A new study discovers that ancient headless skeletons discovered in mass graves in China are the remains of victims who were massacred around 4,100 years ago in headhunting events.
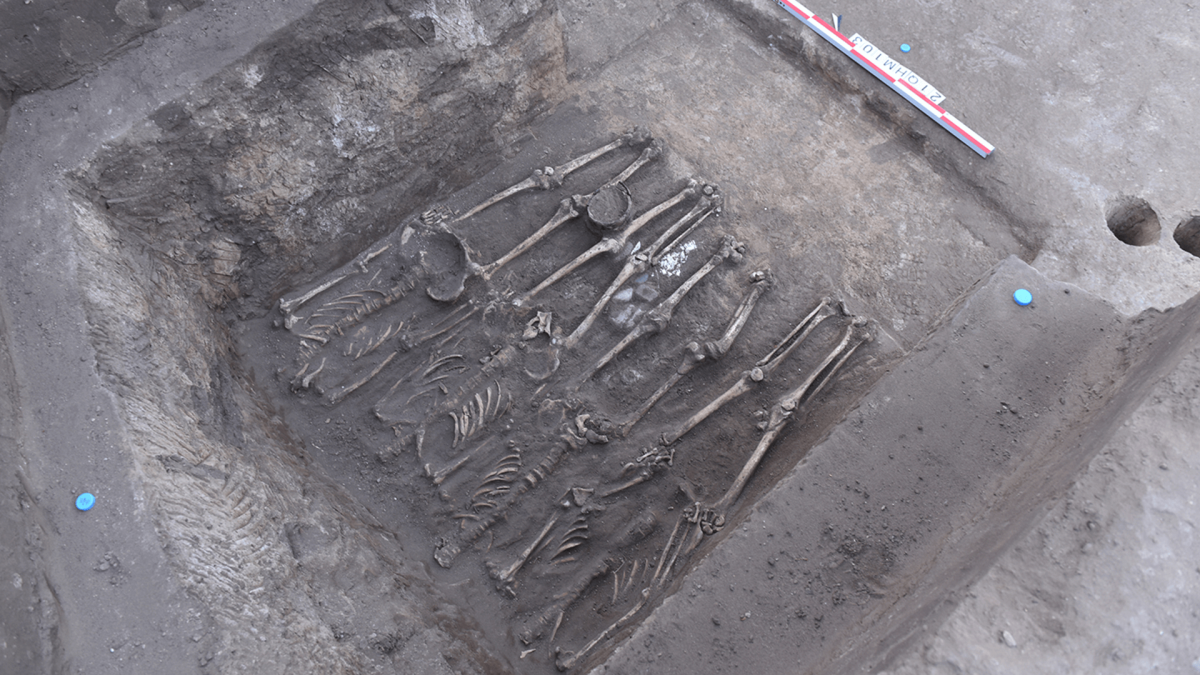
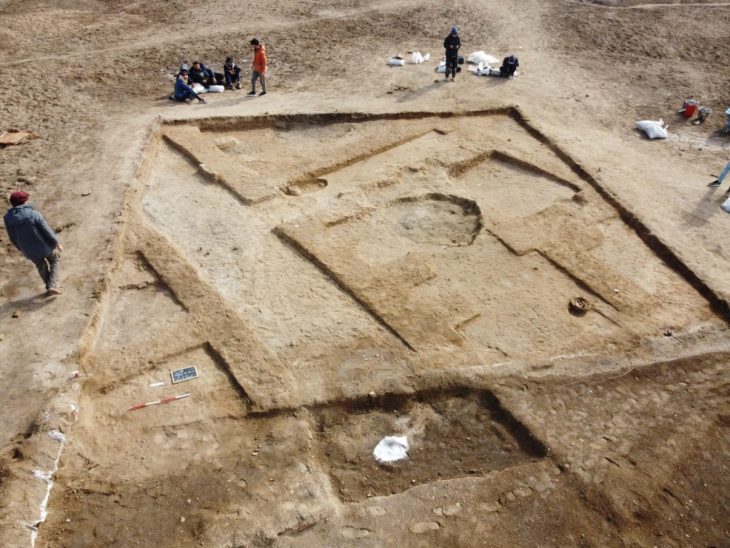
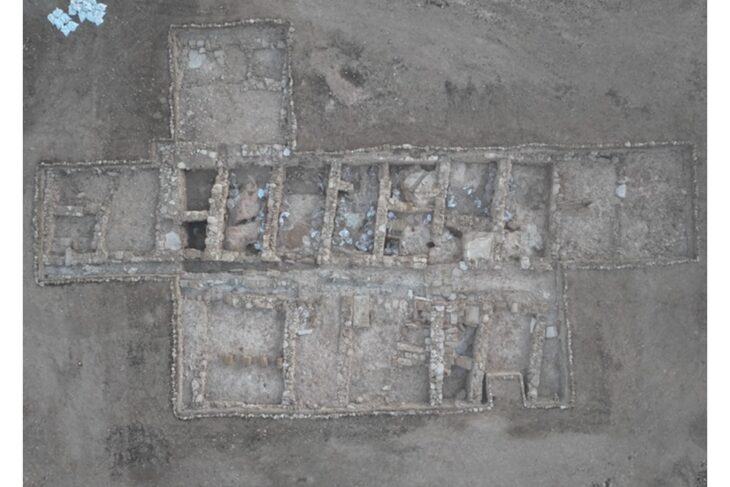
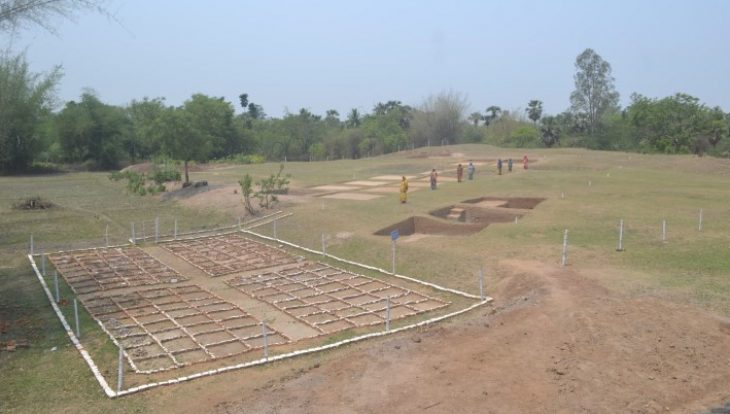
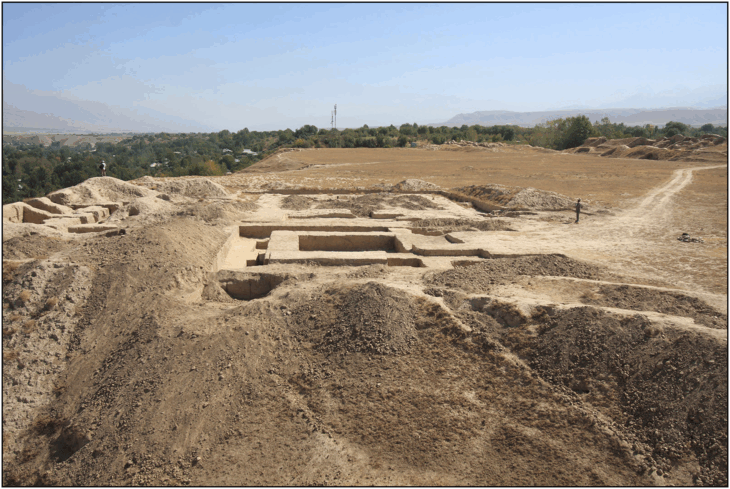
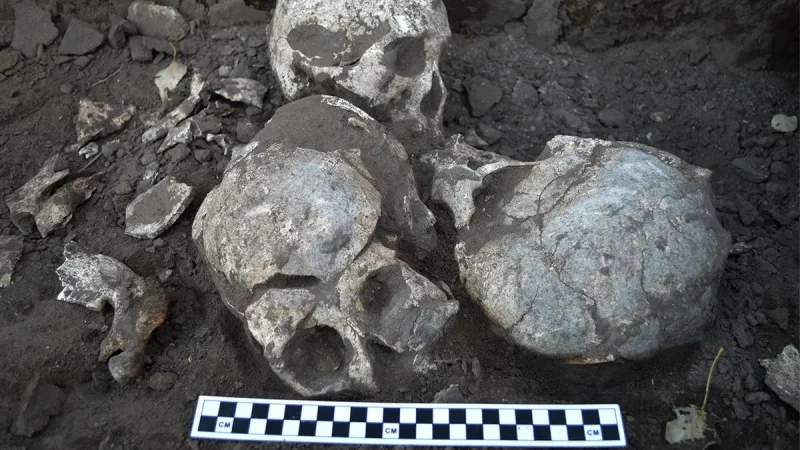
In China, researchers discovered a mass grave containing 41 headless skeletons. The Honghe site grave contains the largest known Neolithic Chinese headhunting massacre. Thrity-two individuals appear to have been killed during the same event.
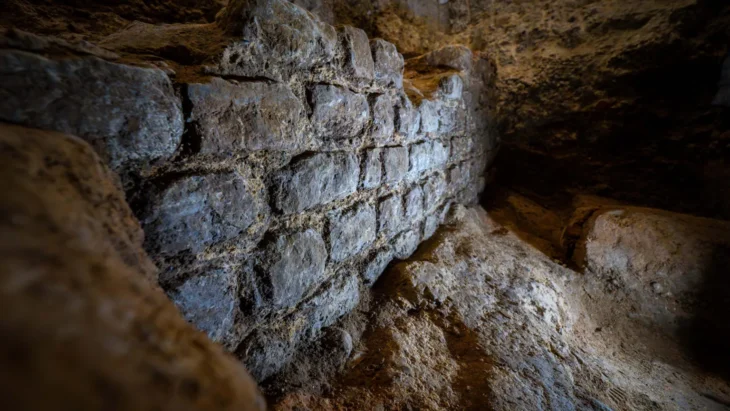
Since its initial discovery in the 1990s, the gruesome site has been the subject of six different excavations. In the most recent, researchers discovered 68 skeletons in two houses and three tombs, including 41 without heads. The bodies are 4,100 to 4,400 years old. In addition, the team also found the skulls of four men in a pit outside the house and several bone tools buried alongside the skeletons.
Unusually, all the victims were women or children. Every skeleton has cut marks across the neck vertebrae and several have V- and U-shaped cuts on the second vertebra. The assailants used bone-handled knives with stone blades. The similarity of these markings suggests that the killings were part of the same attack.
These cutting tools were likely bone-handled instruments with stone blades, consistent with findings in the Honghe area, paralleling the same technique across the board in the perpetrator’s techniques and weapons. They indicate “the presence of a conscious head-hunting behavior”.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The study, published in the Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences journal, employed visual inspections and imaging techniques to identify signs of decapitation. The researchers found that 32 of the 41 beheadings had occurred in a single event!
Headhunting was a common practice in many Asian countries, particularly in Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands. Headhunting was frequently motivated in this context by a combination of ritualistic, social, and territorial factors. Tribes and indigenous groups used headhunting to gain spiritual power, demonstrate dominance over rival communities, and appease ancestral spirits.
The study speculates on two possibilities for the beheadings. Their first theory is that it was a ritual.
It’s possible that when rivals attacked the settlement, they targeted women and children, resulting in an “interpersonal conflict with a high level of cruelty,” the researchers wrote in the study. It’s also possible that interlopers used a “ritual of selective decapitation” when choosing their victims, the team wrote.
“Heads of enemy tribes were sought after for a specific ritual meaning, to conquer and/or possess the soul and energy of the enemies,” Qian Wang, co-author of the recent study, told LiveScience. This specific ritual might have required the heads of women and children.
The second theory involved settlement rivalry. The site had three defensive trenches around it, suggesting there was a conflict between the Honghe people and other communities.

The vast majority of those living at Honghe would have been farmers, fishers, and hunters. By choosing women and children as victims, a rival group would have caused the most outrage because of the “high level of cruelty.” In this scenario, the attackers took the heads as trophies.
The researchers suggest that the men may have been away working during the attack and returned to find the massacred bodies of their loved ones. They then chose to bury them in the houses before abandoning the settlement.
Meanwhile, researchers believe that the four skulls found in the pit may be “trophies” brought by members of the Honghe settlement from another enemy tribe.
Cover Photo: Part of the burial site. Photo: Qian Wang/Texas A&M University School of Dentistry