Turkey’s Izmir Archaeological Museum is hosting a different exhibition this month.
A bronze strigil is the museum’s guest this month as part of its “You Will See What You Can’t See“ project, in which a new, special artifact is introduced to visitors every month.
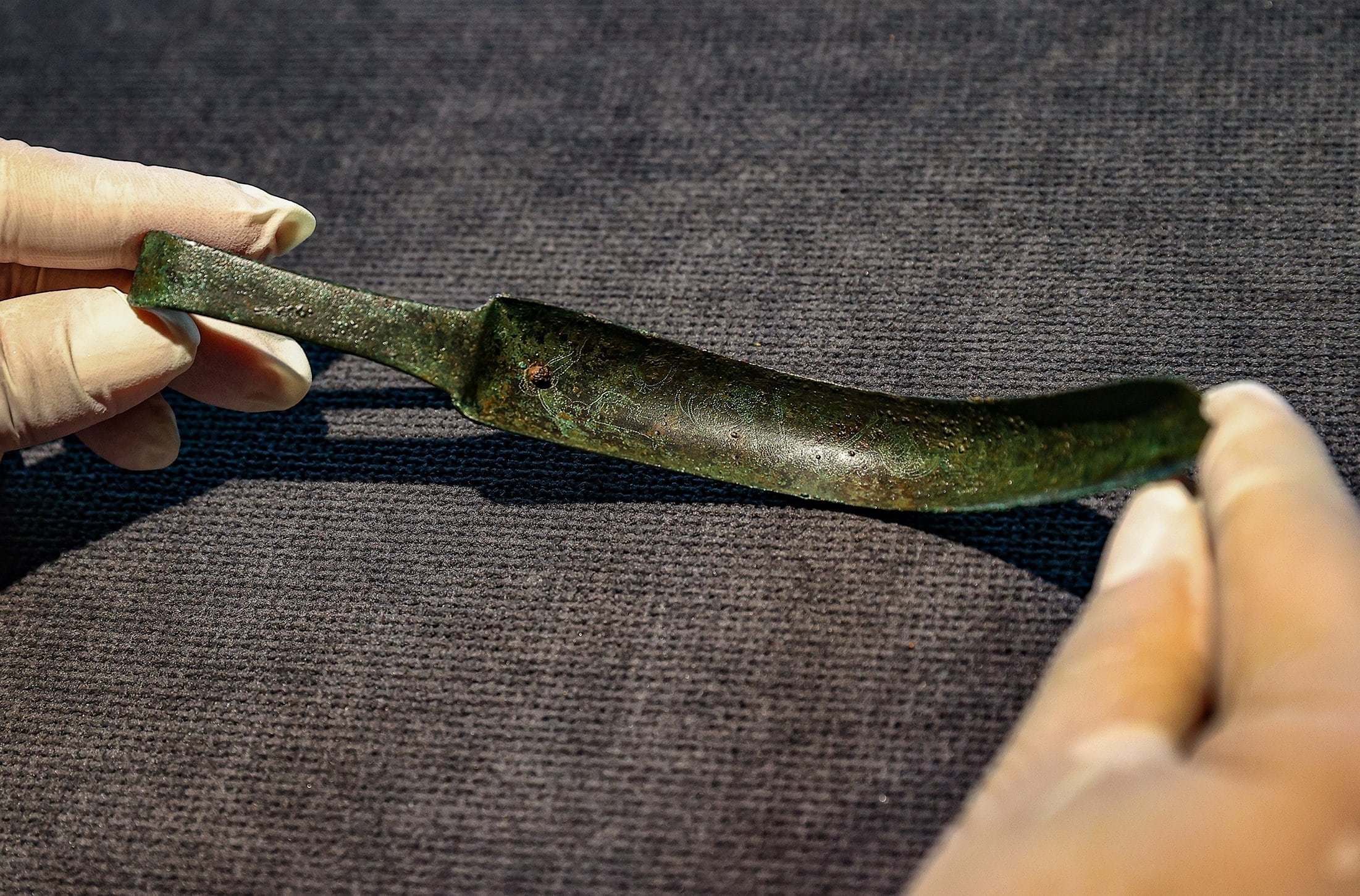
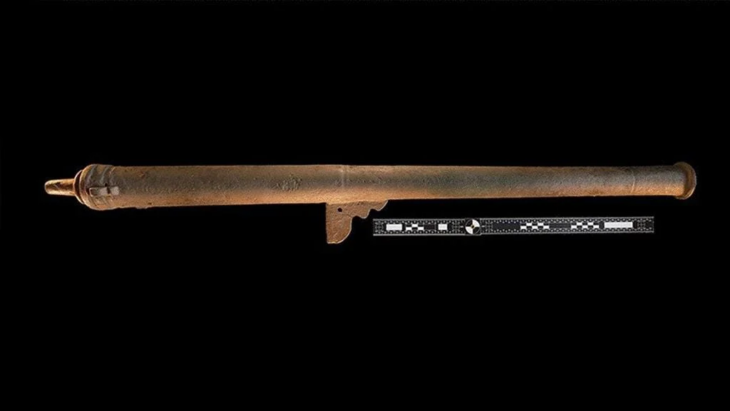
The Izmir Archaeology Museum recently opened a new, unique exhibition focusing on the historical relic known as a “strigil,” which was used to cleanse the body 2,300 years ago by scraping off dirt, perspiration, and oil.
The strigil in issue was unearthed during archaeological digs at Teos, one of the 12 ancient Greek towns that made up the historical Ionian League.
The tool was used in ancient Roman and Greek cultures, and the one on display is believed to have belonged to an athlete or a gladiator.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
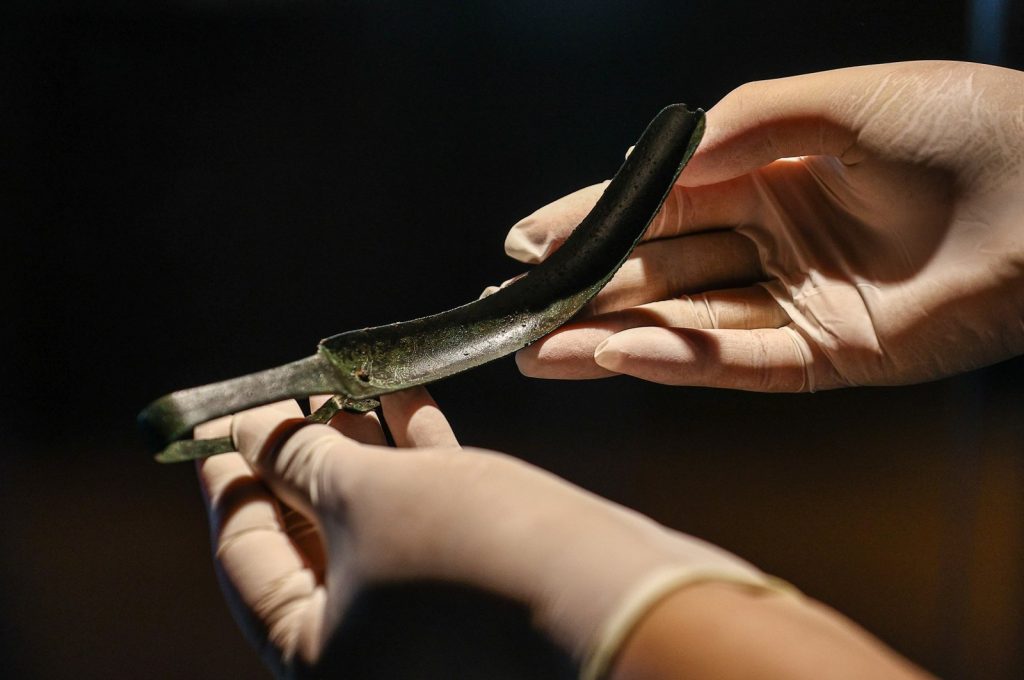
Hünkar Keser, director of the museum, said that the word “strigil” could be translated as “cleaning spoon,” as he explained the historical use of the artifact.
“We know that athletes covered their bodies with olive oil before they practiced sports. After completing their workouts in sandy areas, they had to clean their bodies,” Keser told Anadolu Agency (AA). “They used to scrape their bodies with this spoon-like strigil, and thus (remove) the coarse dirt.”
At approximately 16 centimeters (nearly 6.3 inches) long, and shaped in a form that evokes the image of a crescent moon, the strigil has unique engravings on its surface that depict scenes from a cockfight.
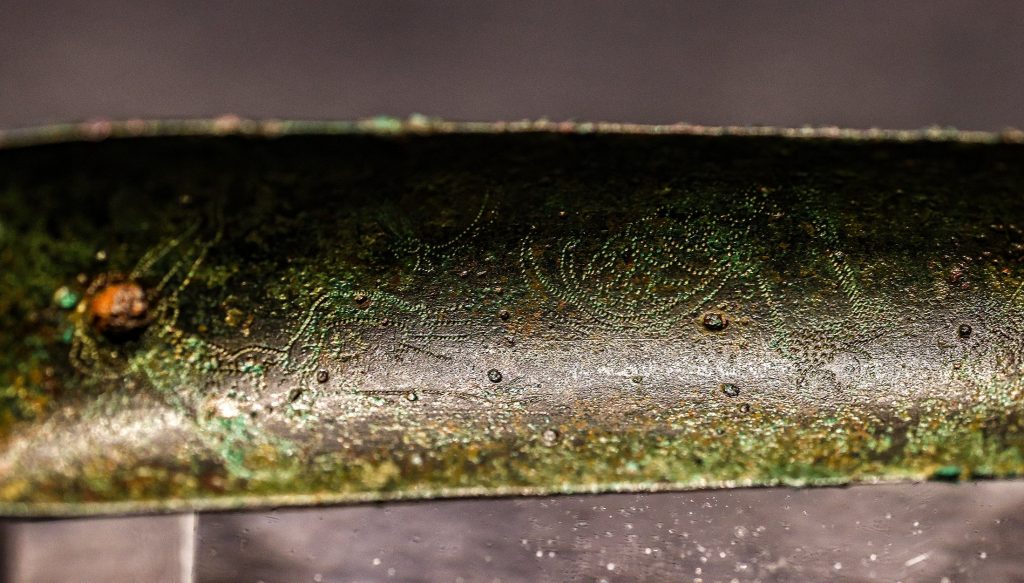
“We know that it is a custom-made spoon. The cockfighting figure on it is also an interesting detail. In those times, fighting is a form of entertainment used to attract people’s attention. The use of the strigil is also specific to that period.”
Keser noted that the strigil was unique, just like the other ancient artifacts of the museum. He added that the rare and special strigil had attracted a lot of attention from visitors.
Keser said that some visitors would examine the artifacts that were exhibited as part of the “You Will See What You Can’t See” project for hours.
The “You Will See What You Can’t See” exhibition is due to run through January 2022.