Archaeologists conducted a DNA analysis of the tooth enamel of a person who died more than two millennia ago on Bryher, one of the islands Isles of Scilly, an archipelago off the southwest of England. It was buried with a beautiful bronze mirror and a costly sword.
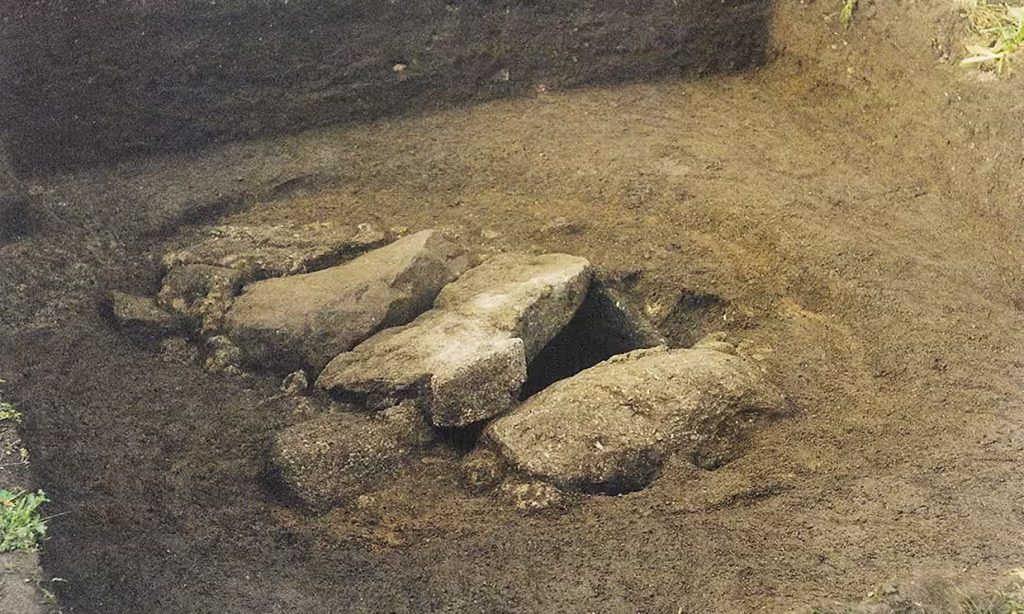
Archaeologists have debated for years whether the burial chamber with stone walls that were found on Bryher in 1999 held the remains of a man or a woman.
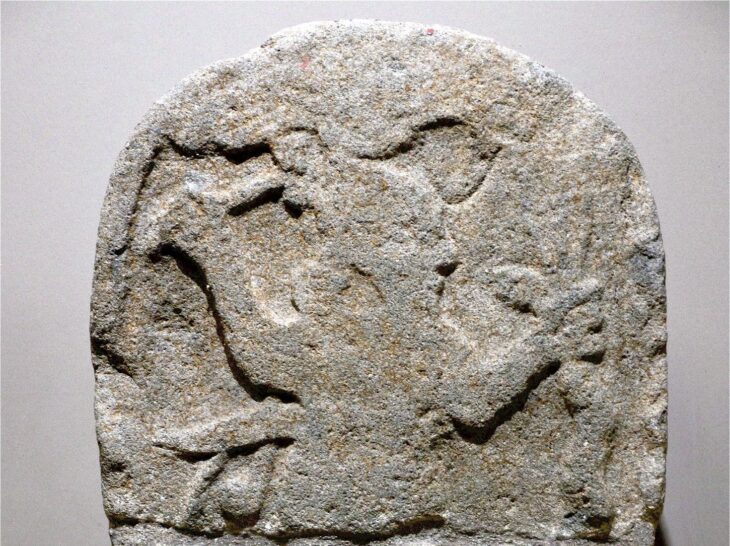
Along with the sole person’s remains, excavations turned up a sword in a copper alloy scabbard and a shield, both of which are typically associated with men. But there were also a brooch and a bronze mirror that had what appeared to be a sun disc motif and was typically associated with women. Due to the presence of both a mirror and a sword, the grave is unique in iron age Western Europe.
It was previously thought that only Iron Age women were buried with mirrors and only warrior men with swords, but the body now identified as a woman owned both, in death and presumably in life.
The discovery could shed light on the role of women warriors at a time when violence between communities is considered a fact of life.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
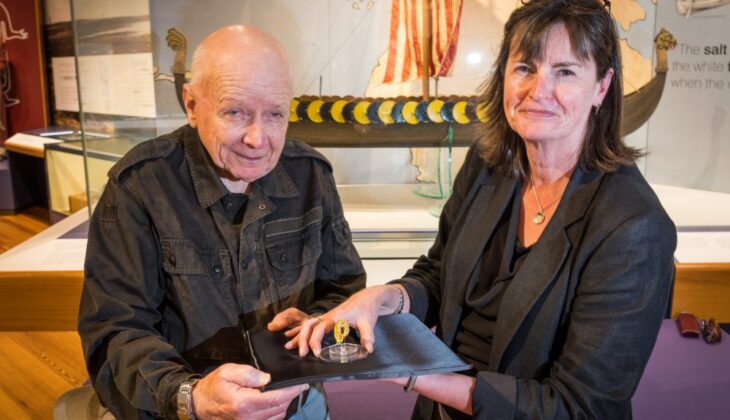
Dr. Sarah Stark, a human skeletal biologist from Historic England, said the findings could shed light on the role of women in Iron Age Britain.
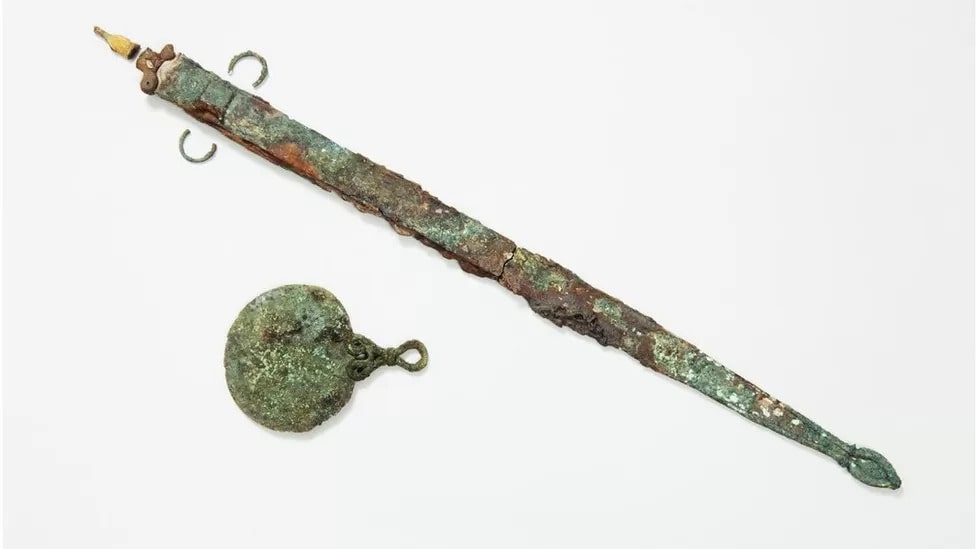

“Although we can never know completely about the symbolism of objects found in graves, the combination of a sword and a mirror suggests this woman had high status within her community and may have played a commanding role in local warfare, organizing or leading raids on rival groups,” Stark says.
She adds: “This could suggest that female involvement in raiding and other types of violence was more common in Iron Age society than we’ve previously thought, and it could have laid the foundations from which leaders like Boudicca would later emerge.”
A farmer on the island of Bryher accidentally discovered the grave, a neatly built stone-lined pit, in 1999. The majority of the crouching skeleton was reduced to a single soil stain, with only a few scattered pieces of bones and teeth remaining. The University of California at Davis scientists developed a method that extracts proteins from tooth enamel that can be linked to the X and Y chromosomes, which determine sex. Earlier attempts to extract DNA from bones failed because they were too decayed, but new evidence has come from this method.

Dr. Glendon Parker, an adjunct associate professor in the Department of environmental toxicology at the University of California, Davis, said: “Tooth enamel is the hardest and most durable substance in the human body. It contains a protein with links to either the X or Y chromosome, which means it can be used to determine sex. This is useful because this protein survives well compared to DNA.
“Our analysis involved extracting traces of proteins from tiny pieces of the surviving tooth enamel. This allowed us to calculate a 96% probability that the individual was female.”
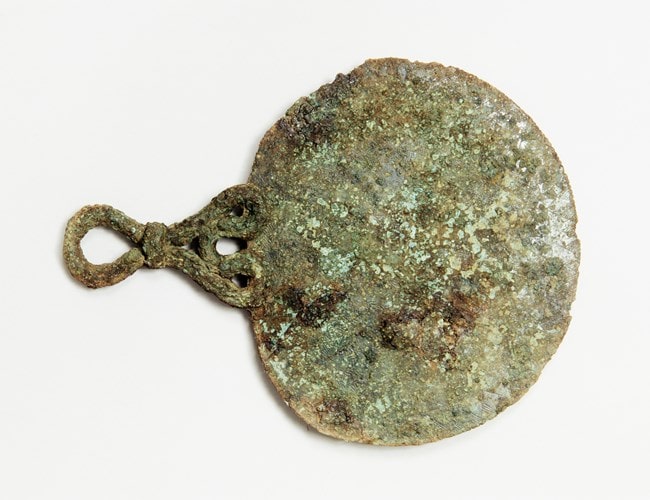

The grave held the richest collection of grave goods from the southwest of England: as well as the crouched skeleton there were shield fittings, a ring for a sword belt, a copper brooch and ring, fibres from woven textiles, and what may have been a sheep or goat skin.
The mirror and weapons found in the grave are all associated with warfare. It is thought that mirrors may have be used in the iron age for signalling, communicating and coordinating attacks. They also had ritualistic functions, as a tool to communicate with the supernatural world to ensure the success of a raid or “cleanse” warriors on their return.
The research was published in the Journal of Archaeological Science Reports.
Cover Photo: Historic England