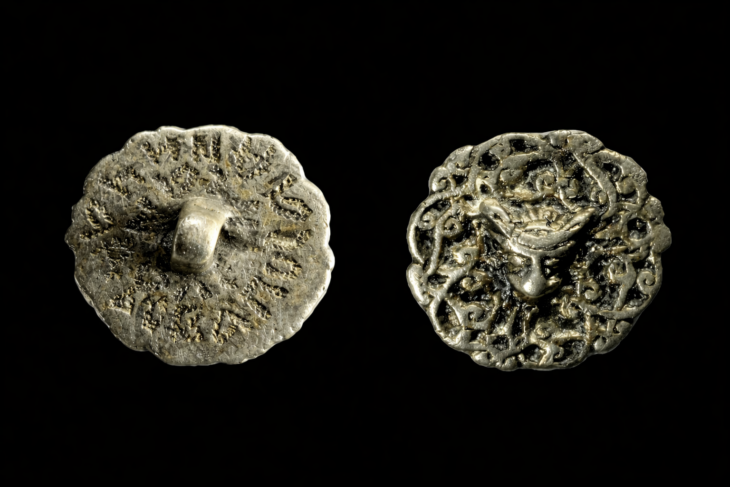
“Then, after 14 seasons of excavation, the archaeologists stumbled upon something unexpected, for the first time ever in archaeological history, they discovered a monumental inscription that names a biblical city and its kings in situ (in its original position) and in a destruction layer that can be dated”, he said. “Dating to around 690 BC, the Ekron Inscription itself is complete and contains five lines of 71 letters written with a Phoenician influence”.
As Meyer pointed out, however, the “destruction layer” where the archaeologists discovered the inscription dates to about 603 BC “which is when the city was destroyed by Nebuchadnezzar of Babylon as Zephaniah predicted some 40 years beforehand”.
“Though it took around 2,600 years to correctly identify the Philistine city of Ekron and prove that the city was indeed destroyed by the Babylonians around 603 BC as Zephaniah the prophet predicted, this one-of-a-kind discovery once again validates the Bible’s historical accuracy”, he remarked.
And while the newspaper pointed out that “whether the inscription proves the Old Testament prophet right or simply proves the city was destroyed might be a matter of personal belief”, Meyer further insisted: “In every case where the historicity of the Biblical account can be tested, the Bible has demonstrated again and again to be historically accurate”.
Cover photo: Wikimedia Commons