From 1096 to 1291, waves of Europeans took up arms and marched into the Middle East. They hope to “take back” the Holy Land. But many of these Christian crusaders never returned home, and a mass grave found in Lebanon provided grisly evidence of their violent deaths.
Much of what we know about crusaders’ lives and deaths come from historical documents, and while the prior studies have concentrated on human remains from crusader period cemeteries in Europe and the Middle East, relatively few conflict-related mass burial sites have been found or investigated.
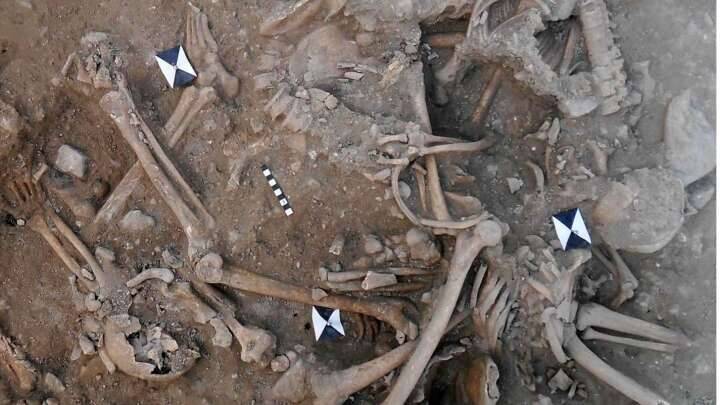
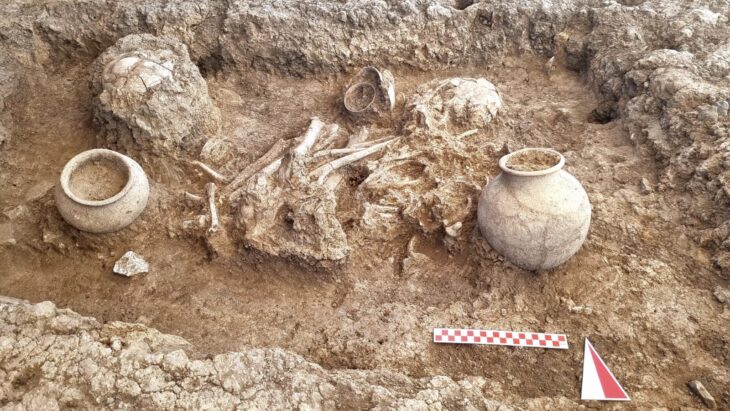
At least 25 young men and teenage boys’ chipped and burned bones were discovered inside the dry moat of the remains of St. Louis Castle in Sidon, Lebanon.
A team of international researchers explains their findings from examinations of human skeletal remains unearthed at Sidon Castle on the eastern Mediterranean coast of south Lebanon in a new article published in PLoS ONE.
Their findings add to our understanding of combat throughout the Crusades, notably during the 13th century, and shed insight on crusader demography, weapon techniques, and injuries, as well as how the treatment of the dead.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
After the First Crusade, the crusaders took Sidon for the first time in 1110 CE. However, the crusaders’ military power waned in the second part of the 13th century, and they battled to retain control of the city.
The researchers used DNA and naturally existing radioactive isotopes in the men’s teeth to prove that some of them were born in Europe, and an examination of various versions, or isotopes, of carbon in their bones, indicates that they died around the year 13th century.
According to crusader chronicles, Sidon was besieged and devastated in 1253 by Mamluk soldiers, and again in 1260 by Mongols. It is highly likely that these soldiers died in one of these battles.
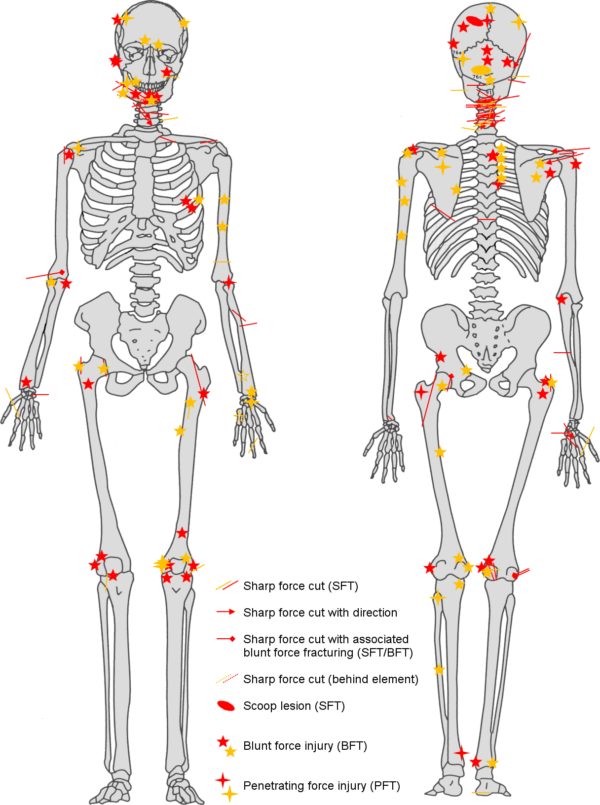
Some of the skeletal remains have sword wounds in the rear of the corpse, indicating that the troops were assaulted from behind and were most likely fleeing when they were killed. Others have sword wounds across the back of their necks, indicating that they may have been captured and decapitated after the conflict.
“One individual sustained so many wounds (a minimum of 12 injuries involving a minimum of 16 skeletal elements) that it may represent an incident of overkill, where considerably more violent blows were applied than was actually required to overcome or kill them,” the researchers wrote in their study.
Dr. Piers Mitchell of the University of Cambridge, who was the crusader expert on the project, explained “Crusader records tell us that King Louis IX of France was on crusade in the Holy Land at the time of the attack on Sidon in 1253. He went to the city after the battle and personally helped to bury the rotting corpses in mass graves such as these. Wouldn’t it be amazing if King Louis himself had helped to bury these bodies?”
Mitchell continued “So many thousands of people died on all sides during the crusades, but it is incredibly rare for archaeologists to find the soldiers killed in these famous battles. The wounds that covered their bodies allow us to start to understand the horrific reality of medieval warfare,” he said.