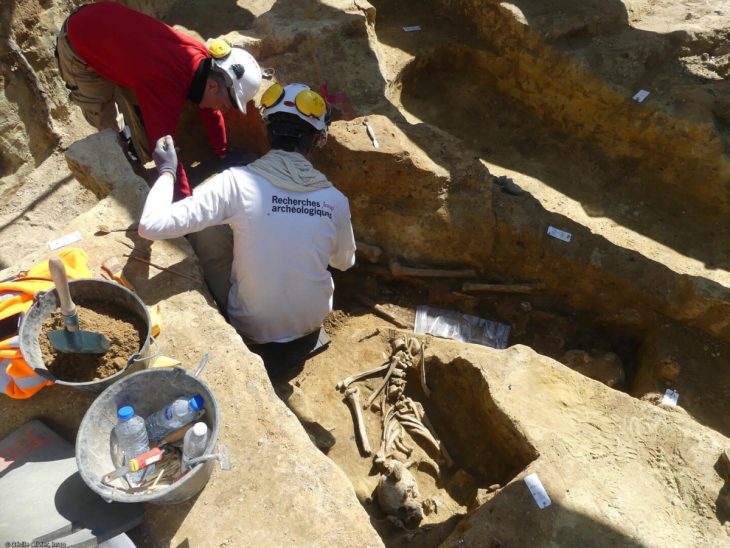
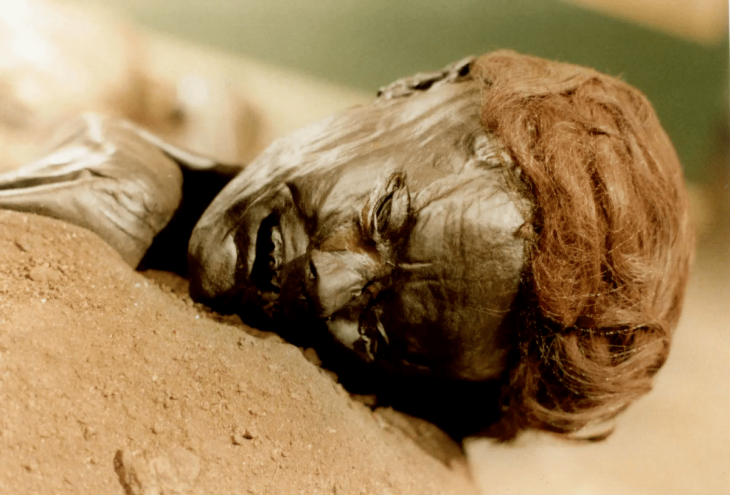
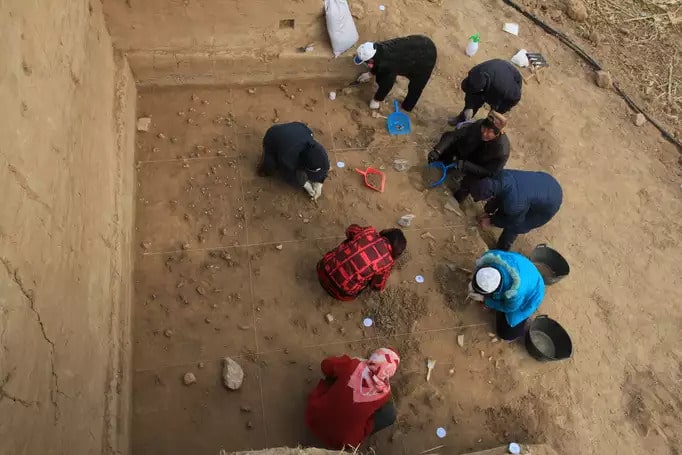
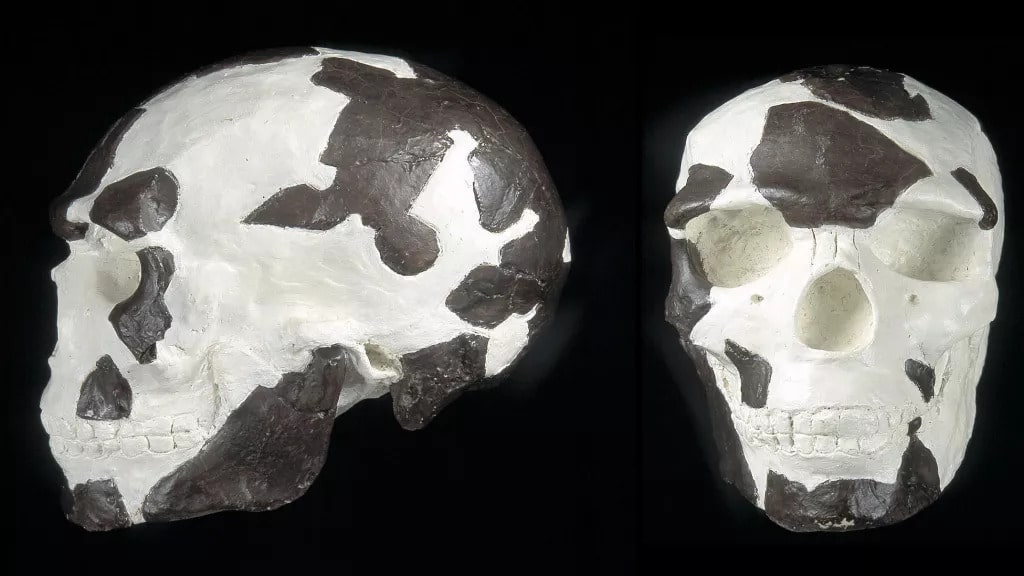
Researchers have discovered that Omo I skeletons, previously thought to be less than 200,000 years old, are 230,000 years old. This shows that Homo Sapiens was at least 30,000 years older than scientists previously thought.
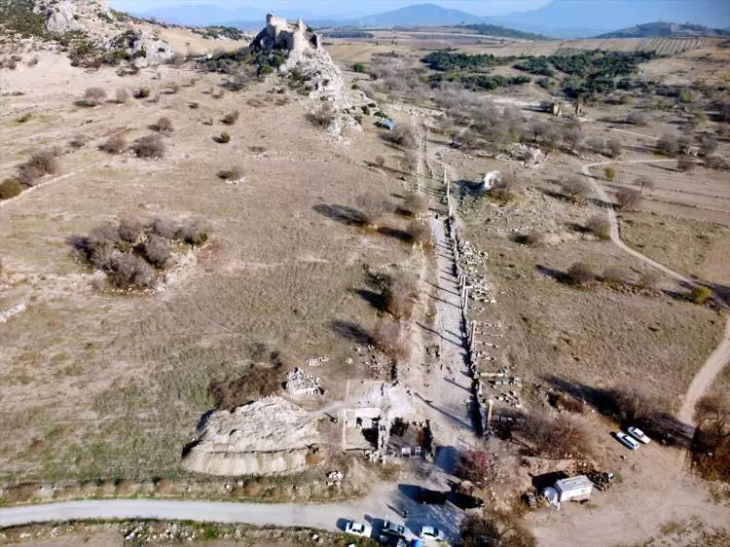
The Omo I remains were discovered in 1967 at the Omo Kibish site near Ethiopia’s Omo River. The human remains were previously estimated to be roughly 195,000 years old. Now, according to a new study published in Nature on Jan. 12, the bones are older than a massive volcanic explosion that shook the region around 233,000 years ago.
Volcanologist Céline Vidal of Cambridge University, paleoanthropologist Aurélien Mounier from the Musée de l’Homme in Paris, and their colleagues wanted to date the Omo I samples again because they apparently coincided with a prehistoric volcanic eruption. An age of 200,000 years didn’t align. After studying the samples, they realized they were looking at the earliest evidence of Homo sapiens ever unearthed.
Dr. Céline Vidal, the lead author of the study, and her colleagues have been trying to date all major volcanic eruptions in the Ethiopian Rift around the time of the emergence of Homo sapiens – a period known as the late Middle Pleistocene – during a four-year project.
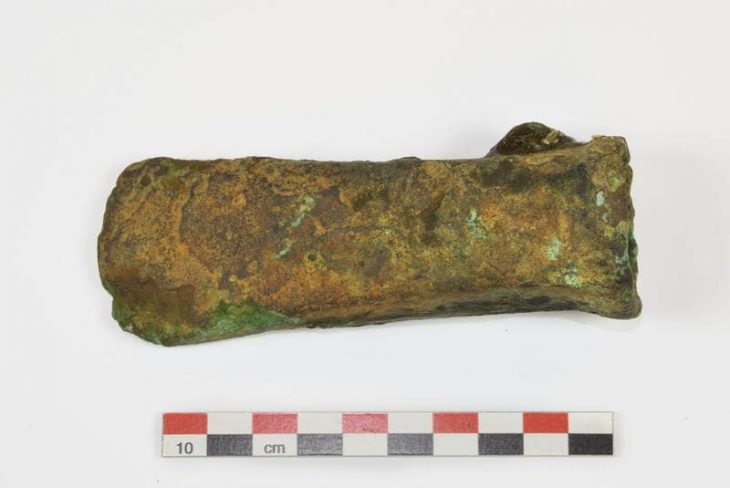
The team collected pumice rock samples from the volcanic deposits and ground them down to sub-millimeter size.

By dating the chemical “fingerprints” of the volcanic ash layers that sat below and above the fossil, the experts were able to calculate that the fossil could be in the region 30,000 years earlier than previous estimations of early human life forms.
“Each eruption has its own fingerprint – its own evolutionary story below the surface, which is determined by the pathway the magma followed,” Dr. Vidal said.
“Once you’ve crushed the rock, you free the minerals within and then you can date them, and identify the chemical signature of the volcanic glass that holds the minerals together.”
Another co-author Dr. Aurélien Mounier, of France’s Musée de l’Homme, added: “Unlike other Middle Pleistocene fossils which are thought to belong to the early stages of the Homo sapiens lineage, Omo I possesses unequivocal modern human characteristics, such as a tall and globular cranial vault and a chin.”
“In my opinion, Omo I represents the oldest occurrence of our species in the fossil record.”
Despite having discovered the minimum age of the Omo I samples, the researchers now need to determine the maximum age of these fossils as well as the wider emergence of Homo sapiens in eastern Africa. They want to do this by connecting more buried ash to more volcanic eruptions in the region, providing a stronger geological history for the sedimentary strata in which the region’s fossils are formed.