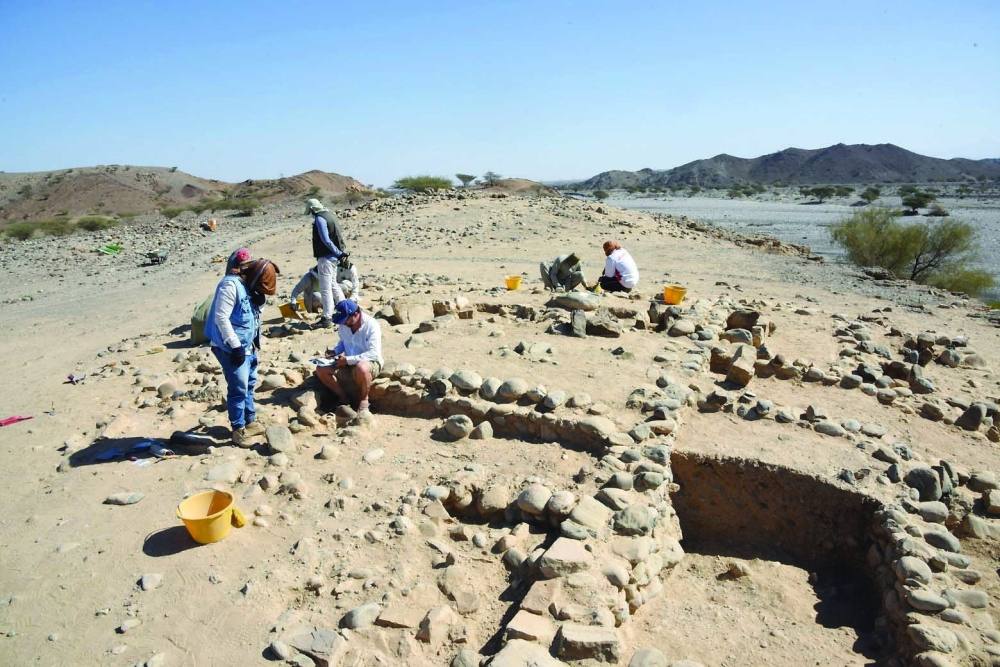
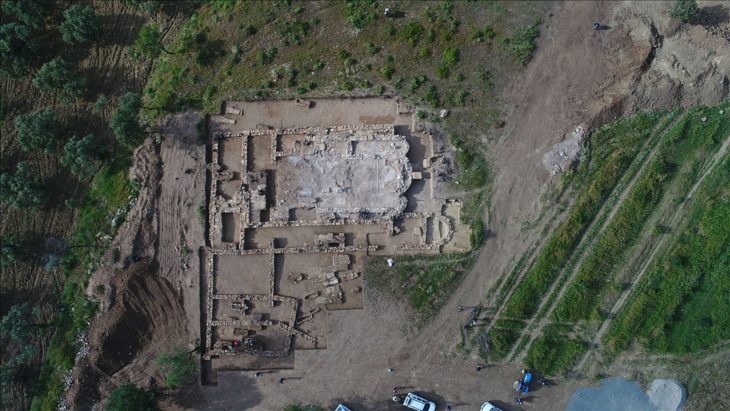
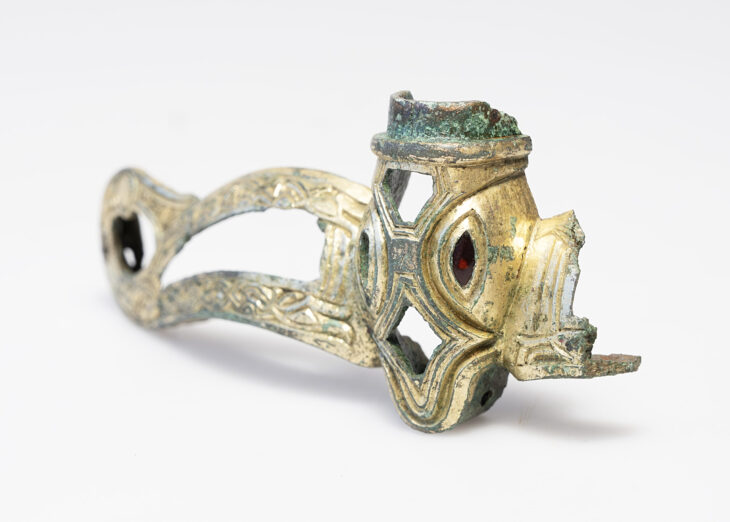
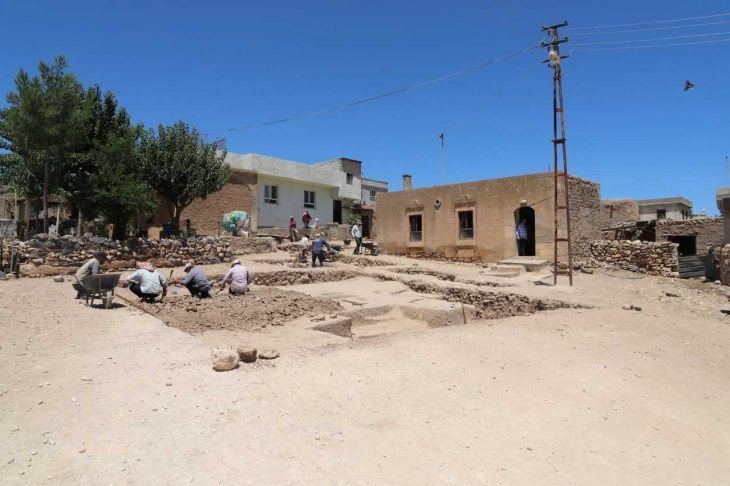
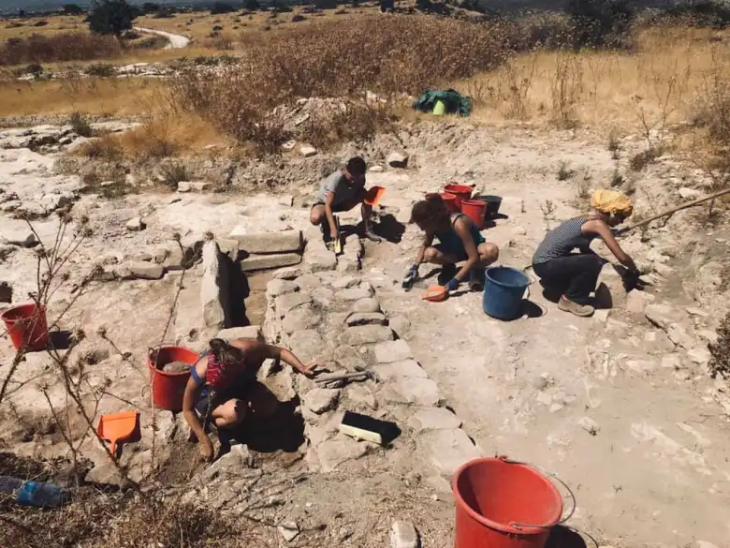
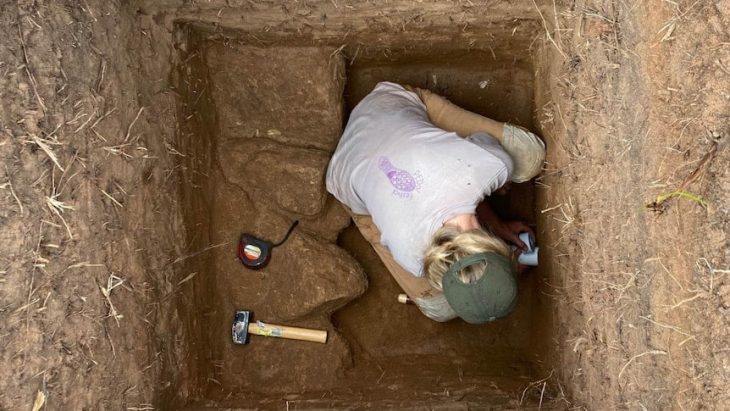
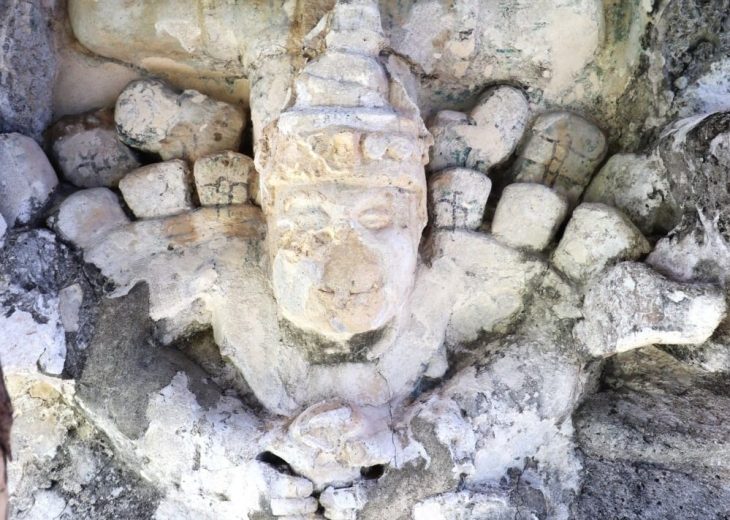
Archaeologists have uncovered a unique Iron Age children’s funerary building at the Manaqi archaeological site in Rustaq, South Al Batinah Governorate, Oman. This discovery, the first of its kind in the region, dates back three thousand years.
The discovery is the result of joint work by archaeologists from Oman’s Sultan Qaboos University and Sorbonne University archaeologists.
The discovery marks an important turning point in the understanding of funerary rituals on the Omani peninsula, as it is the first funerary building dedicated to the burial of children to be uncovered so far in the region.
The ‘Manaqi’ site is one of the largest Iron Age settlements in the South Al Batinah Governorate. The excavations, conducted by the Department of Antiquities in collaboration with a team from Sorbonne University in Paris and overseen by the Ministry of Heritage and Tourism, wrapped up their first season in February. Excavations are expected to continue over the next five years.
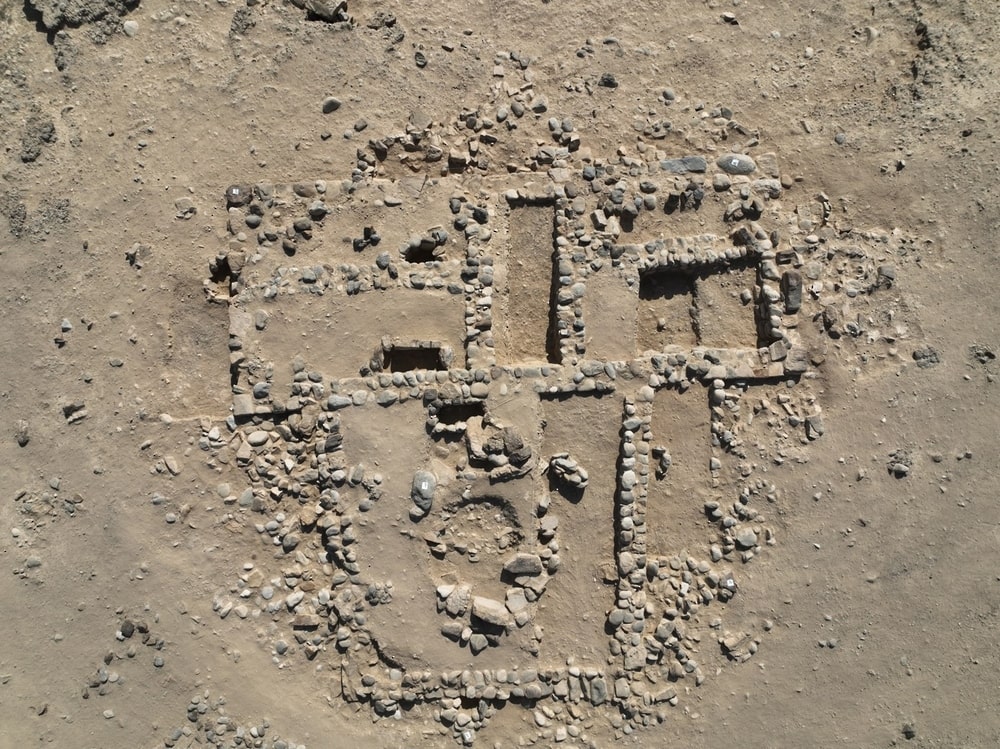

Following a preliminary site survey conducted by the joint archaeological team, two buildings, S1 and S2, were chosen for excavation during the first season. Building S2, which stood out from the other buildings in the settlement with its unique T-shaped geometric plan, was especially noteworthy.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Archaeological excavations within and around the building revealed over thirty children’s graves, including newborns. This distinguishing feature raises questions about the motivations and beliefs that led to the allocation of a separate building for the burial of children in that era, which contradicted the funerary customs prevalent in the Iron Age.
Dr. Mohammad Abdul Hamid Hussein, the research team’s leader, emphasizes the importance of this discovery in understanding the social and religious practices of ancient Omani societies.

Dr. Hussein stated, “This discovery opens new horizons for research and study about funerary rituals and religious beliefs in the Iron Age in the Omani Peninsula, and focuses on an important and unknown part of the history of this region, and deepens our understanding of the cultural and social traditions of the societies that lived in that period.”
The discovery of a large number of residential buildings, in addition to many cemeteries, spread over a wide area of the site and several defensive towers have been interpreted by archaeologists as an indication of the major and central role the settlement played in the region in the 1st millennium BC.
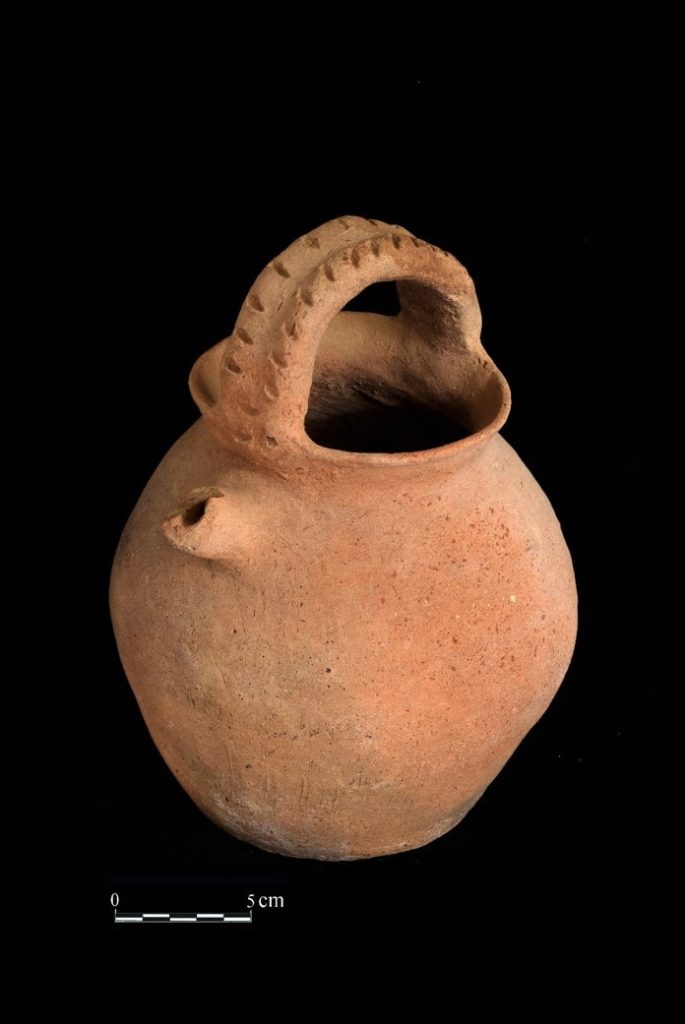
Among the artifacts discovered were jars with basket-shaped handles and a rare piece of pottery adorned with a seal print depicting two men.
Cover Photo: Oman News Agency