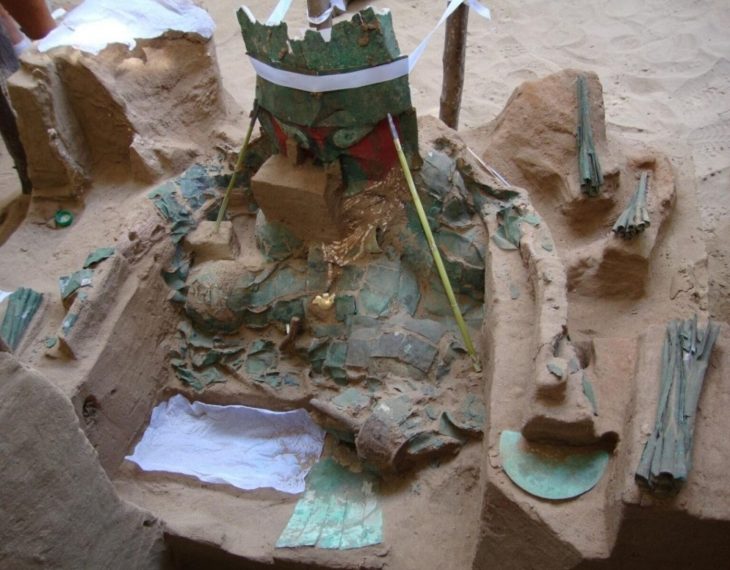
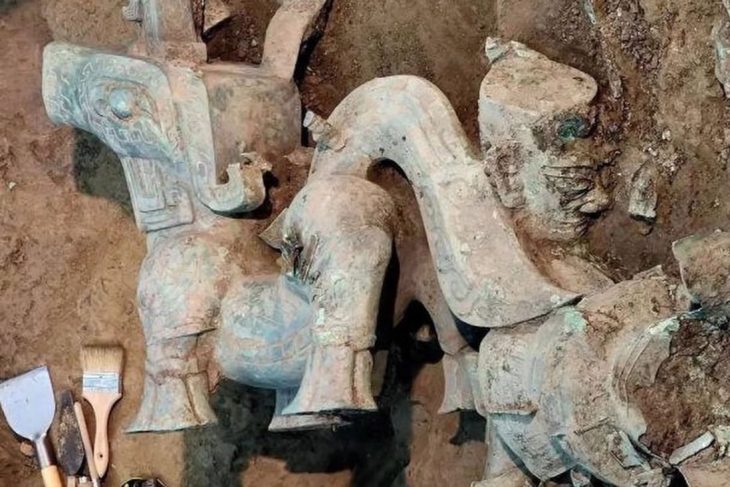
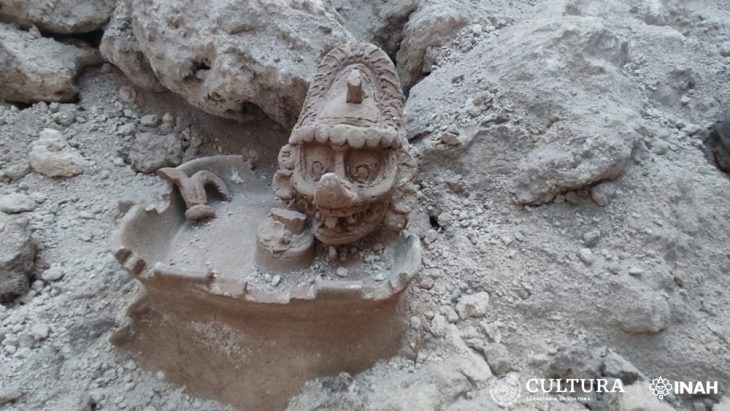
Israeli archaeologists have been discovered ancient artifacts and treasures amid the wrecks of two ships on the seafloor off the coast of Caesarea, the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA) revealed on Wednesday.
The finds made near the ancient city of Caesarea were dated to the Roman and Mamluk periods, around 1,700 and 600 years ago, archaeologists said.
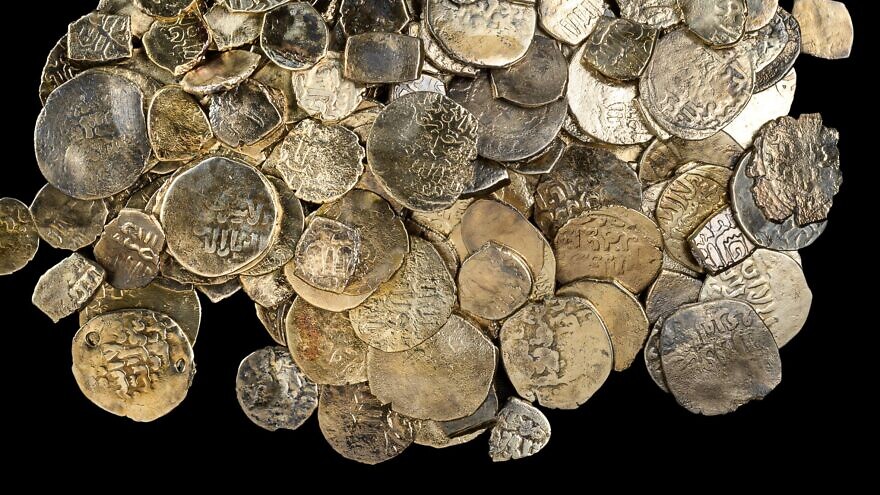
Hundreds of Roman silver and copper coins from the mid-third century, as well as more than 500 Middle Ages silver coins, were discovered among the debris.
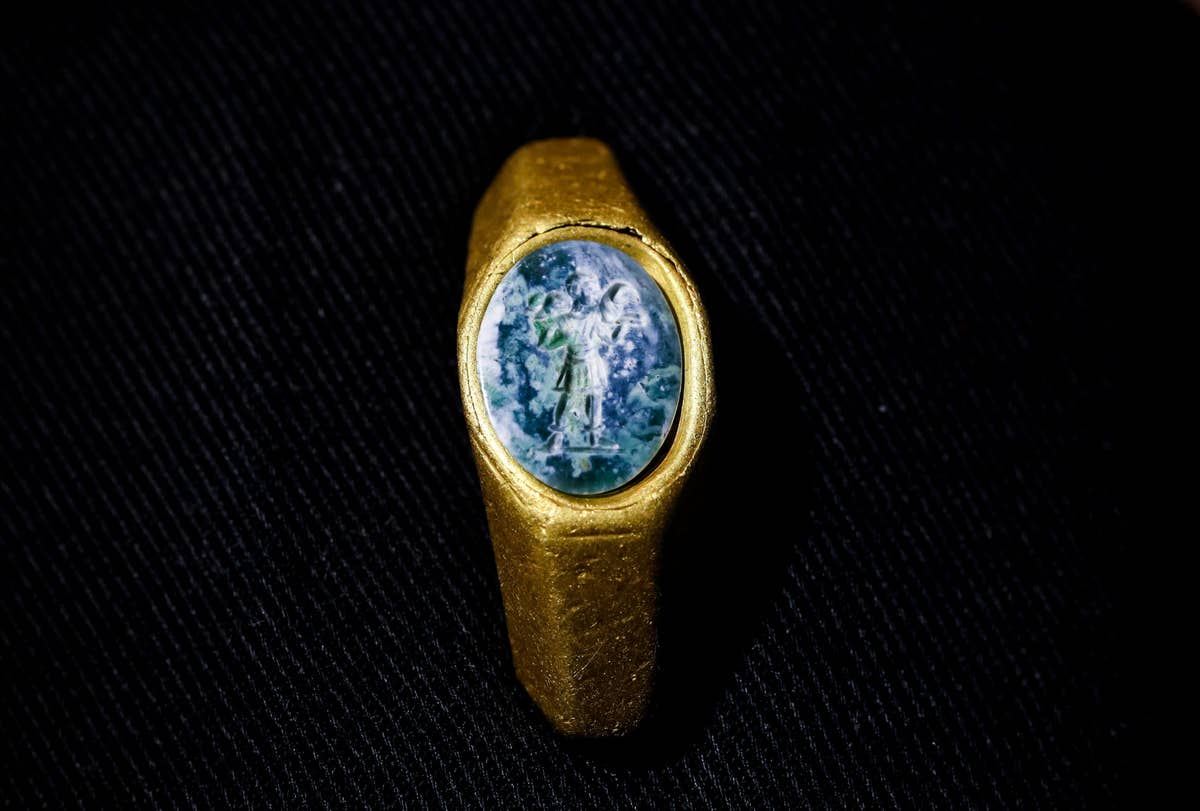
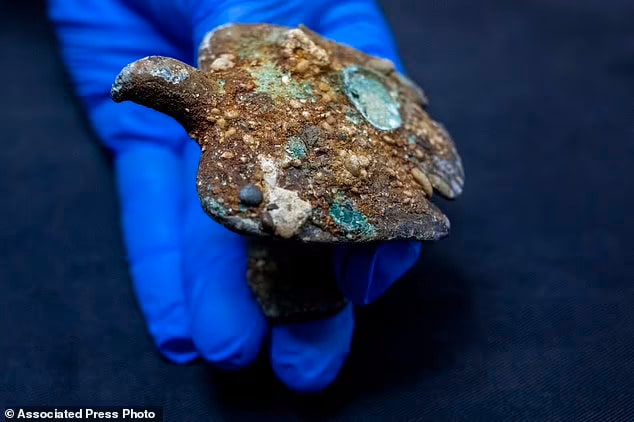
According to the authority, the treasure —a gold ring engraved with the figure of the Good Shepherd, a well-known symbol of Jesus in early Christian art, and a bronze figurine in the form of an eagle, symbolizing Roman rule — was found scattered four meters (13 feet) down on the seafloor near the remains of the ships’ wrecked hulls.

Other discoveries included a statue of a Roman pantomimus wearing a comic mask, several bronze bells used to fend off bad spirits, and earthenware containers, as well as dozens of big bronze nails, lead pipes from a bilge pump, and a broken massive iron anchor.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
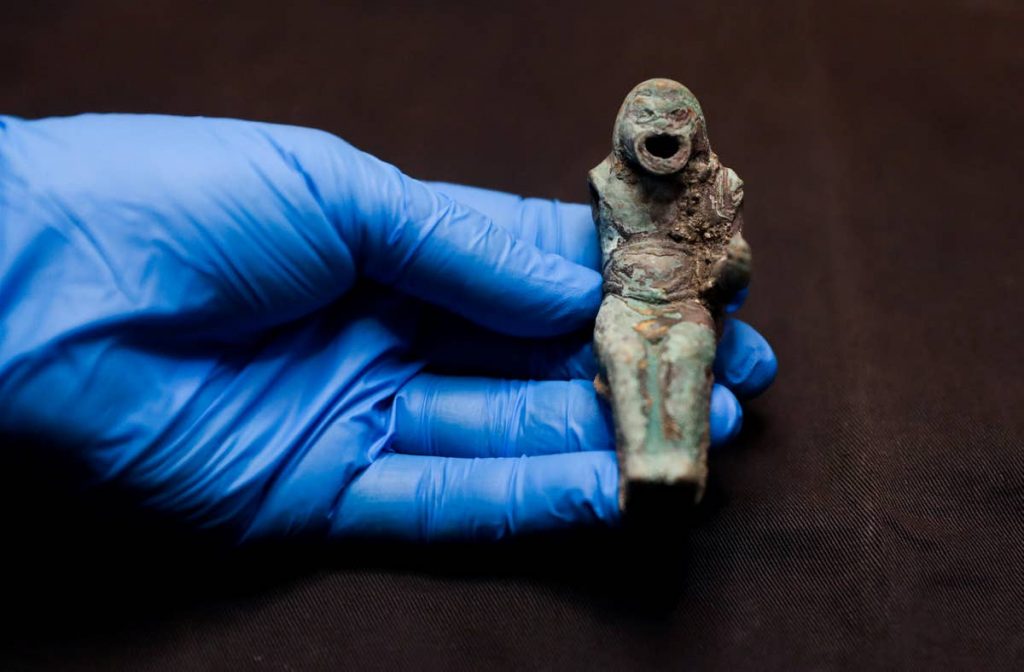
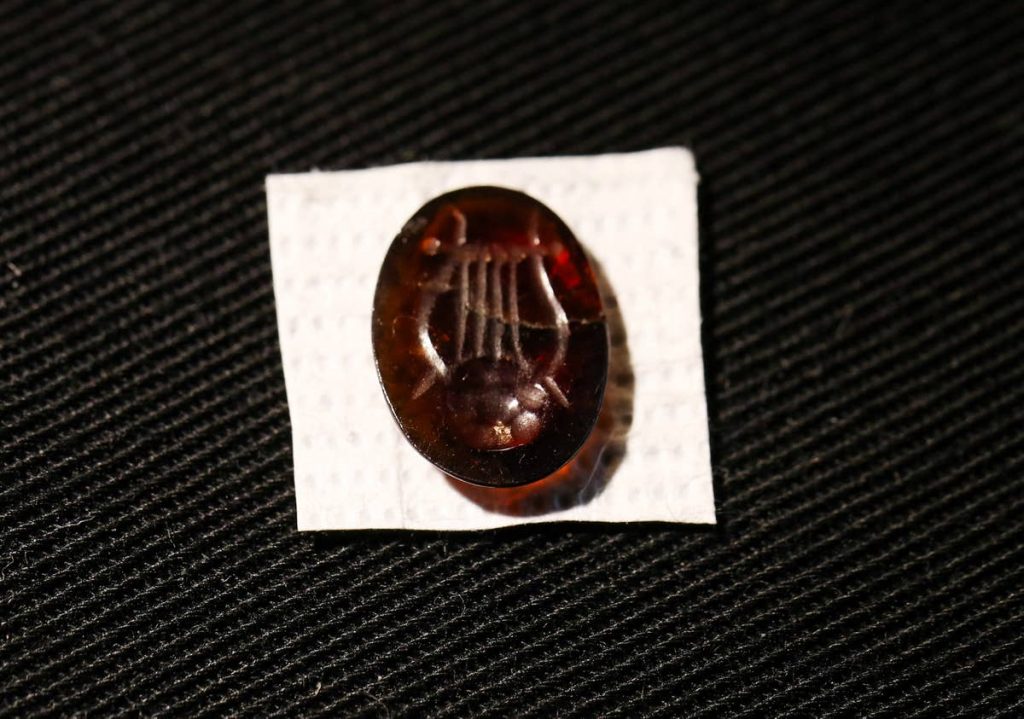
Among the items found are a red gemstone engraved with a lyre, and a gold ring with a green gemstone depicting a shepherd boy in a tunic bearing a ram or sheep on his shoulders, the IAA said in the announcement.

According to the IAA, the carving on the red stone points to the Hebrew Bible and Greek mythology, as the lyre, “David’s Harp,” appears in the Book of Samuel. Greek myth features “Apollo’s Lyre,” made by the infant Hermes on the morning of his birth, causing Apollo to make him and his mother gods.
The “good shepherd” engraving on the green stone is one of the oldest images used to symbolize Jesus, possibly indicating that the ring’s owner was an early Christian.

Robert Cole, head of the authority’s coin department, called the item “exceptional.”
“On the gemstone is engraved an image of the `Good Shepherd,´ which is really one of the earliest symbols of Christianity,” he said.
Caesarea, where it was found, was where Christianity “began to be disseminated across the world,” said the IAA Marine Archeology Unit’s Jacob Sharvit.

Sharvit said that the Roman ship is believed to have originally hailed from Italy, based on the style of some of the artifacts. He said it remained unclear whether any remnants of the wooden ships remained intact beneath the sands.
“Israel’s coasts are rich in sites and find that are immensely important national and international cultural heritage assets,” said IAA director Eli Eskozido, adding that they are “extremely vulnerable, which is why the IAA conducts underwater surveys to locate, monitor, and salvage any antiquities.”
“The discovery and documentation of artifacts at their original findspot have tremendous archeological importance, and sometimes even a small find leads to a great discovery,” he stressed.
Cover Photo: A gold ring engraved with the figure of the Good Shepherd was discovered off the coast of Caesarea. Photo: Ohad Zwigenberg