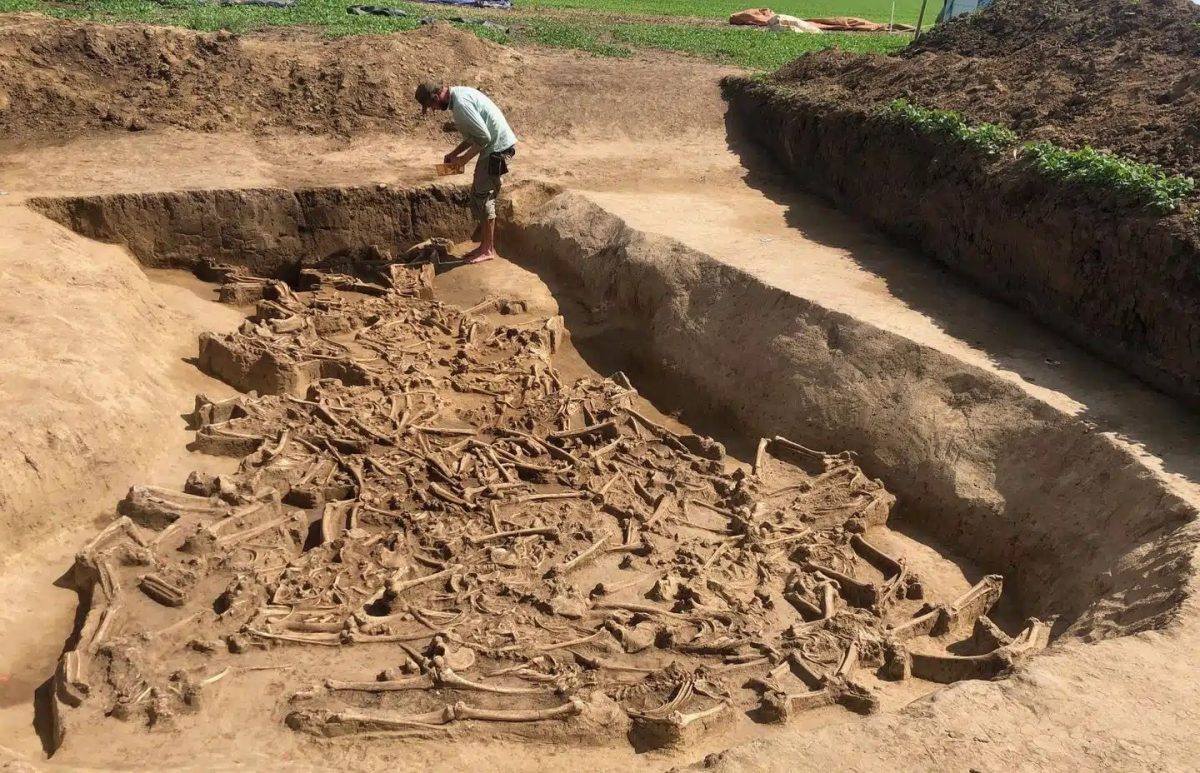
Archaeologists have found a mass grave site containing 38 decapitated burials at a Neolithic settlement in Vráble, Slovakia.
The remains of 38 people were discovered in a ditch surrounding the settlement by archaeologists from the Collaborative Research Center (CRC) 1266 of Kiel University (CAU) and the Archaeological Institute of the Slovak Academy of Sciences (Nitra) during this year’s excavation in Vráble. Their well-preserved skeletons were jumbled together and all of them were missing their heads, with the exception of a young child.
“We assumed to find more human skeletons, but this exceeded all imaginations,” reports project leader Prof. Dr. Martin Furholt.
There are three Linear Pottery Culture settlements at the Vráble-Ve’lke Lehemby site (5,250-4,950 B.C.). A geophysical survey found 313 homes inside the perimeters of the three villages, which were inhabited around 5110 B.C. That makes Vráble one of Central Europe’s biggest Early Neolithic settlements. Not all of the houses were occupied at the same time. At its peak, there were approximately 600 people living in 80 homes, making it a very large community for the Early Neolithic.
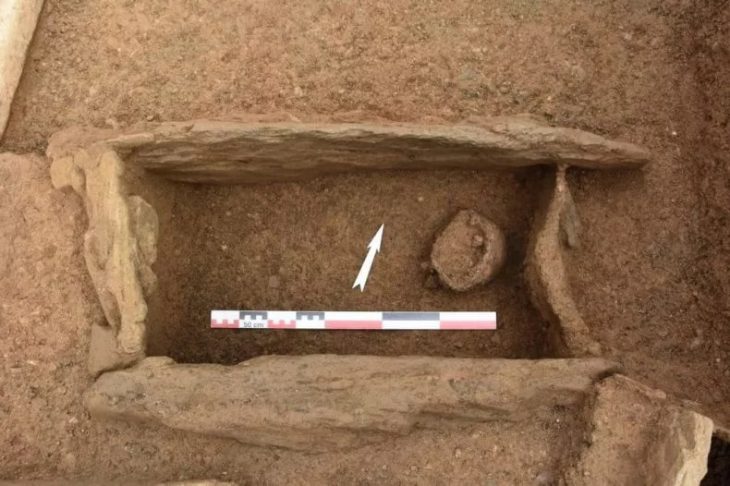
During the excavations in the summer of 2022, the Slovak-German team uncovered the remains, spread over an area of about 15 square meters. One on top of the other, side by side, stretched out on their stomachs, crouched on their sides, on their backs with their limbs splayed out – the position of the skeletons does not suggest that the dead were carefully buried. Rather, the positions suggest that most of them were thrown or rolled into the ditch. All of them, with the exception of one infant, are missing their heads, including their lower jaws.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
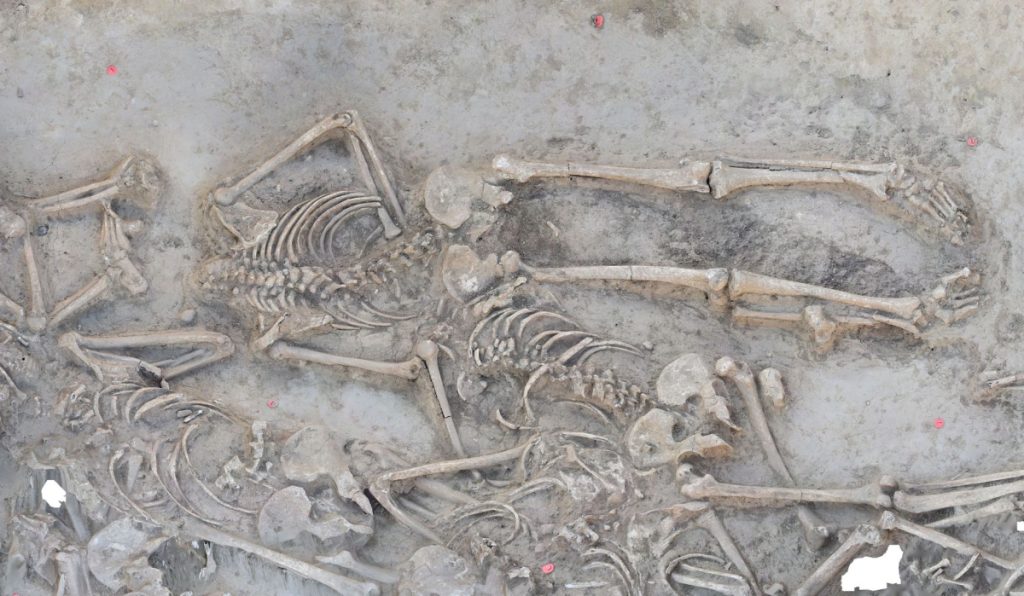

“In mass graves with an unclear positioning, the identification of an individual is usually based on the skull, so for us this year’s find represents a particularly challenging excavation situation,” says Martin Furholt.
The discovery raises many questions. Several bones out of place suggest that the already-skeletonized bodies were pushed into the trench’s center to make room for new ones. Some skeletons also have the first cervical vertebra preserved, indicating that the head was removed with care rather than in a rash violent action.
“It may seem obvious to assume a massacre with human sacrifices, perhaps even in connection with magical or religious ideas. Warlike conflicts may also play a role, for example, conflicts between village communities, or even within this large settlement. Did these people fall victim to head-hunters, or did their fellow villagers practise a special death cult that had nothing to do with interpersonal violence?” says project leader Dr. Maria Wunderlich.
An important part of further research is to find out more about the dead. An interdisciplinary team of researchers will examine the skeletons using archaeological DNA analysis, radiocarbon dating, and stable isotope analysis to shed light on the dead’s age at death, where they were raised, whether they came from somewhere else, whether they had any close family ties, what they ate, any illnesses they may have had, and what may have been their causes of death.
Cover Photo: Prof. Dr. Martin Furholt – Archaeology/Kiel University