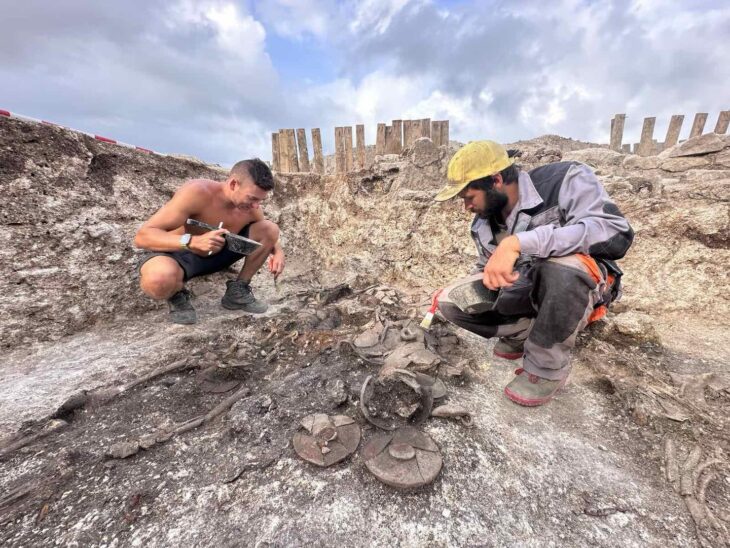
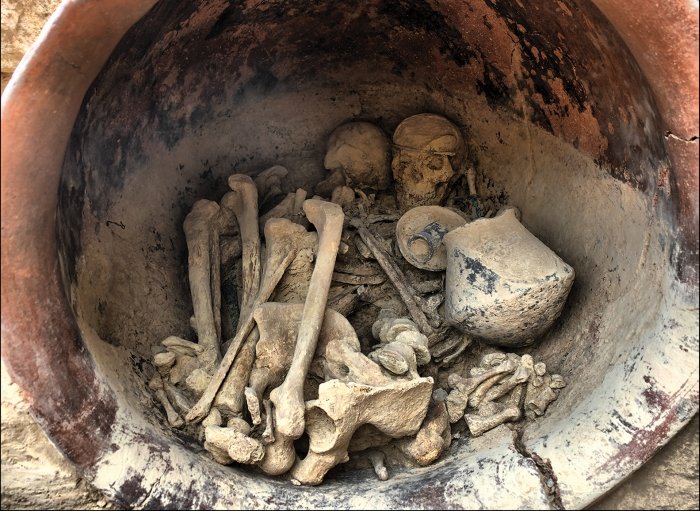
An important Christian settlement was discovered with mosaics bearing clear inscriptions in Greek during the excavations carried out by the Cyprus Department of Antiquities in the Akrotiri peninsula.
New mosaic panels were discovered, including an inscription with the desire ΚΕ ΒΟΗΘΙ ΤΟΙΣ ΤΟ ΩΝΟΜΑ ΣΟΥ ΦΩΒΟΥΜΕΝΟΙΣ (My Lord help those who honor your name), as well as limestone and marble chancels from the Holy Bema, one of which is entirely in marble.
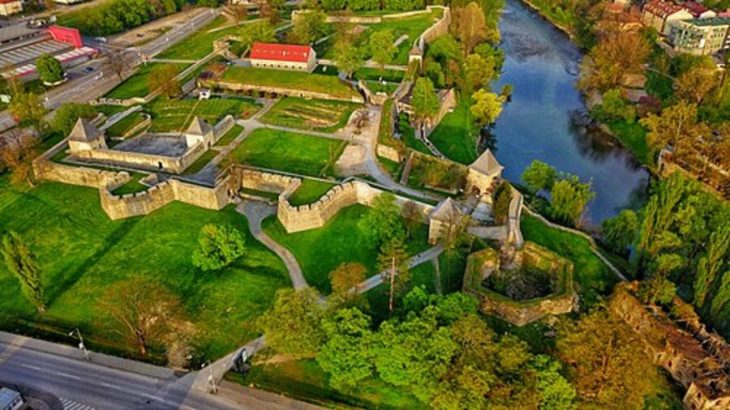
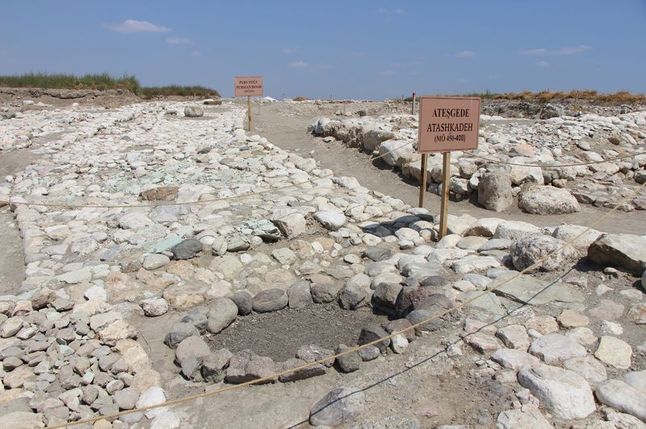
Excavations focused on the south wing of a massive complex comprised of two colossal religious buildings on the west and east sides of a 100-meter-long atrium. Adjacent living areas are mostly to the south and east but have yet to be dug. To the north of Church B’, a second atrium was discovered and partially exposed.
The first church was studied between 2007 and 2010, and it is of the three-aisled transept basilica type, which is a variant of the cruciform type. It is 36 meters broad and 29 meters long, excluding the apse that protrudes to the west and is part of an elevated central platform. The structure is paved with mosaic ornamentation that has been well preserved.
The cleaning of the south and center aisles, as well as a portion of the northern one, was finished during the 2018 season, which was focused on exploring the second church to the east. The central platform of the Holy Bema was also partially exposed, with a lower level podium, the ambo, along its western side, to which an axial corridor (Solea) ends, indicating a prominent Introitus ceremony of pre-sanctified Holy Gifts.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
![Remains Church B [Photo: Department of Antiquities, The Republic of Cyprus]](https://arkeonews.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/Remains-Church-B-min.jpeg)
The foregoing confirms the original judgments of the role of Church A’ as a location for pre-Introitus services, and correlations with the ancient Liturgical Typika of Jerusalem and Alexandria (of St. Jacob and notably of St Marcus) have been verified. Church B’ is a semi-inscribed cruciform three-aisled Basilica with a hexastyle propylon to the west, measuring 46.47 meters in total length (including the propylon and the projecting eastern branch) and 20 meters in width.
The particular architectural form of the entire complex, as well as its decorative richness, confirm that it can be considered an extremely important monument of Christianity during the reign of Emperor Herakleios, referring in various ways to the Persian invasions in the eastern provinces of the empire and the hospitality of refugees, both clergy and secular, they showed it to the Amatuesian prelate of the Alexandrian headquarters, John the Almighty, during his forced return to Cyprus and before his departure on November 11, 619.
![Marble chancel from the Holy Bema of Church B [Photo: Department of Antiquities, Cyprus]](https://arkeonews.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/Marble-chancel-min.jpeg)
Cyprus-Akrotiri is an important site in Christian World
According to Dimitris Triantafyllopoulos, a former professor of Byzantine archeology at the University of Cyprus, “this is a monument of martyrdom, a site of burial and worship of holy persons, similar to the site of St. Minas of Egypt.”
Cyprus is particularly significant in Christian history. The narrative of Jesus Christ reviving Lazarus of Bethany after he had been dead for four days is told in the Gospel of John. Saint Lazarus went on to become the first bishop of the region after being raised by Christ and traveling to Cyprus.
According to tradition, Lazarus’ tomb was plundered and lost during the time of Arab rule beginning in 649 AD. In 890, a tomb in Larnaca was discovered with the inscription “Lazarus, four days dead, a friend of Christ.”
In 898, Byzantium’s Emperor Leo VI had Lazarus’ remains transported to Constantinople. Every year on October 17, the Orthodox Church commemorates the transfer. The relocated relics were then plundered by members of the Fourth Crusade in the early 13th century and taken to Marseille, France, before being lost again.
Cover Photo: The Christian site found in Cyprus features many mosaics. Photo: AMNA