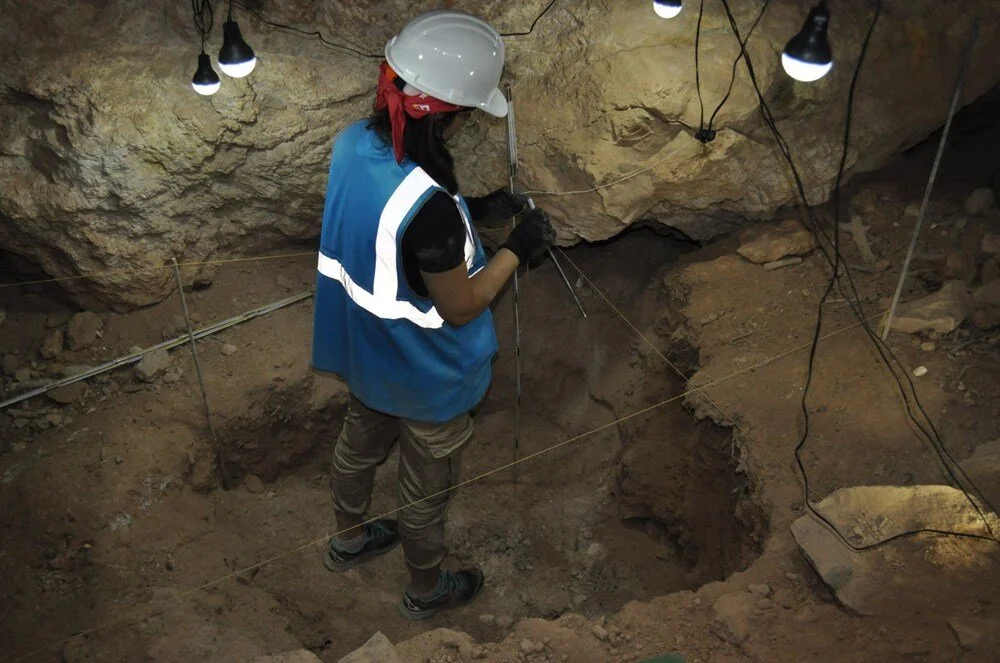
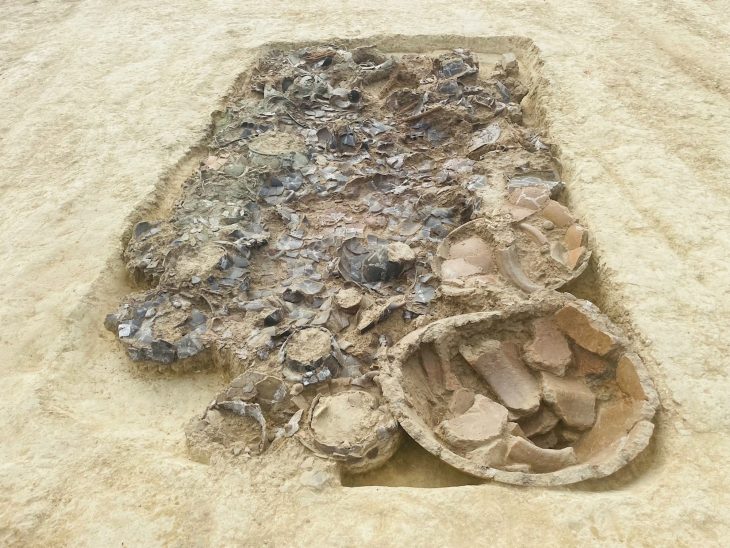
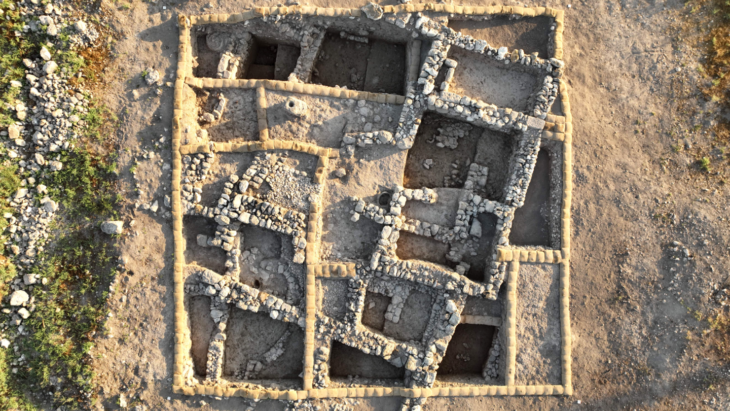
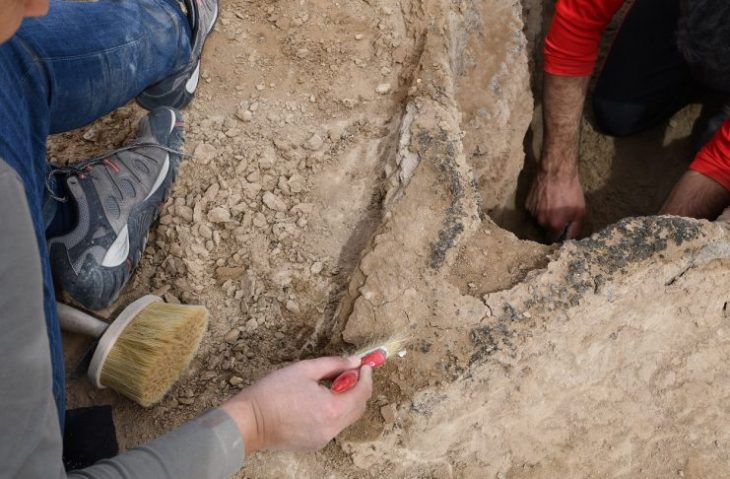
In the excavations carried out in the İnkaya Cave in Çanakkale, located in the northwestern part of Türkiye, in addition to the traces of 86 thousand years of human life in the layers of the cave, many tools made of flint for various purposes were also found.
İnkaya Cave, located within the borders of Bahadırlı village in the Çan district, was found during the Muğla and Çanakkale Provinces Survey conducted in 2016 under the direction of İsmail Özer, a lecturer at Ankara University, Department of Paleoanthropology.
Excavations in the cave, which will shed light on Paleolithic period migrations between Anatolia and the Balkans, were carried out by an international team between 2017 and 2020 under the presidency of the Troy Museum Directorate.
During the excavations carried out last year, the Middle Paleolithic period workshop part of the cave was unearthed.
The İnkaya Cave excavations, which have been ongoing, were granted supported status by the Turkish Historical Society this year. Carried out by a team of 20 people, this year’s excavation revealed that humans from the Middle Paleolithic Period resided in the region for extended periods due to the availability of flint raw material and water resources.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Evidence of the Paleolithic era in Çanakkale was previously limited. Through our research, it became evident that Çanakkale is actually one of the very rich provinces in Türkiye in terms of the Paleolithic period,” said excavation director Professor Ismail Ozer.
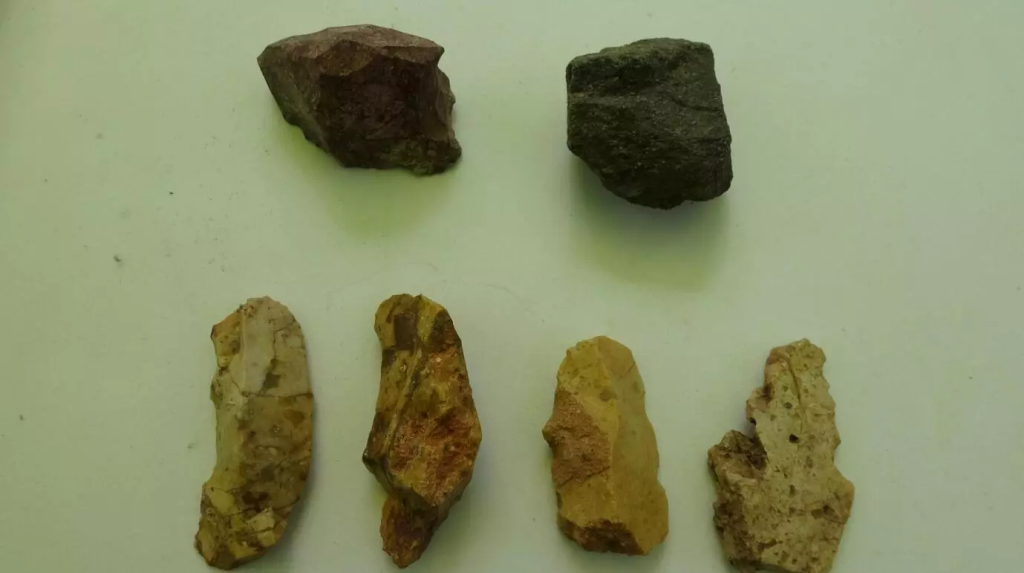

Özer pointed out that despite the numerous excavation studies in the country, the majority of these are conducted in open areas, and there are very few cave excavations currently ongoing in Turkish provinces.
Most of these are concentrated in the southern regions, with only the İnkaya excavation continuing in Western Anatolia, he said.
“Our work in this area has taken us to the Middle Paleolithic Period, roughly dating back from 250,000 to about 50,000 years ago. Our findings indicate that people lived here intensely during this period.”
The finds on the eastern slopes of the cave provide researchers with more precise information in terms of dating, taking them back to 86,000 years ago, Özer stressed.
Noting that the remnants obtained during the excavation are currently limited to flint artifacts, Özer said that they have not yet found organic remnants, such as skeletal remains of the humans who lived in the cave during that period, animal bones or plant residues, which are the kitchen scraps humans consumed.
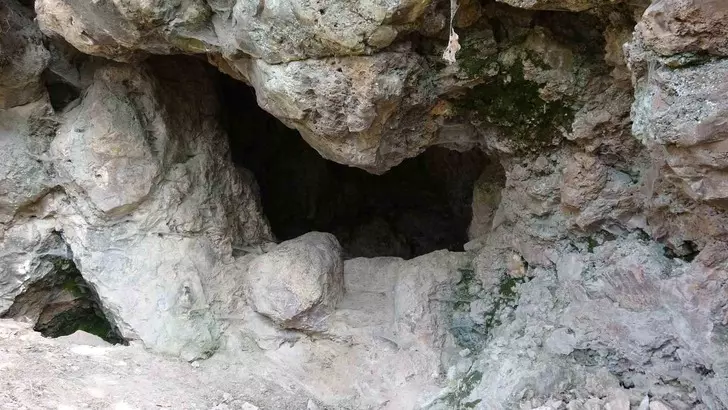

Stating that İnkaya Cave is essentially composed of a flint rock formation, Özer noted that the main reason people chose this place is that while crafting tools for their daily needs, they could also obtain the necessary raw materials from the cave.
“A toothed tool we found in the excavations could have been used for a purpose similar to today’s saw. As for the tools with handles, they might have been inserted into a tree branch or perhaps into bone or horn using resin, after thinning out the handle part of the tool. The edges would be worked on to make them functional. These tools could have been used for digging the soil or scraping the skin of animals. We will determine their specific purposes in the coming years through microscopic analysis of the stones,” he explained.
Özer said that the İnkaya Cave excavations continue inside the cave and the open area settlement around it.
Cover Photo: Ankara University