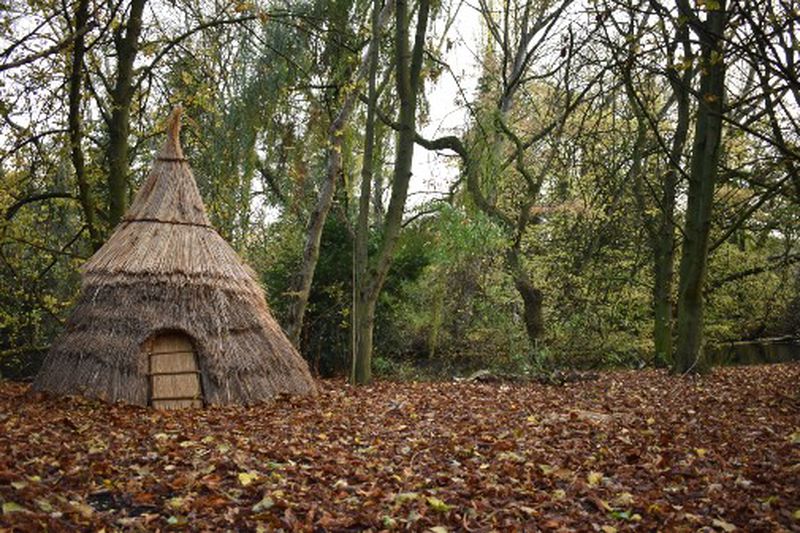
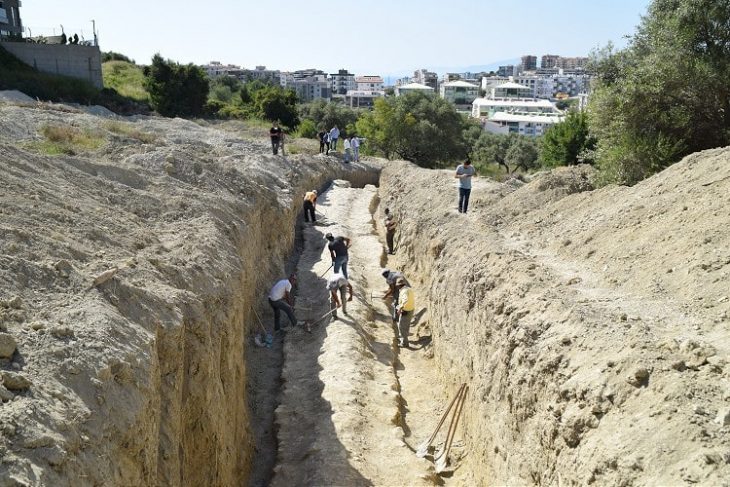
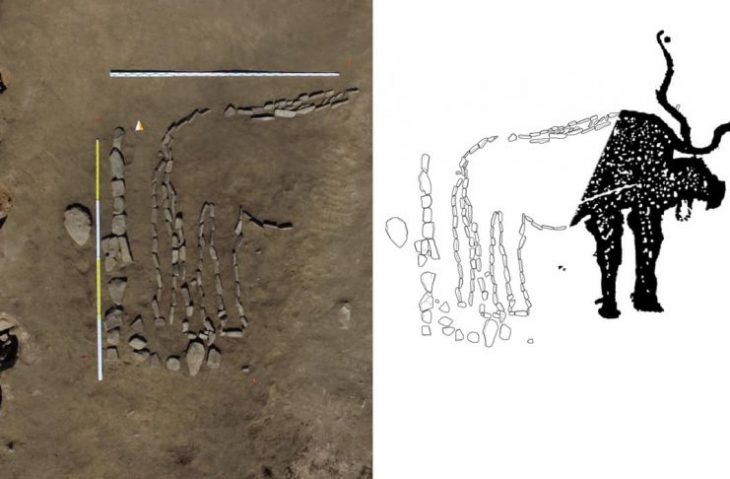
Based on archaeological evidence from a Yorkshire site, new research suggests that hunter-gatherers probably kept an organized home with designated ‘zones’ for domestic activities. Star Carr in North Yorkshire is a world-famous Mesolithic site, providing some of the earliest known evidence of British dwellings and examples of architecture.
Now research teams, from the Universities of York and Newcastle, have been able to in-point where in the home various domestic duties would have been carried out.
Archaeological evidence from Star Carr has shown that hunter-gatherers likely kept an orderly home by creating ‘zones’ for particular domestic activities.
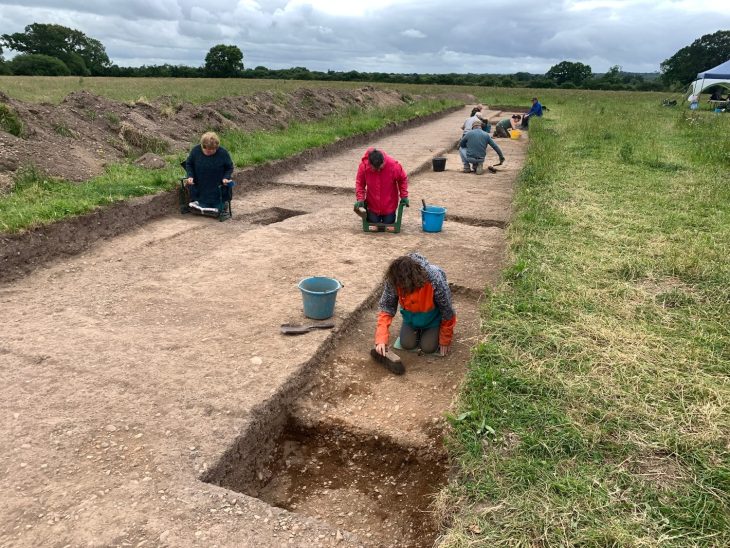
The research team from the University of York and the University of Newcastle looked at microscopic evidence from the use of stone tools found inside three structures – potentially cone-like in shape or domed – dating to over 11,000 years ago at the Star Carr site.
They found that there was a range of activities that were likely to have taken place inside the ‘home’, including wood, bone, antler, plant, hide, meat and fish related work. The researchers then plotted out spatial patterns for these activities to pin-point where within the dwelling these activities might have occurred.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Distinct areas
Dr Jess Bates, from the University of York’s Department of Archaeology, said: “We found that there were distinct areas for different types of activity, so the messy activity involving butchery, for example, was done in what appears to be a designated space, and separate to the ‘cleaner’ tasks such as crafting bone and wooden objects, tools or jewellery.
“This was surprising as hunter-gatherers are known for being very mobile, as they would have to travel out to find food, and yet they have a very organised approach to creating not just a house but a sense of home.

“This new work, on these very early forms of houses suggests, that these dwellings didn’t just serve a practical purpose in the sense of having a shelter from the elements, but that certain social norms of a home were observed that are not massively dissimilar to how we organise our homes today.”
Clean home
Previous work has also shown that there is evidence that hunter-gatherers kept their dwellings clean, as well as orderly, with indications that sweeping of the inside of the structure took place.
Star Carr provides the earliest known evidence of British dwellings and some of the earliest forms of architecture. One of the structures found was believed to be shaped like a cone and was constructed out of wood from felled trees, as well as coverings possibly made from plants, like reeds, or animal hides. There is still very little known about why hunter-gatherers would build such structures and continued to throughout the Mesolithic period.
Micro-scale analysis
Dr. Bates said: “Not only do we now know that hunter-gatherers were constructing these dwellings, but they had a shared group understanding of how to organize tasks within them.
“In modern society, we are very attached to our homes both physically and emotionally, but in the deep past communities were highly mobile so it is fascinating to see that despite this there is still this concept of keeping an orderly home space.
“This study shows that micro-scale analysis can be a really exciting way of getting at the details of these homes and what these spaces meant to those who lived there.”