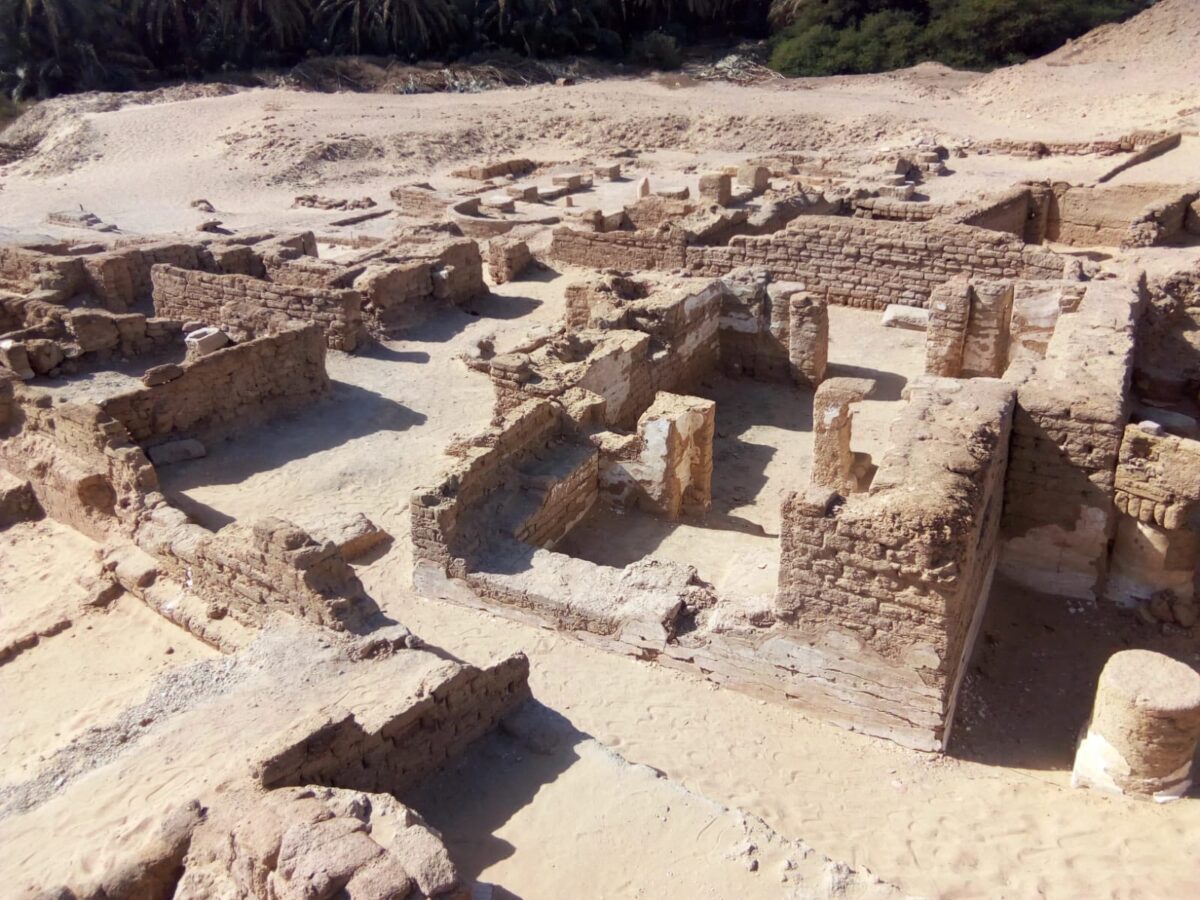
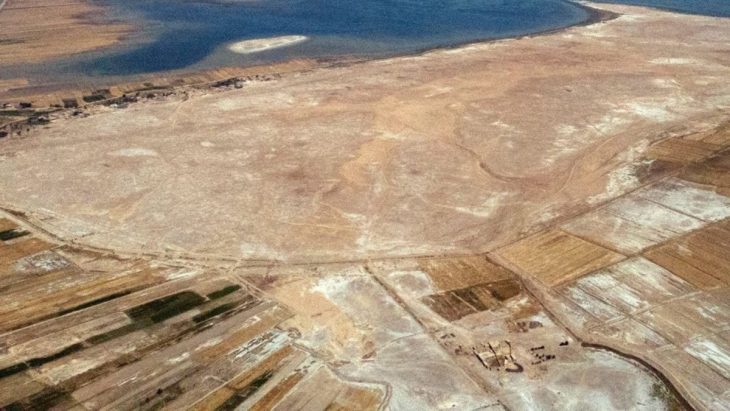
In the vast silence of Egypt’s Western Desert, archaeologists have stumbled upon a remarkable piece of history — the ruins of a complete Coptic Christian city dating back to the early centuries of Christianity in Egypt. The site, Ain al-Kharab, located deep in the Kharga Oasis, reveals not just ancient walls and artifacts, but a vivid story of faith, resilience, and cultural transformation.
At the heart of this discovery are two ancient churches — one grand and basilica-like, the other intimate and inscribed with the Coptic language — alongside residential homes, burial sites, and a rare mural of Jesus Christ healing the sick.
From Pagan Outpost to Christian Stronghold
Originally settled during the Ptolemaic and Roman periods, Ain al-Kharab began as a thriving pagan community. Archaeological evidence shows that by the early centuries AD, many Roman-era buildings were repurposed for Christian worship and community functions. This transformation mirrors Egypt’s broader religious revolution following the legalization of Christianity under Roman rule and its eventual rise to the dominant faith.
Egypt’s Minister of Tourism and Antiquities Sherif Fathy described the discovery as “a reflection of Egypt’s cultural diversity and resilience,” emphasizing how it deepens our understanding of early Christianity’s spread into Egypt’s most remote regions. He praised the Egyptian teams’ achievements, noting their role in placing Egypt prominently on the global cultural tourism map.
Who Were the Copts — and Why This Matters
The Copts are the native Christians of Egypt, direct descendants of the ancient Egyptians. Speaking the Coptic language — the final stage of the Egyptian tongue written in Greek script — they carried the spiritual and cultural legacy of one of the world’s oldest civilizations into the Christian era.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Christianization of Egypt in the 3rd to 7th centuries AD was not just a religious shift; it was a cultural turning point that blended ancient traditions with a new faith. In a world still dominated by the Roman Empire’s pagan roots, Egypt became one of Christianity’s earliest strongholds outside the Holy Land, giving rise to monasticism and influencing Christian thought across the Mediterranean.
Discoveries like Ain al-Kharab are rare windows into this transformation, showing how Christianity didn’t just flourish in the Nile Valley’s great cities but reached remote desert oases, shaping communities far from the imperial centers of power.
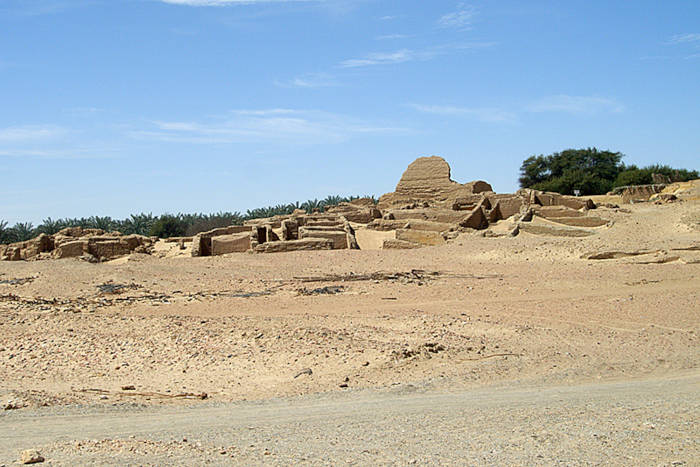

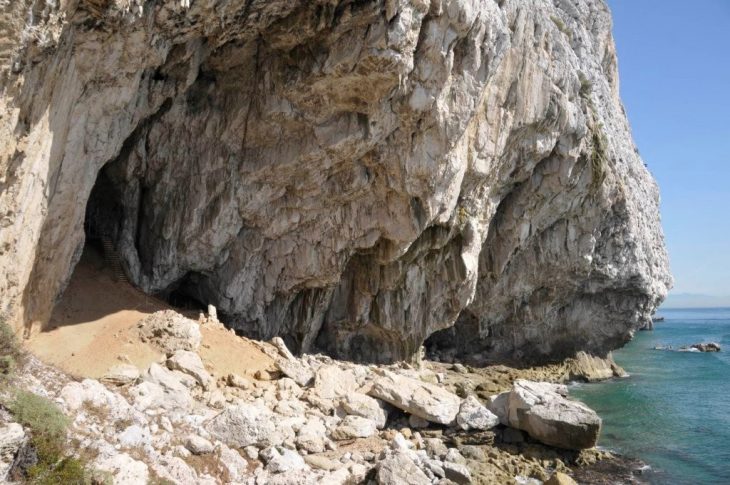
Ancient settlement of Ain al-Kharab/Ain al-Turba, Kharga Depression, Libyan Desert, Egypt. Credit: Public Domain
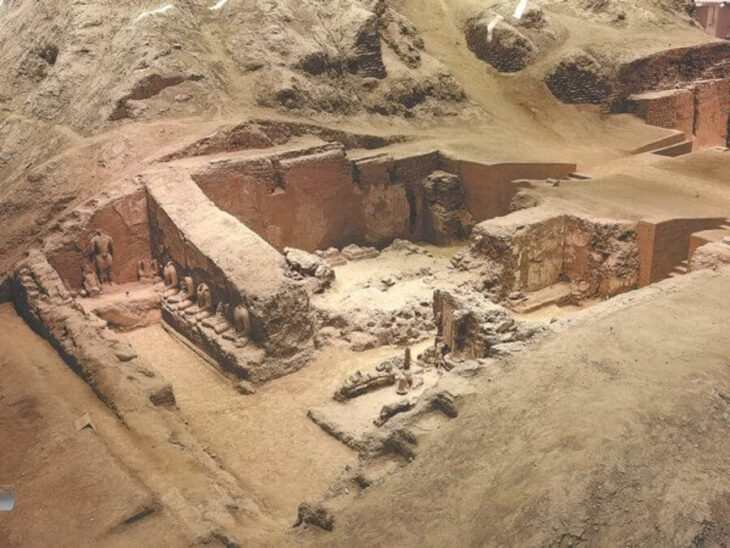
A Desert City Built for Faith
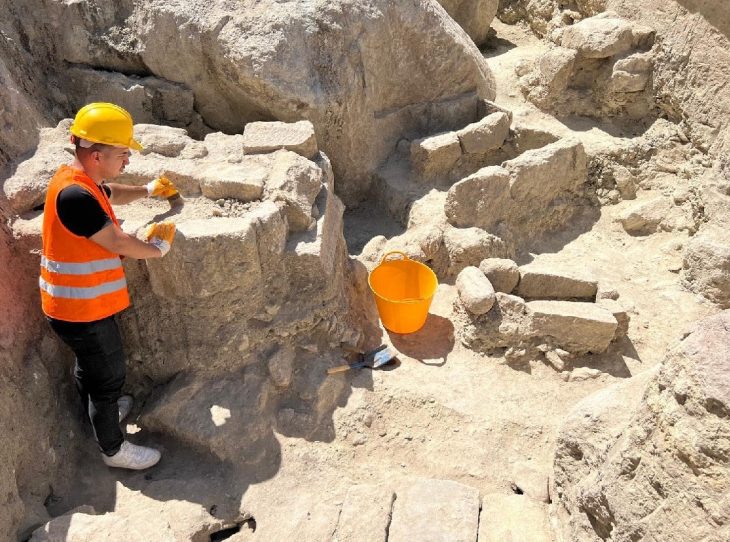
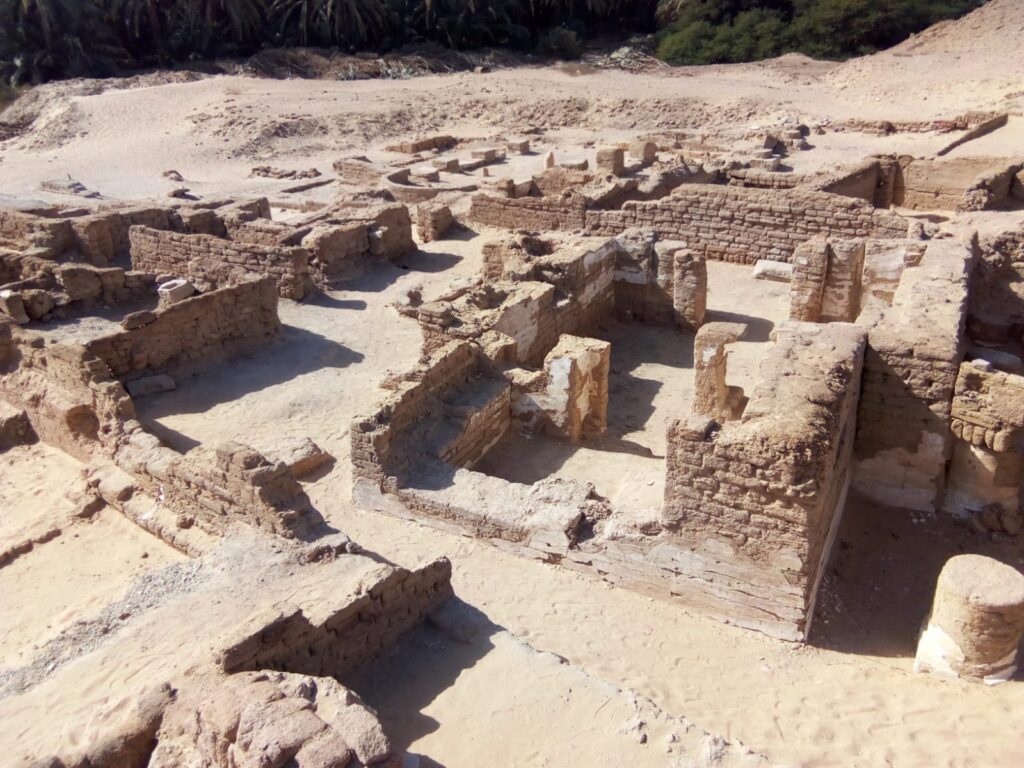
The larger of Ain al-Kharab’s two churches follows the basilica design familiar to early Christianity: a wide central hall flanked by aisles, divided by rows of square columns. South of the main hall, archaeologists found service buildings — possible storage rooms, kitchens, or meeting areas — suggesting that the church was the spiritual and social heart of the community.
The second church, more modest in scale, is rectangular and surrounded by the remnants of seven exterior columns. Inside, faint yet legible Coptic inscriptions speak of prayers and dedications made over 1,500 years ago. These writings are not just decorative; they are voices from Egypt’s Christian ancestors, preserved in the arid stillness of the desert.
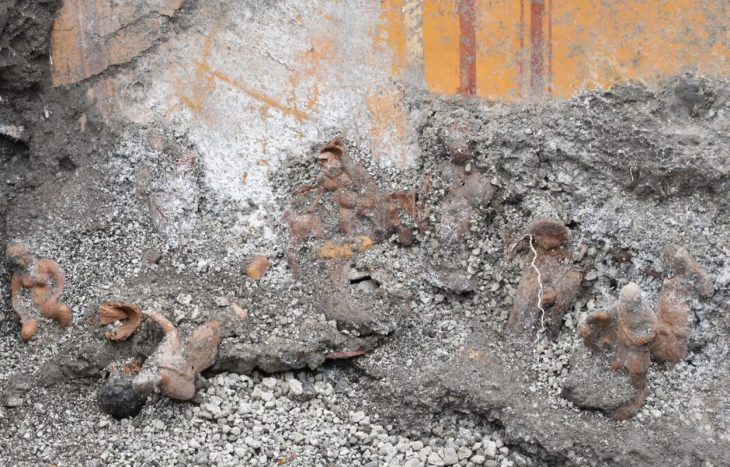
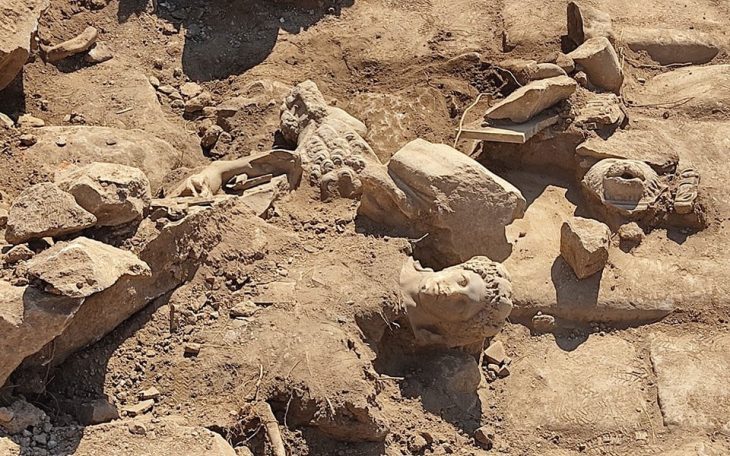
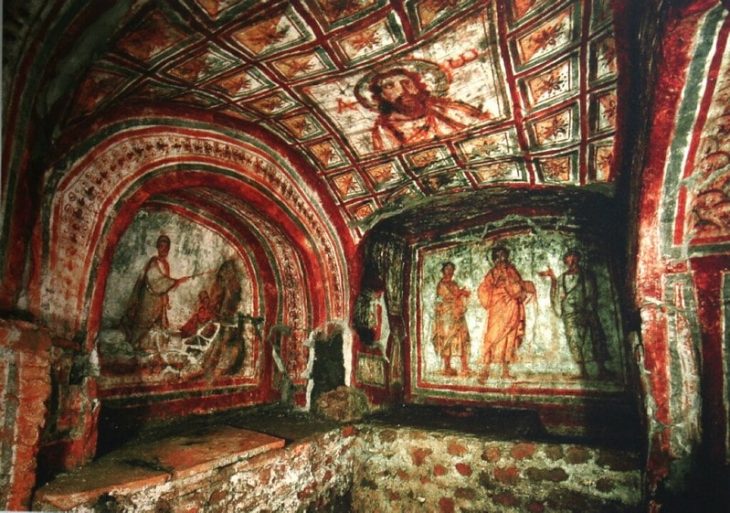
The Mural of Christ Healing the Sick
Perhaps the most captivating find is a painted mural of Jesus Christ performing a healing miracle. Art historians note that such depictions are extremely rare in Egypt’s Western Desert. The artwork blends Egyptian artistic techniques — strong outlines, earthy pigments — with new Christian iconography, capturing a moment when two worlds of symbolism met.
In a time when literacy was limited, murals like this were powerful teaching tools, conveying the core messages of Christian faith through images understood by all.
Life in an Early Coptic Settlement
The city’s mudbrick homes, some still showing traces of white plaster, reveal a society both practical and resourceful. Large clay jars set into the ground stored grain and food, ovens baked bread for daily meals, and workrooms kept tools and goods.
Fragments of pottery, glass vessels, and ostraca (pottery sherds with inscriptions) paint a picture of a self-sustaining community that balanced agricultural labor with religious devotion. Human burials, oriented in line with Christian traditions, underscore the settlement’s deep spiritual identity.

A Crossroads of Faith and Culture
The Kharga Oasis was more than an isolated desert outpost — it was a crossroads of trade, ideas, and cultures. Here, Roman roads met ancient caravan routes, and here too, pagan temples gave way to Christian sanctuaries. The transformation of Ain al-Kharab is a microcosm of Egypt’s broader journey from the polytheistic world of the Pharaohs to the Christian Middle Ages.
For modern-day Copts, discoveries like this are more than archaeology — they are a direct link to their ancestors’ faith and endurance.
Why This Discovery Resonates Today
In a world where heritage can be fragile, Ain al-Kharab stands as a reminder of the enduring legacy of Egypt’s Christian communities. It tells a story of adaptation — how ancient people took familiar spaces and reshaped them for a new spiritual vision, leaving traces that would survive for over a millennium under desert sands.
As excavation continues, each new find brings us closer to understanding not just how the Copts lived, but how faith itself reshaped Egypt’s landscapes and identities.
Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities of Egypt
Cover Image Credit: Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities of Egypt