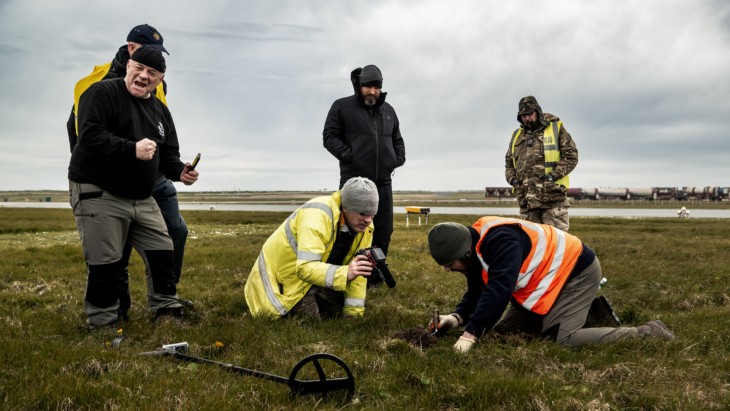
Kazakhstan is witnessing one of its most productive archaeological years in recent decades, and at the center of this scientific momentum stands the Dauylbai necropolis in the Zhetysu region. The site, located at the foot of a scenic ridge in the Karatal district, has long been known to contain burial mounds, yet its true scientific potential remained largely untapped. Excavations conducted between 2023 and 2024 under the leadership of Doctor of History Dossbol Baigunakov have now revealed an extraordinary collection of artifacts dating to the 4th–3rd centuries BCE. These discoveries provide new insight into the cultural identity and ritual traditions of the Saka people, who left an especially rich material legacy across the Eurasian steppe.
The necropolis itself consists of 23 burial mounds, 11 of which belonged to the elite. This concentration of high-status burials immediately suggested the area’s importance, but archaeologists were nonetheless surprised by the scale and richness of the objects uncovered. By November 2024, all finds had been transferred to the Mukhamedzhan Tynyshpaev Regional Local History Museum, where restoration specialists began preparations for exhibition.
Gold Jewelry and Ritual Objects that Illuminate Saka Culture
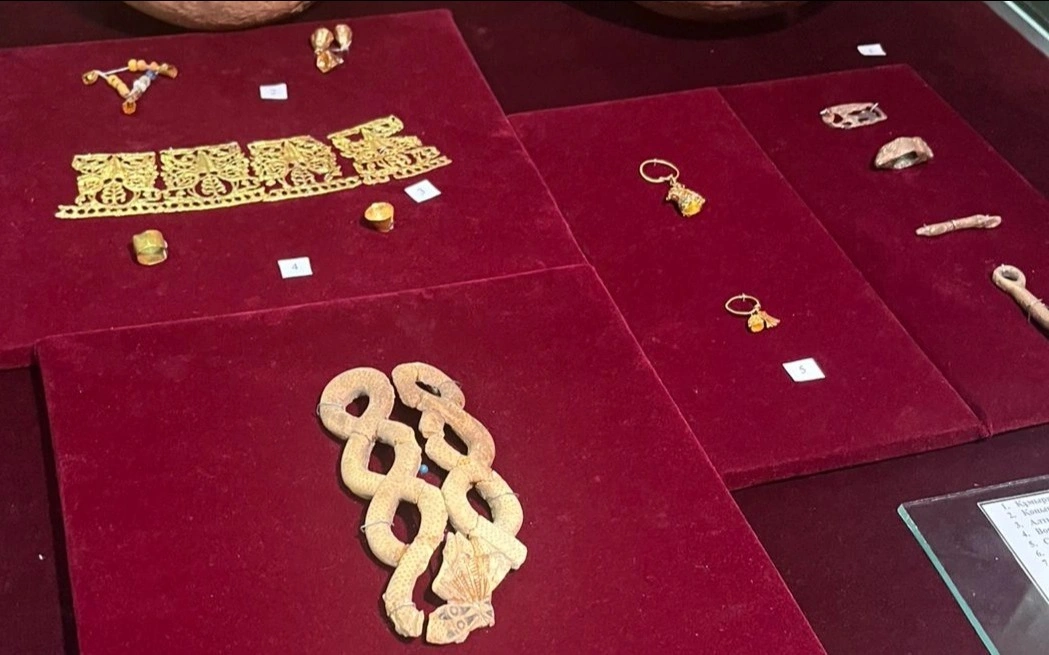
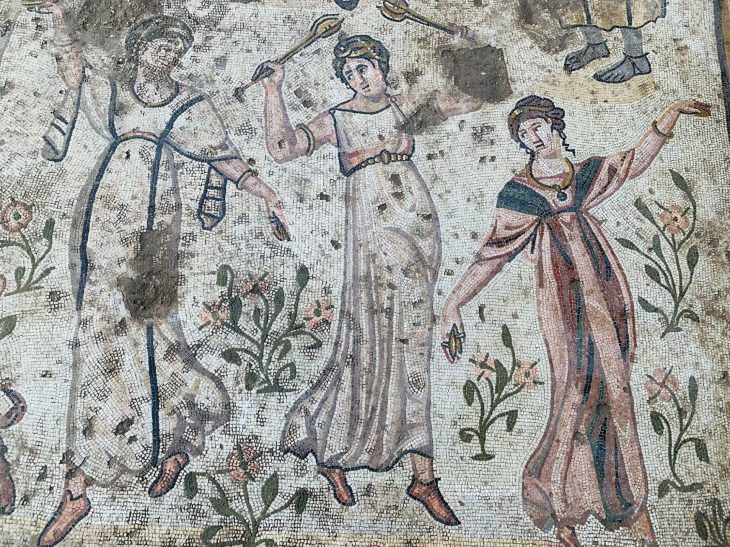
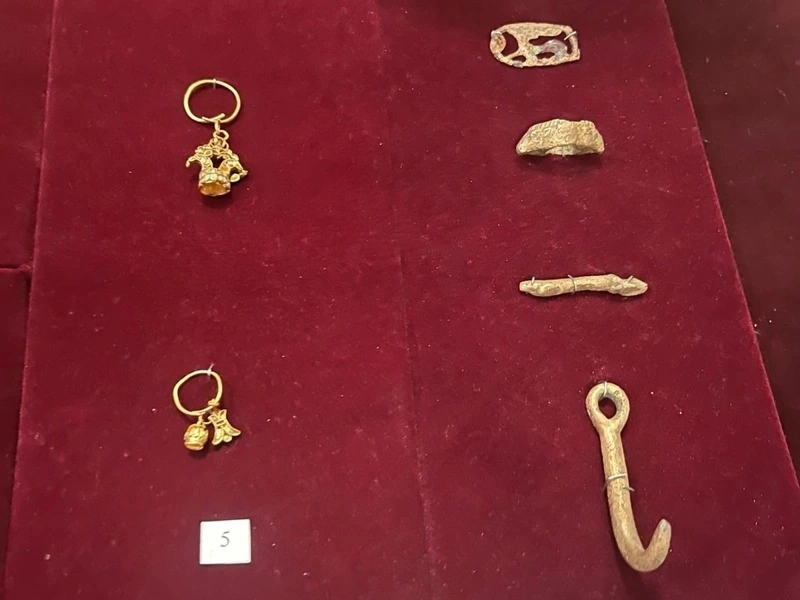
The heart of the discovery lies in the gold ornaments and ceremonial artifacts unearthed from multiple mound structures. Archaeologists recovered gold beads, earrings, decorative plates, bronze pins, bone buttons, and a variety of ceramic vessels—objects that collectively reflect a sophisticated artistic and metallurgical tradition. These items are especially valuable because organic materials rarely survive in the steppe environment, meaning most information about Saka clothing and decorative culture must be gleaned from metalwork and ritual objects.
Among the most remarkable discoveries is the varvorka, a delicate gold ornament once sewn onto ceremonial attire. Its presence confirms that elite Saka individuals adorned themselves with intricate metal decorations during rituals and official gatherings. Another distinctive artifact—a bone object carved in the shape of a snake-dragon—has sparked strong academic interest. Specialists believe it may have been used in ceremonial contexts, possibly symbolizing mythology or spiritual beliefs related to protection and transformation. While interpretations remain open, its detailed craftsmanship illustrates the symbolic complexity of Saka visual culture.

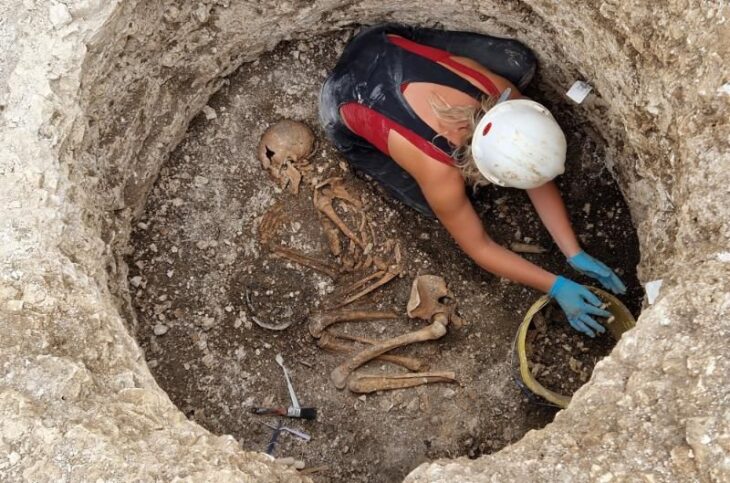
Elite Burials and Insights into Social Hierarchy
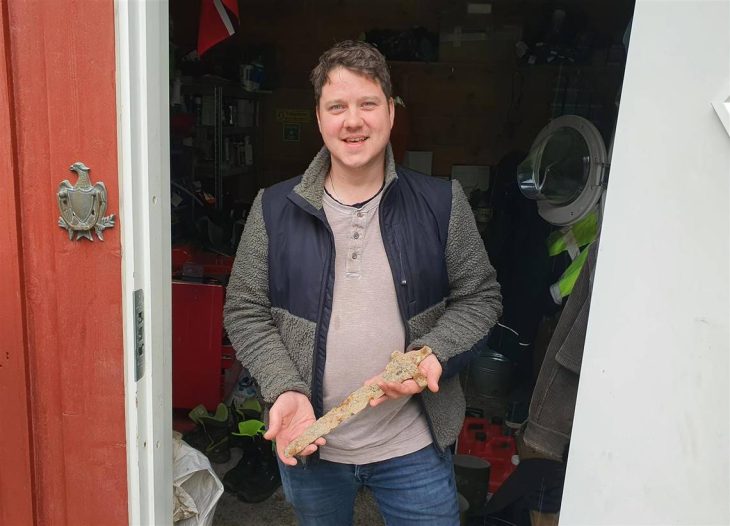
One of the largest mounds explored during the excavation season measured around 40 meters in diameter and stood up to four meters high. Inside this impressive structure, researchers found the remains of a man buried with an iron akinak sword, a weapon strongly associated with Saka warriors. The presence of gold plates and ornaments beside him indicates that he was a member of the ruling class or an individual who held political or military power. Such burials contribute to a deeper understanding of Saka social hierarchy, in which warrior status and lineage played an essential role.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The 2024 excavation season added a further layer of significance when archaeologists uncovered a paired burial containing a woman and a child. This discovery is considered a scientific sensation because paired burials of this kind are extremely unusual in the Zhetysu region. The child’s skull was found near gold earrings, an unexpected detail given that children were rarely buried with precious metals. Based on skeletal analysis, the child’s height is estimated to have been around 95 centimeters. The inclusion of gold jewelry suggests that the child belonged to a family of high status or held symbolic importance within the community. Alongside the human remains, bronze plaques crafted in the iconic Saka animal style—featuring imagery of deer and other sacred animals—were also recovered, reinforcing the burial’s ceremonial character.
Restoration Efforts and Museum Display
Throughout 2025, specialists undertook intensive restoration work to preserve the newly uncovered artifacts. Metal objects were cleaned of corrosion, while bone and ceramic materials were carefully stabilized to prevent further deterioration. These efforts allow modern audiences to appreciate the original detail and craftsmanship of the objects, while giving researchers the ability to study them more accurately. The artifacts have now been incorporated into a temporary exhibition at the Tynyshpaev Museum, where they help tell the broader story of Saka culture and ancient life in southeastern Kazakhstan.
A Rich Archaeological Landscape Beyond Dauylbai
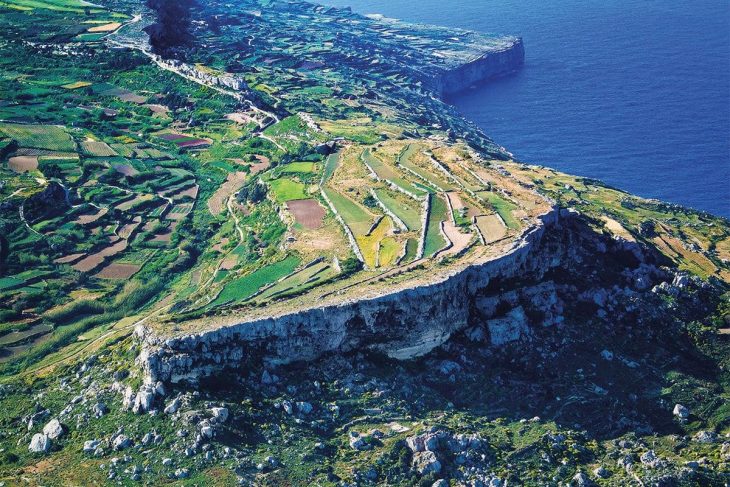
The Dauylbai ridge covers more than 100 square kilometers and hosts over 190 archaeological sites, including burial complexes, settlement remains, and clusters of petroglyphs dating from the Bronze Age to more recent historical periods. Its long-neglected status is now being reconsidered as excavations continue to reveal its exceptional scientific value. The discoveries support the theory that the region was a significant cultural and ceremonial hub for ancient nomadic societies.
Importantly, the Zhetysu finds are not the only major discoveries made in Kazakhstan this year. In the Turkistan region, archaeologists unearthed unique Bronze Age artifacts, including finely decorated tools and ritual objects that complement the cultural narrative emerging from Zhetysu. Together, these findings show that 2024–2025 marks a breakthrough era for Kazakh archaeology, providing new opportunities to understand the connections between early nomadic cultures across Central Asia.
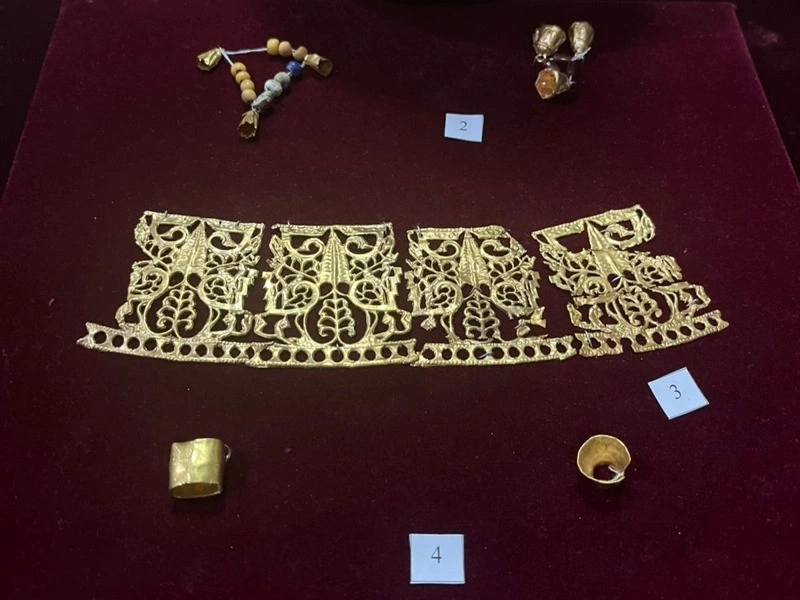

Expanding Knowledge of Ancient Nomadic Life
From a scholarly perspective, the discoveries at the Dauylbai necropolis fill important gaps in the archaeological record. They reveal new details about social structure, gender roles, ritual practices, and artistic traditions within Saka communities. The paired burial, in particular, challenges existing assumptions about family dynamics and the symbolic treatment of children in elite contexts. Additionally, the presence of expertly crafted gold items demonstrates that the Saka had access to high-quality materials and possessed advanced metalworking skills, likely supported by extensive trade routes or local artisanal networks.
As research continues, the significance of these discoveries will only grow. The artifacts now on display represent more than scientific finds; they are a testament to the depth and complexity of ancient Kazakhstan’s cultural heritage, offering modern audiences a vivid connection to the past.
Cover Image Credit: Kazinform