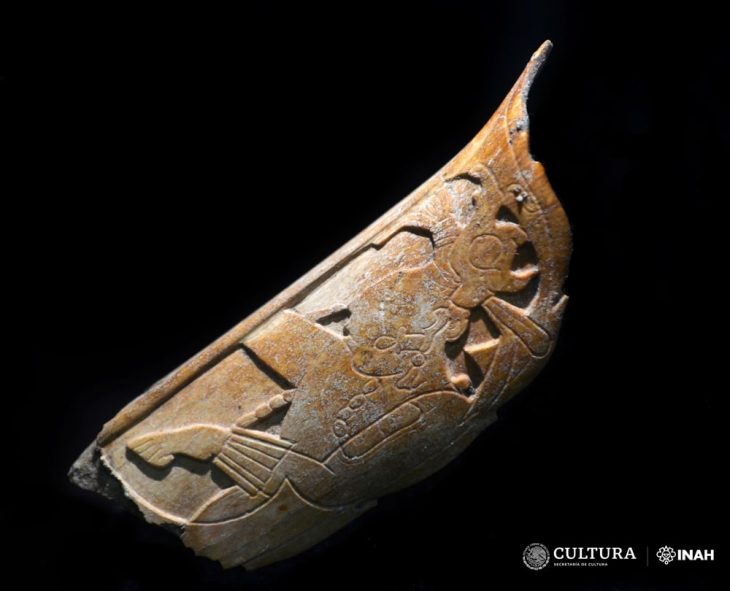
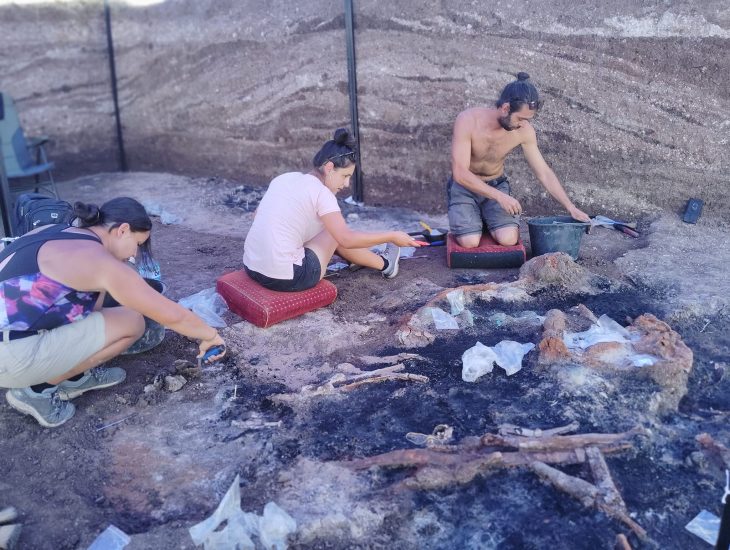
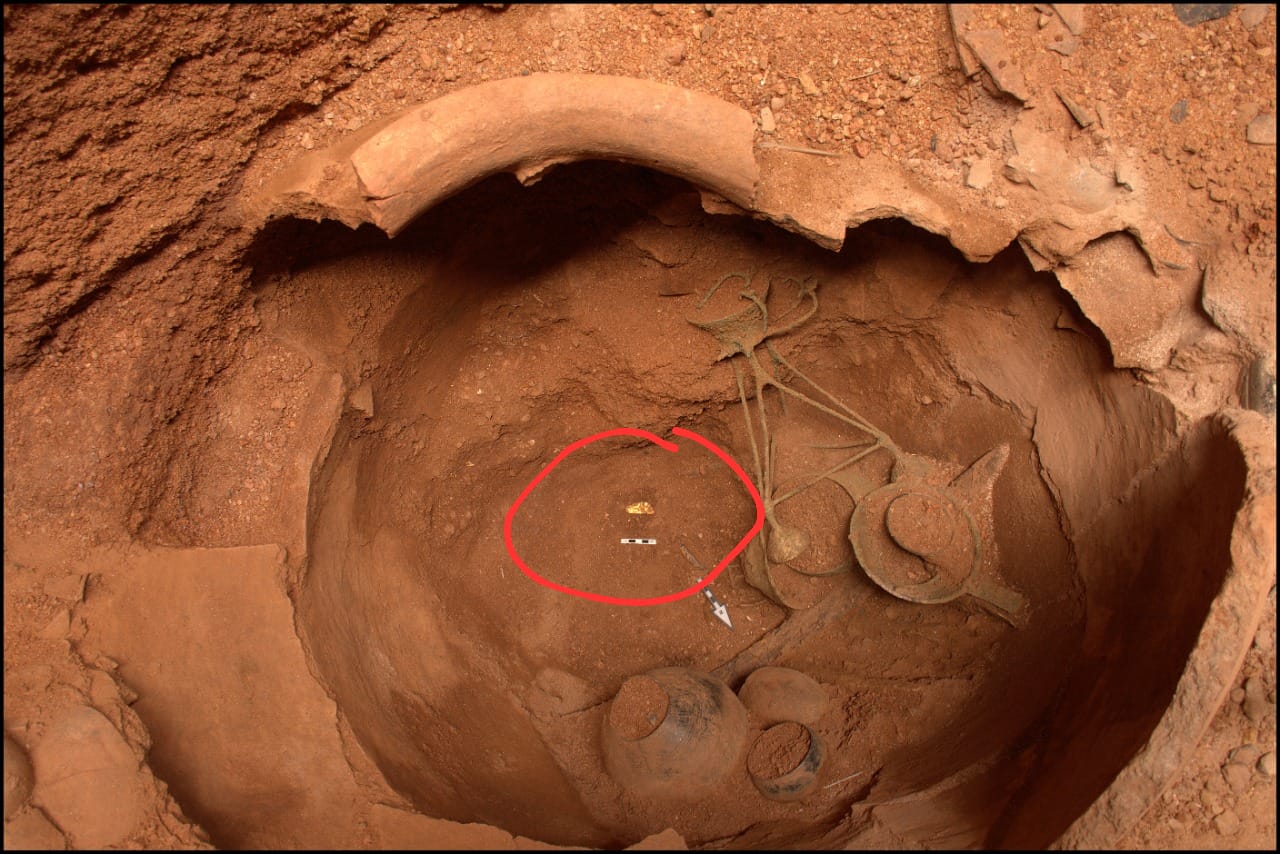
A gold diadem, bronze, iron objects, and pottery were reportedly found in a burial urn at the archaeological site of Adichanallur in southern India by archaeologists led by VP Yathees Kumar of the Archaeological Survey of India.
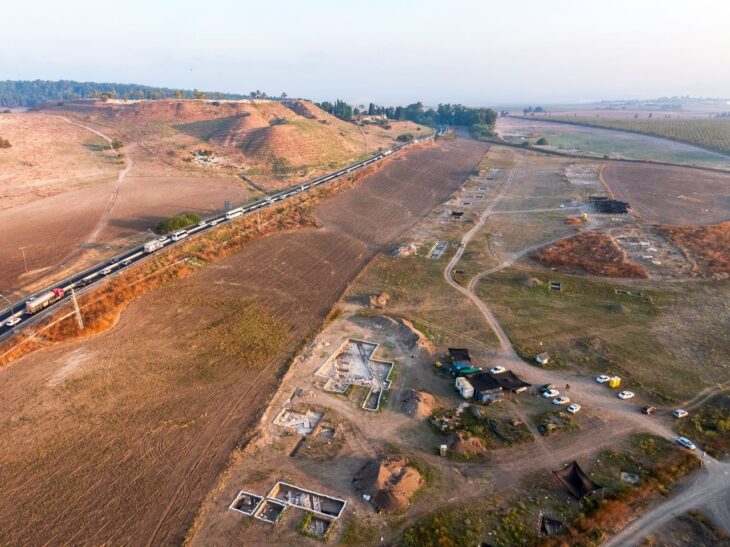
The Adichanallur archaeological site is located in Srivaikuntam taluk of Thoothukudi region of India.
The discovery was made 120 years after British archaeologist Alexander Rea found 20 golden diadems in the same area 120 years ago.
About four months ago, ASI mapped the area with the help of satellite mapping and began excavation. They discovered it in a burial urn with a 2.4-meter diameter after 27 days. The diadem was found at the bottom of the urn along with a few other objects, including a bronze sieve.
The urn contained a number of objects that were made of gold, bronze, or iron. As many as 20 iron objects — two inside and 18 outside the urn burial — were unearthed. On the outside, it contained 11 arrowheads, two spearheads, one hanger, an iron plate, a chisel, and a long spear of 1.75 meters with a decorated handle.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The bronze objects included a circular sieve, a cup with a stand, and two bowls. Interestingly, the cup had a molded decoration. The urn also had a number of pots and red and black earthen wares of varying sizes. As per the ASI expert, the urn also contained paddy husks.
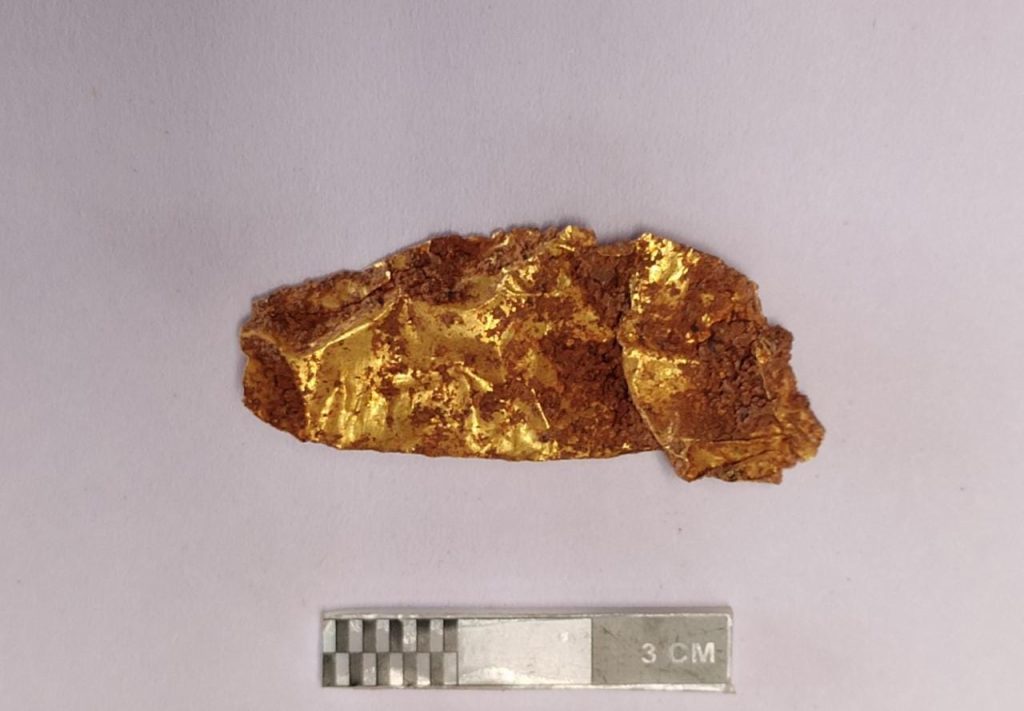

The gold diadem, known as Nettri Pattayam, was hailed as one of the most important archaeological discoveries around the world, the ASI Director said DT NEX.
Evidence suggests that the approximately 3.5 cm long, unshaped gold diadem was used by a royal clan 3,000 years ago.
The diadem has been folded repeatedly, leaving it only 3.5 cm (1.4 inches) long. This was done on purpose, ceremonial destruction of the diadem after the wearer’s death so that no one could wear it after him.
Gold diadems were one of the significant bridal ornaments in the Kongu region, and feudal rulers used them on other auspicious occasions, according to C Santhalingam, a Madurai-based archaeologist and the founder of Pandya Nadu Centre for Historical Research.
At Adichanallur, the first clay jar burials were discovered in 2004. So far 169 urns containing human skeletal remains and rich grave goods have been unearthed at the site. The human bones were buried between 1000 and 600 B.C., according to radiocarbon analysis.
T Arun Raj, Director, ASI, told DT Next that the British archaeologist Alexander Rea, in his report documented the treasures uncovered from 1899 to 1903 with geographical features. Based on Rea’s report, a GIS mapping was done and a site plan was superimposed before uncovering the invaluable treasure. Under the first phase of excavation in October 2021, about 90 urns have been exposed in different sizes. He also hoped that more such treasures could be unearthed in adjacent places.