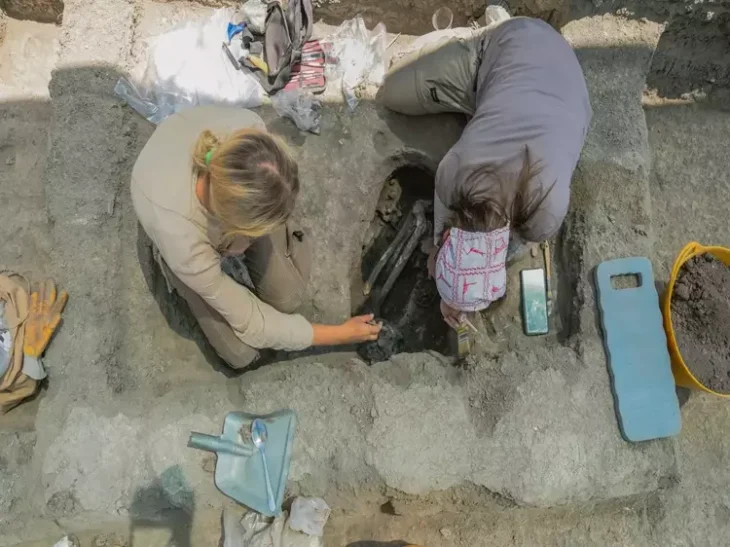
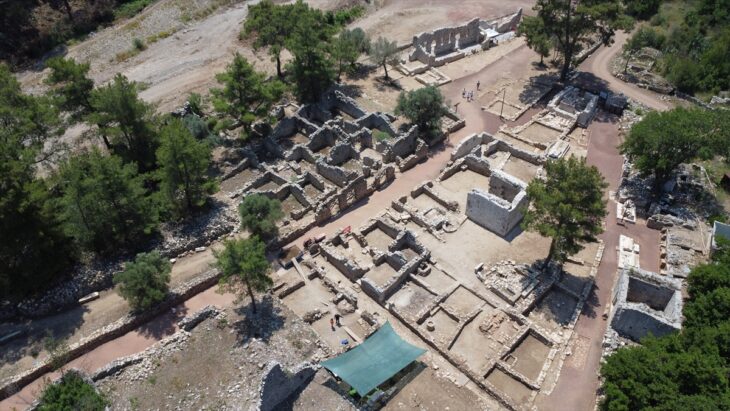
Expansion of research activities in the Terme del Lacus area in the sunken Baia park, known as the ‘Las Vegas’ of the ancient world, has revealed new elements of ancient Roman luxury villas.
In the Gulf of Naples, a few kilometers from Pompeii, Baia was a vacation city for the capital’s rich and powerful during the Roman era, drawn to its natural volcanic vents and medicinal hot springs. Some of the most important names in Roman history such as Caesar, Cicero, Mark Antony, Brutus, and Nero had villas in Baia.
The luxurious town was abandoned in the 8th century after being raided by a Muslim army, and in the 16th century, the underlying volcanic magma chamber emptied, a process known as bradyseism. The land dropped about 20 feet below sea level, drowning more than half of Baia beneath shallow bay waters.
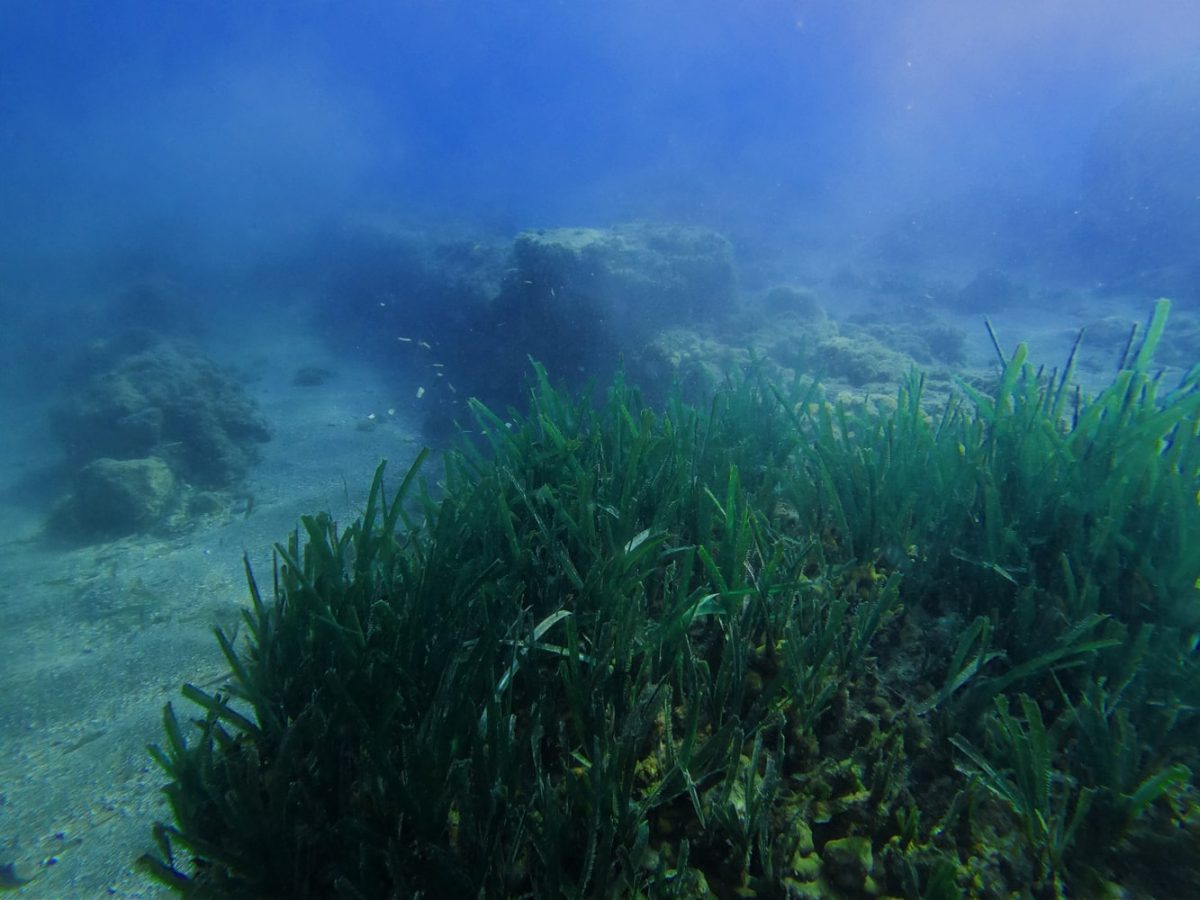
A section more than 260 feet long with visible remains, including a stone colonnade with collapsed columns made of fine imported Portasanta marble from Chios in Greece, was discovered during an exploration of the Baths of Lacus, a private thermal bath built inside a domus.
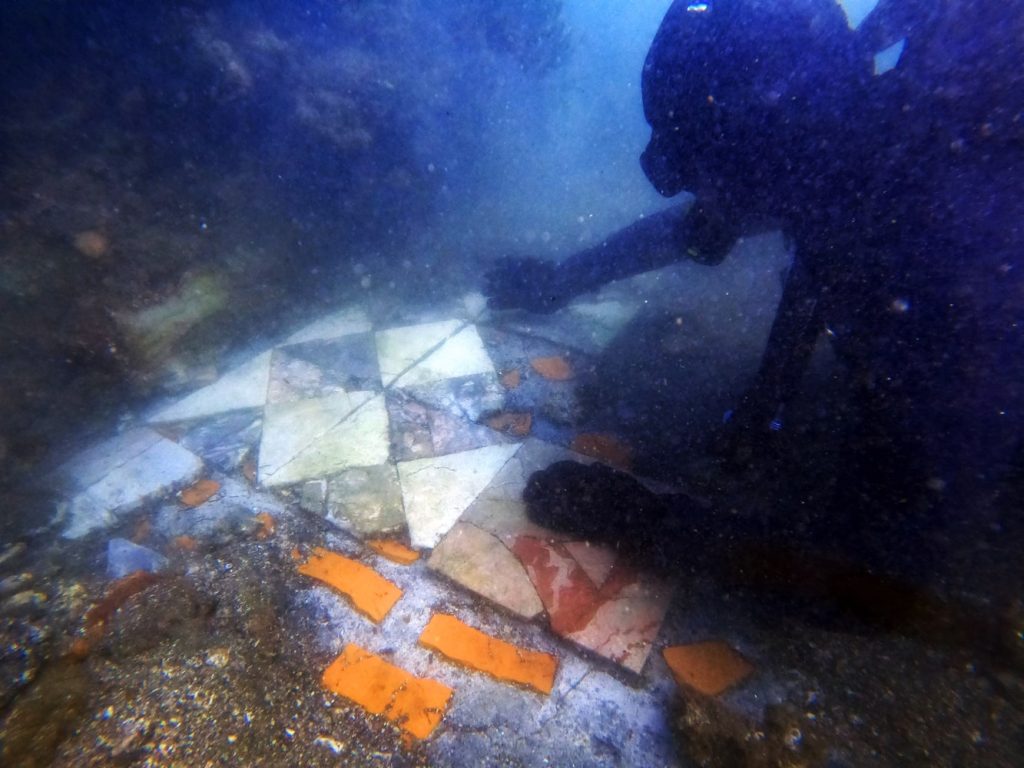

A large piece of marble opus sectile flooring has also been identified, still rendered in Portasanta in chromatic alternation with white or gray marble slabs. This currently appears as the most indicative dating element, being the typology and implementation referable to the Late Antiquity age.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Lacus Baths site, which opened in 2020, allows scuba divers and snorkelers to explore the bath’s exceptional mosaic floors made of white, pink, red, green, grey, and black tiles. It was a spa complex, most likely of a private residence, overlooking Baia’s ancient port, the Lacus Baianus. In addition to the perimeters of various rooms and the thermal baths, three apses walls, which once supported large windows overlooking the Lacus Baianus, can be seen.