According to a study done by an American researcher at the University of Wales, ancient civilizations may have used celestial navigation methods to travel.
Alessandro Berio, a skyscape archaeologist, discovered new evidence that the ancient Minoan civilization developed significant nautical technologies to aid in international sea trade, which is linked to the wealth and expansion of the culture throughout the Mediterranean. Because of its location, Minoan culture was based on open sea navigation and international trade cycles.
The Minoan civilization may have relied heavily on celestial star paths above to help them navigate the Mediterranean. According to a study, the Minoan palaces were even placed to face the rising or setting of a few notable stars, serving as their guide to important commercial centers.
“It is hypothesized that the orienting of palatial architecture toward star paths and specific sea lanes may have symbolized the special relationships between the palaces and distinct foreign emporia, while also being a source of legitimization of power for the local elite who controlled the ideological and technological frameworks of maritime knowledge,” Berio wrote in the paper.
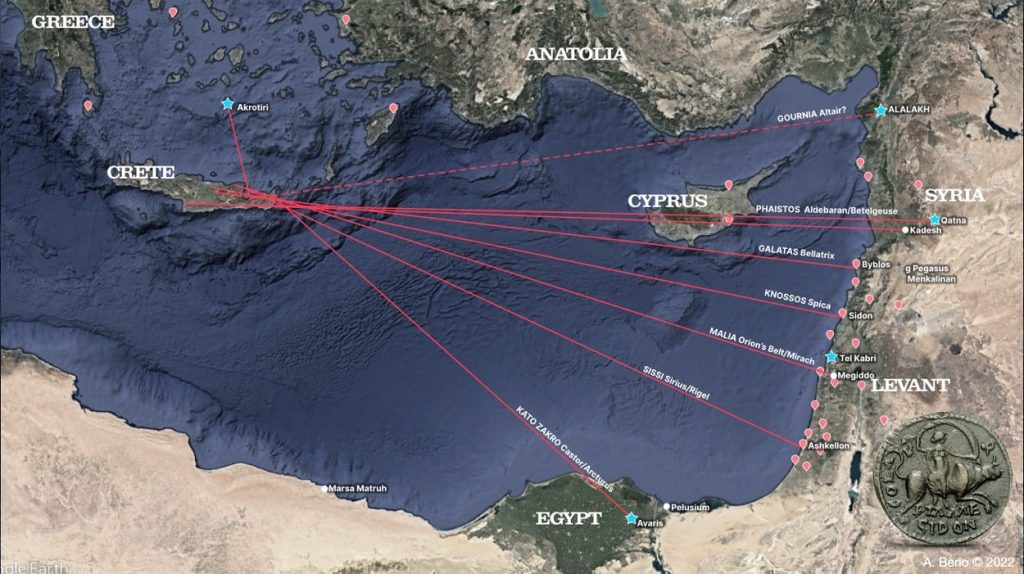
Berio focused his research on the Minoan civilization, a Bronze Age Aegean people who lived on the island of Crete between 2600 – 1100 BC.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Pelusiac branch of the River Nile was exactly parallel to the central court of the Minoan trading post. The study found that Knossos, the largest Minoan palace, was perfectly positioned on a “star path” with the constellation of Virgo and the commercial center of Sidon.
This alignment may have played a critical role in guiding Minoan sailors to critical trading destinations in Egypt and the Levant.
Indeed, the orientation of various palaces toward specific star paths and sea lanes may have symbolized the unique relationship between these palaces and distinct foreign commercial hubs. Furthermore, they may have legitimized the power of the ruling elite, who controlled maritime navigation knowledge and technology, as well as specific sea routes.
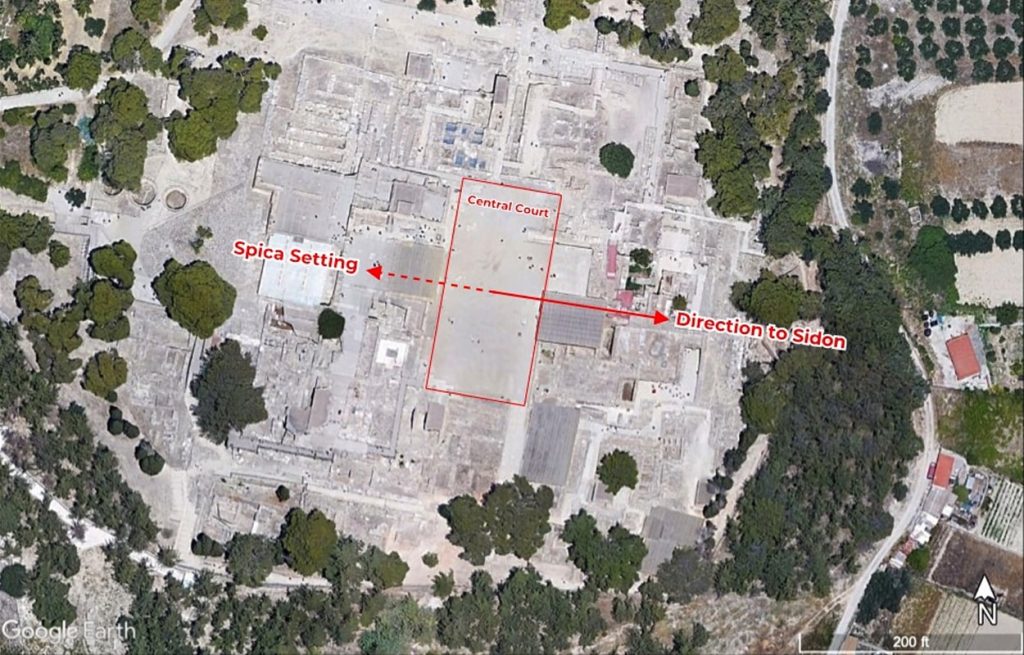
The research discovered that Minoan sailors may have used star paths or linear constellations to guide them to Mediterranean cities where Minoan artifacts and frescoes bear evidence of trade links between them.
The discovery could call into question the previous theory that Homer’s Odyssey was the first historical signal of celestial navigation. We now have more evidence that we need to rewrite history and push back the timeline of human development.
The research was published in the Journal Mediterranean Archaeology and Archaeometry.
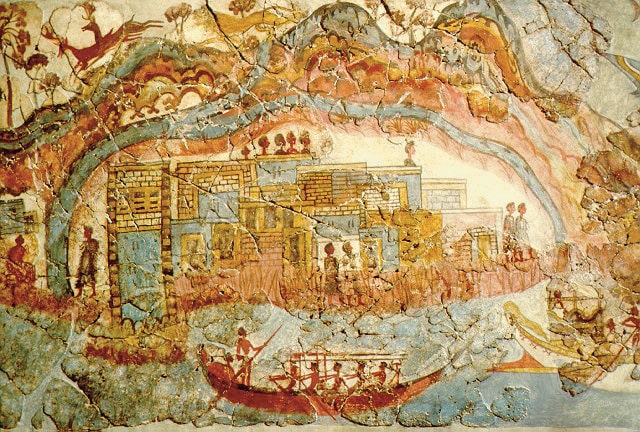
Cover Photo: Minoan fresco, showing a fleet and settlement Akrotiri. Wikipedia