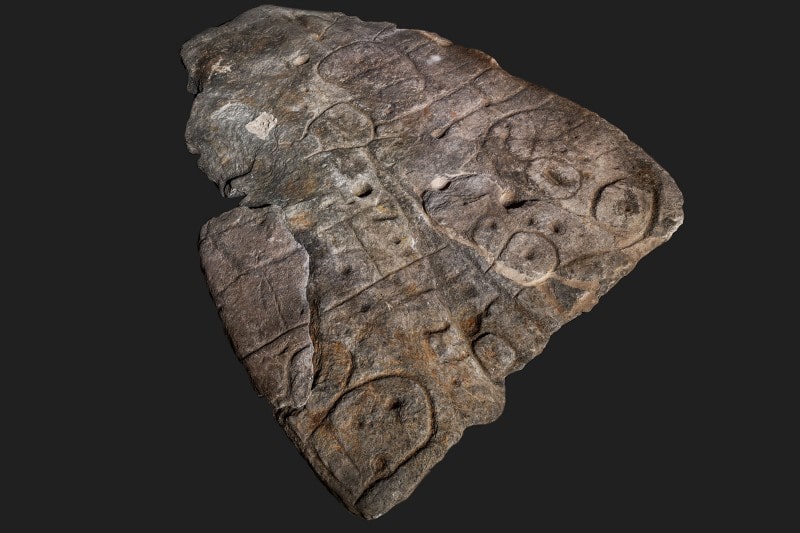
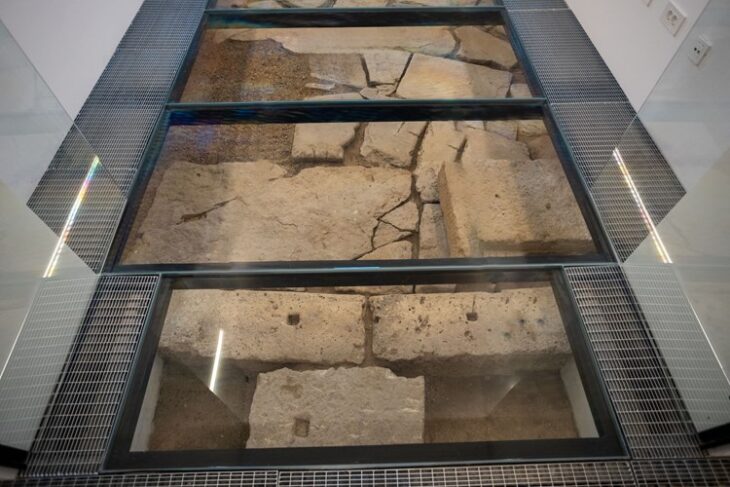
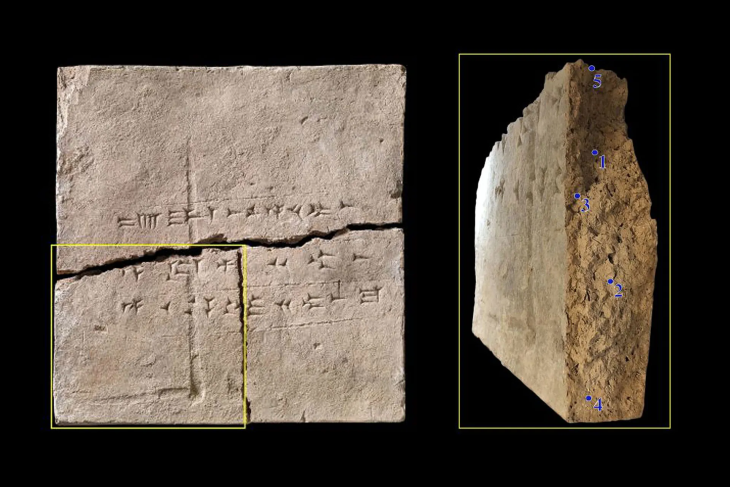
An ornate Bronze Age stone slab (Saint-Bélec slab) that was excavated in France in 1900 and forgotten about for over a century may be the oldest three-dimensional map in Europe.
In 2014, a 2m x 1.5m slab (5 feet x 6.5 feet) was again found in the cellar of a castle in Brittany, France. Archaeologists who study patterns carved on 4,000-year-old stones say they believe these marks are maps of the western region of Brittany. They say this makes the tablet the oldest 3D map of a known area in Europe.
Researchers examined the carved stone slab and dated it to the early bronze age. (MÖ 2150-1600)
Their research, published in the French journal Bulletin de la Société préhistorique française, identified it as the oldest cartographic representation of a known territory in Europe, a likely marker of the political power of the early Bronze Age.
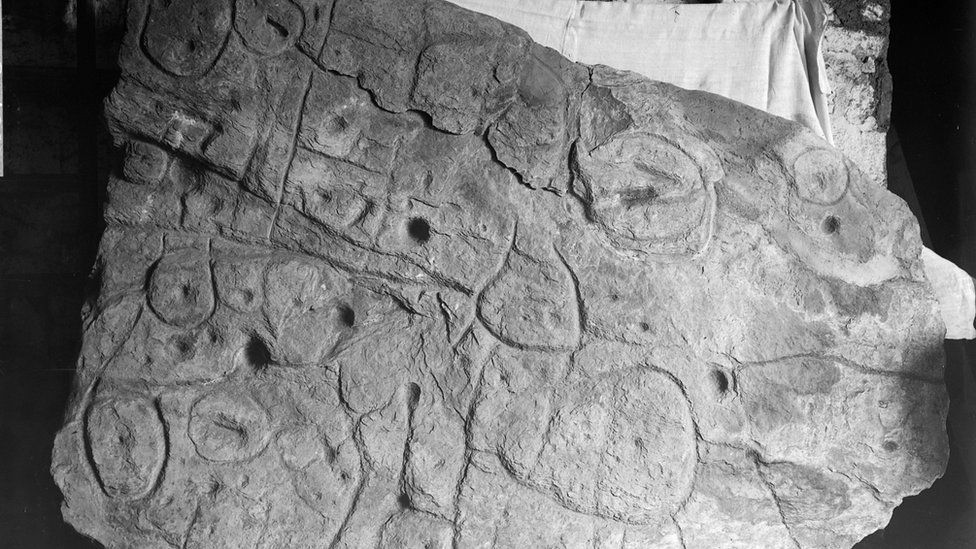
The broken plate was reused for the burial of Saint-Bélec at the end of the Early Bronze Age (ca. 1900-1640 BC). At that time, the slab formed one of the walls of a stone cyst, a small coffin-like stone box used to contain the bodies of the deceased. His engraved face turned towards the inside of the tomb, but its ends were hidden. The plate was transferred to a private museum in 1900 before the collection was taken over by the Musée des Antiquités Nationales (MAN – Museum of National Antiquities) in 1924. Until the 1990s, the Saint-Bélec plate was kept in a niche in the castle cellar. Finally, in 2014, he was found in the castle’s basement.

The research team, including in 2017, began to perform high-resolution 3D research and plate photogrammetry, registering the surface of the plate and its engravings.
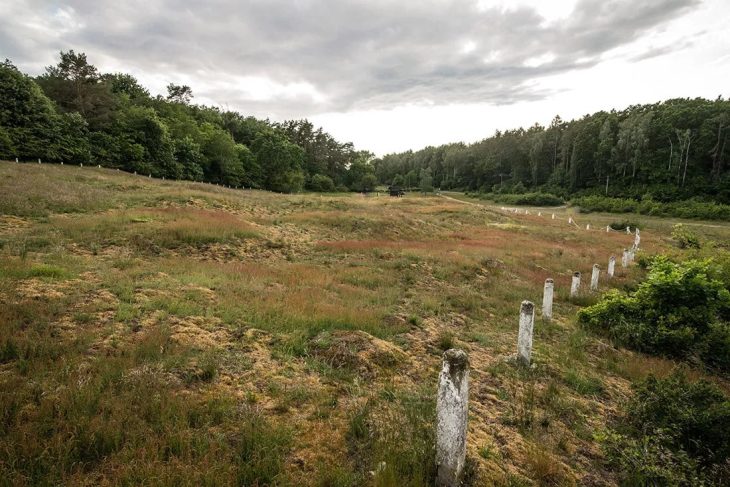
After analyzing the markings and carvings on the stone, the researchers suspected that it might be a map. A study in the Bulletin of the French Prehistoric Society stated that the “repetitive patterns connected by lines” on its surface indicate that it depicts a Finistère region. Researchers say that the dent is a 3D representation of the Odette River valley, and there appear to be several lines that delineate the river network in the area. The geographical location shows that the territory represented on the slab has an accuracy of 80% relative to the 18-mile-long area of the river.
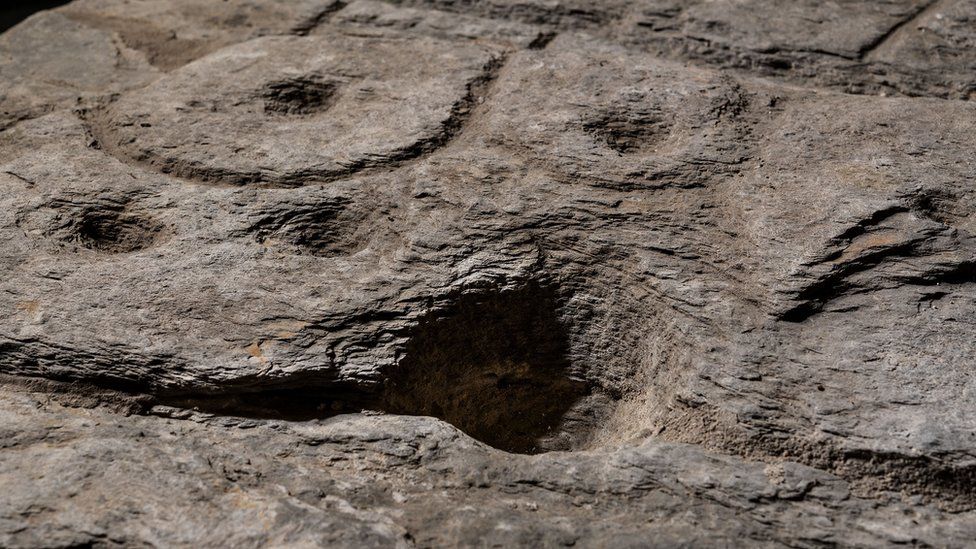

“This is probably the oldest map of a territory that has been identified,” Dr. Clément Nicolas from Bournemouth University, one of the study’s authors, told the BBC.
“There are several such maps carved in stone all over the world. Generally, they are just interpretations. But this is the first time a map has depicted an area on a specific scale.”
Dr. Nicolas said the map may have been used to mark a particular area.
“It was probably a way to affirm the ownership of the territory by a small prince or king at the time,” he said.
“We tend to underestimate the geographical knowledge of past societies. This slab is important as it highlights this cartographical knowledge.”
Saint-Bélec Slab is contemporary with the famous Nebra Nebula Disk discovered in Germany. It is the oldest known specific depiction of the cosmos and highlights the cartographic knowledge of prehistoric society.