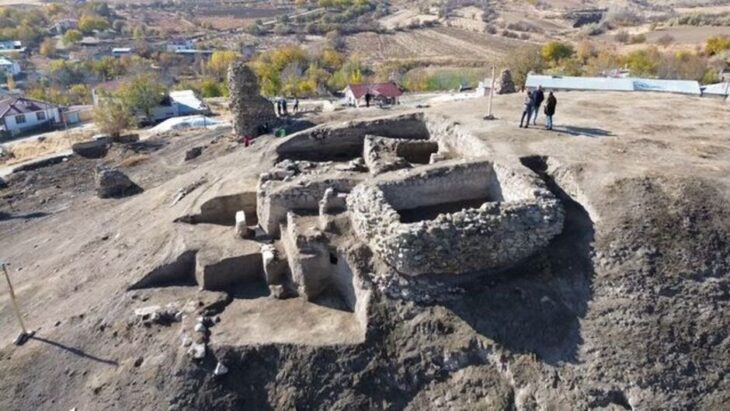
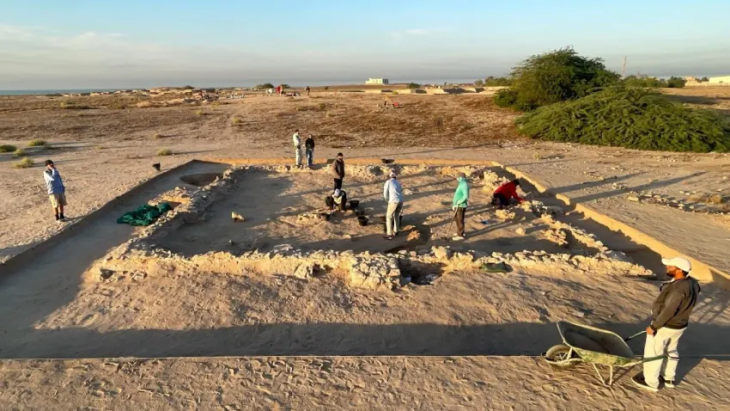
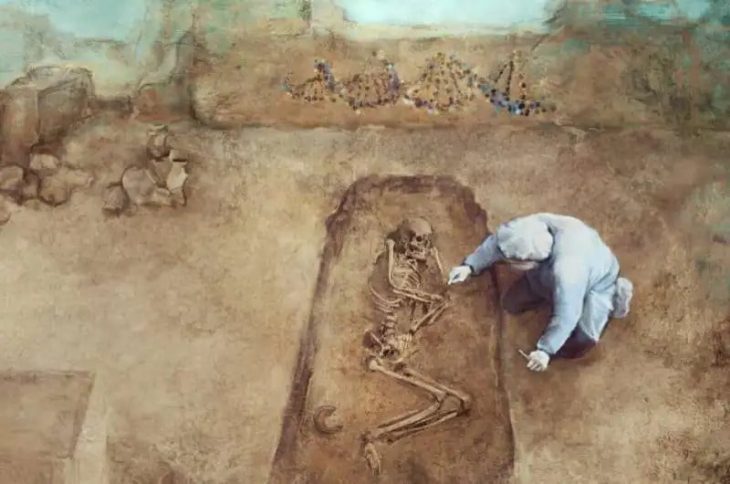
In Queensland’s remote Channel Country of red dirt and gibber rock, traditional owners and archaeologists have unearthed what researchers have dubbed “Australia’s Silk Road”.
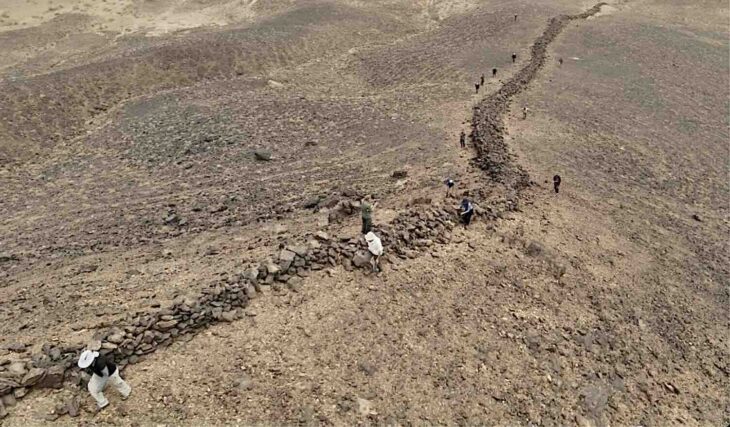
The region is archaeologically significant: the landscape has been dramatically altered by a huge network of quarries, which Mithaka people once used to make seed-grinding implements.
While historical accounts have suggested Aboriginal Australians may have lived in permanent settlements, scientists say there is relatively limited archaeological evidence to back this up.
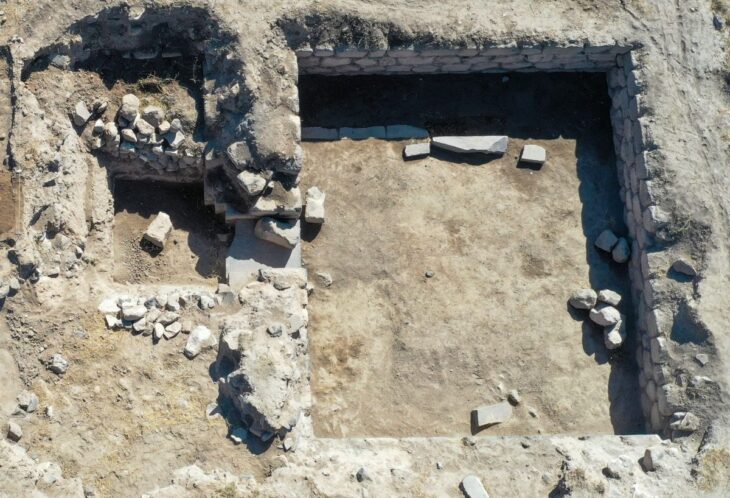
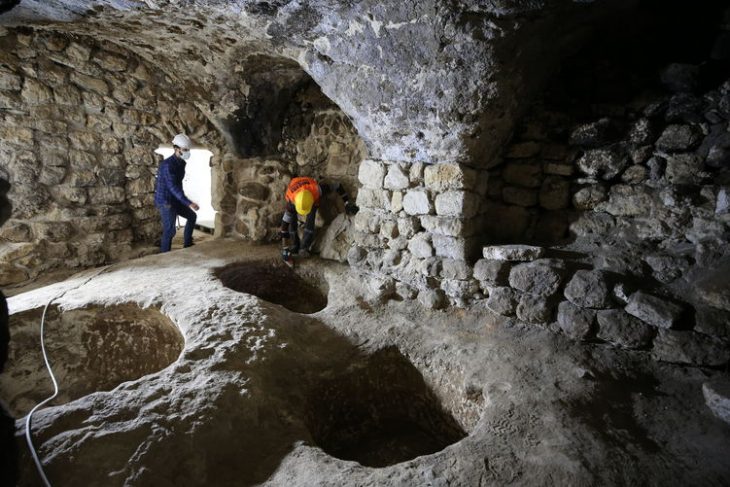
But now, a unique collaboration between Mithaka traditional owners, defence veterans, and scientists is unearthing skeletons and stone circles that experts say may paint a new picture of early Aboriginal lives.
In a research project initiated by the Mithaka people addressing, the results show that Mithaka Country has a substantial and diverse archaeological record, including numerous large stone quarries, multiple ritual structures, and substantial dwellings.
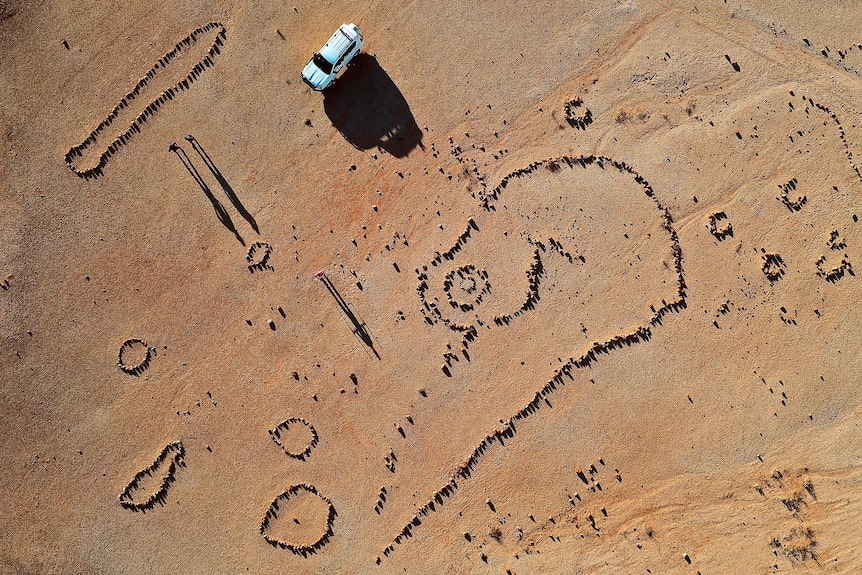
A team involving traditional owners and researchers eventually identified 179 quarry sites, spread over 33,800 sq km – an area about half the size of Tasmania. Some quarry pits are estimated to be more than 2,000 years old.
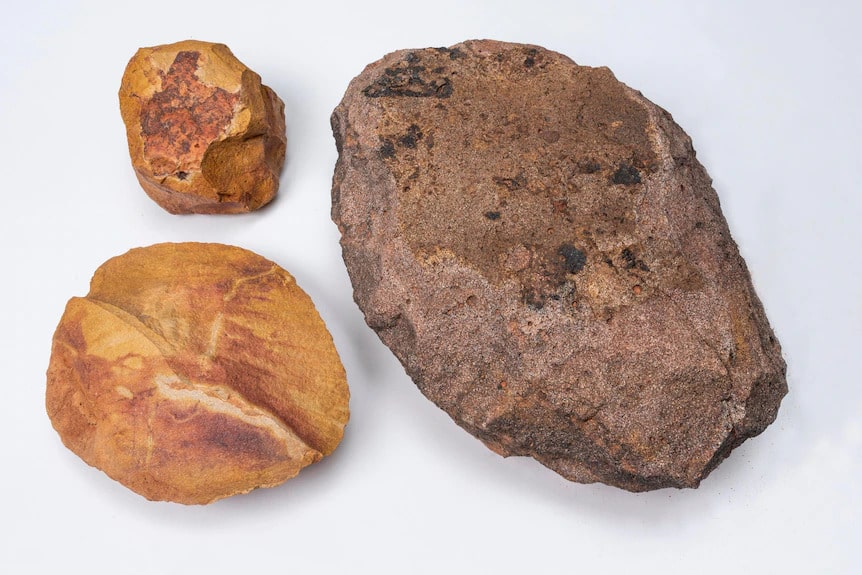

One of the sites comprises 25,000 individual quarry pits, says Shawnee Gorringe, a Mithaka traditional owner. She describes the archaeological research findings as “scientific validation of something that you already knew was pretty special.”
In December, Michael C. Westaway, and collaborators received grant funding to investigate plant domestication and possible village sites on Mithaka land.
Project partner and lead researcher from Michael C. Westaway said he was blown away by the scale and significance of the Mithaka cultural landscape.
“Mithaka country is in the heart of a massive trade and exchange network, which I have referred to as Australia’s Silk Road,” Dr. Westaway said.
The researchers say archaeological research has uncovered unknown aspects, such as the scale of Mithaka quarrying, that could spur a reassessment of Aboriginal socio-economic systems in parts of ancient Australia.

Australia’s Silk Road
The Channel Country is so named for its intertwined channels, in which monsoonal rains transform from arid desert into lush greenery. A complex exchange system once operated up and down along these rivulets.
Mithaka land was once at the heart of a vast transcontinental exchange route that spanned from the Gulf of Carpentaria in the north, down to the Flinders Ranges in South Australia – a system Westaway describes as “Australia’s Silk Road”.
“It connected large numbers of Aboriginal groups throughout that arid interior area on the eastern margins of the Simpson Desert,” he says. “You get people interacting all across the continent, exchanging ideas, trading objects and items and ceremonies and songs.”
Grindstones mined and produced on an industrial scale on Mithaka land were exchanged for ochre, wooden objects, stone axes, and pituri, a narcotic. “We don’t really know how far and wide they were being distributed, but they were an important element,” Westaway says.
Some of the archaeological findings are on show in an exhibition touring Queensland titled Kirrenderri, meaning the heart of Channel Country.
Cover Photo: Lyndon Mechielsen/Mithaka Aboriginal Corporation