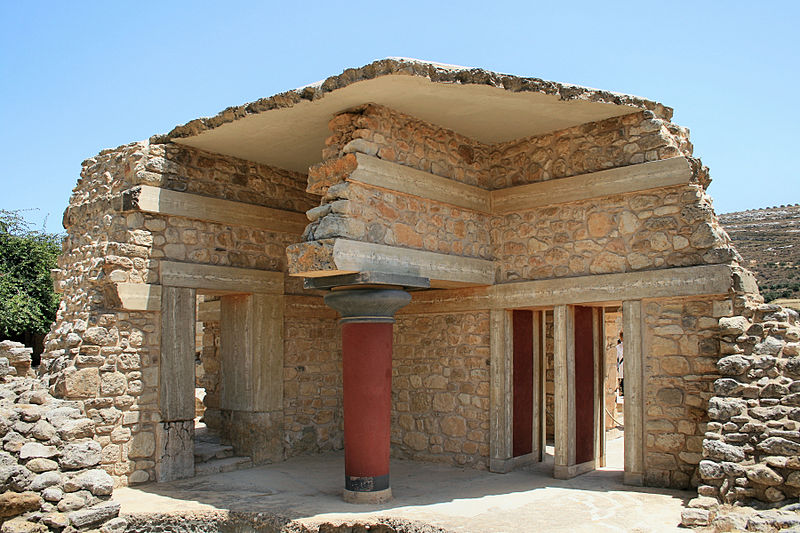
Knossos Palace is a famous architectural structure of ancient Knossos, which was the capital of the Minoan Civilization. Archaeologist Arthur Evans has unearthed the famous palace of Knossos, located in the north of Crete near the city of Heraklion. Evans has provided us with a lot of information about the Minoan civilization.
Although settlements dating back to the Neolithic period are seen in Knossos, the most magnificent period of time was experienced with the Minoan Civilization. By 1500 BC, the population of Knossos had reached 100 thousand.
Knossos Palace regained its former glory days in a virtual environment
For those who wonder how Knossos Palace looked in its former glory days, Australian insurance company Budget Direct has virtually rebuilt the palace, Natalie Martin reports.
A team of architects and a large number of desk employees contributed to the virtual construction of the Palace.

Knossos Palace was the center of the Minoan Civilization
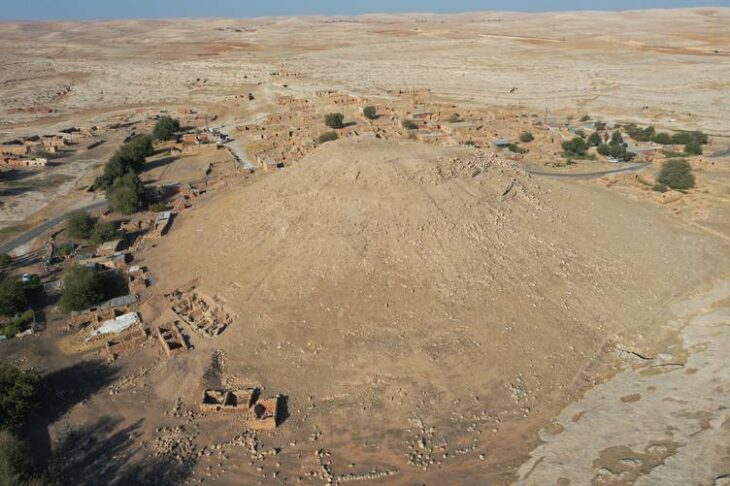
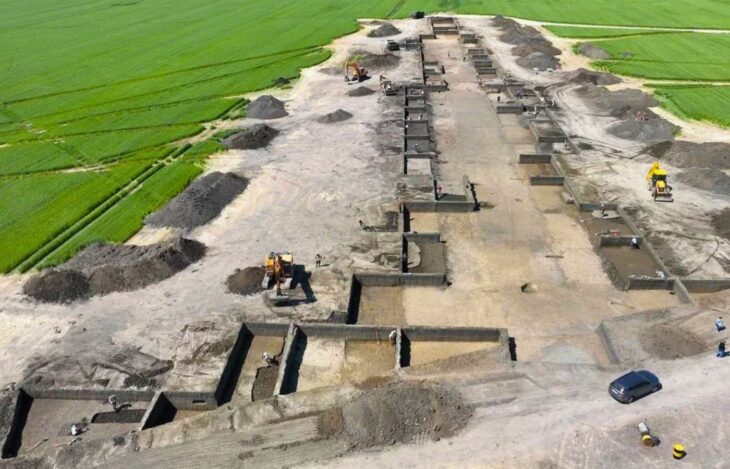
Knossos Palace is located just south of present-day Heraklion, near the northern coast of Crete. As a result of the excavations initiated by Arthur Evans, the palace was first It is thought to have been built around 1900 BC. The palace resembled a labyrinth as it consisted of many courtyards and rooms.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Knossos Palace, built around 1900 BC, is thought to be the most complex in Greece and the first palace built during the Middle Minoan IO period. The palace was abandoned in the Late Minoan IIIC, 1380 – 1100 BC, largely for unknown reasons.
During the Bronze Age, the palace was the ceremonial, religious, economic, and political center of the Minoan Civilization.
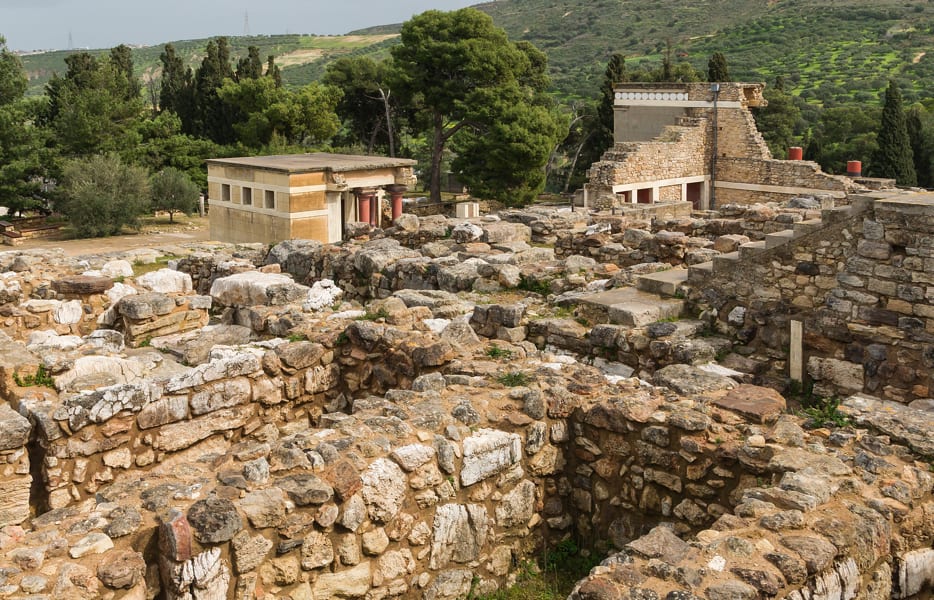

The archaeological site of Knossos Palace covers approximately 20,000 square meters, spreads over three acres, and consists of more than 1,500 rooms.
The excavation of the area has provided historians with a rich insight into the Minoan Civilization.
Tools such as pulleys and spindle whorls, carved from clay and stone, obtained in palace excavations are indicative of an existing fabric-making industry.
Remains of the foundations of the palace reveal a vast interconnected labyrinth of small corridors, staircases, and private rooms containing residences, workshops, and administrative areas.
As the intricate interior of the Palace of Knossos was unearthed, this intricate structure combined with the bull symbolism always present throughout the ruins is predicted to be the distant inspiration behind the labyrinth in Theseus and the Minotaur Greek myth.
Wooden stairs have not survived through the ages leading to the great upper rooms, but they are probably estimated to have once been five stories high.
An elaborate and advanced sewage system, canals, and terracotta pipes provided water and sanitation.
Vertical shafts in the structure known as light wells created an airy and comfortable atmosphere designed to bring natural light to lower levels.