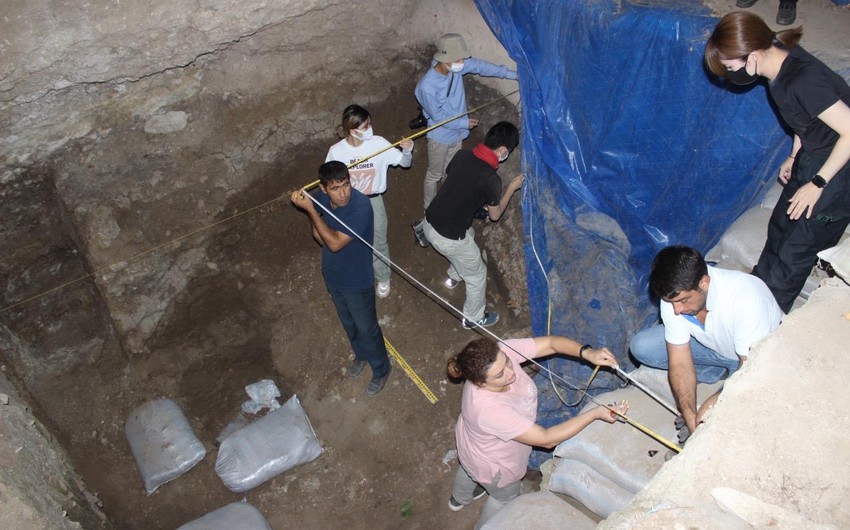
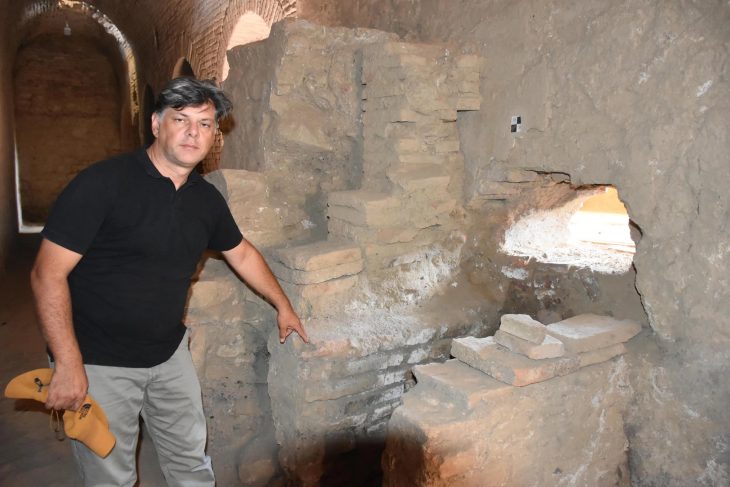
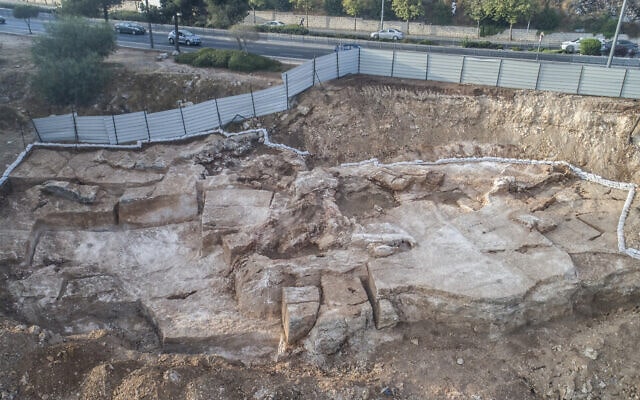
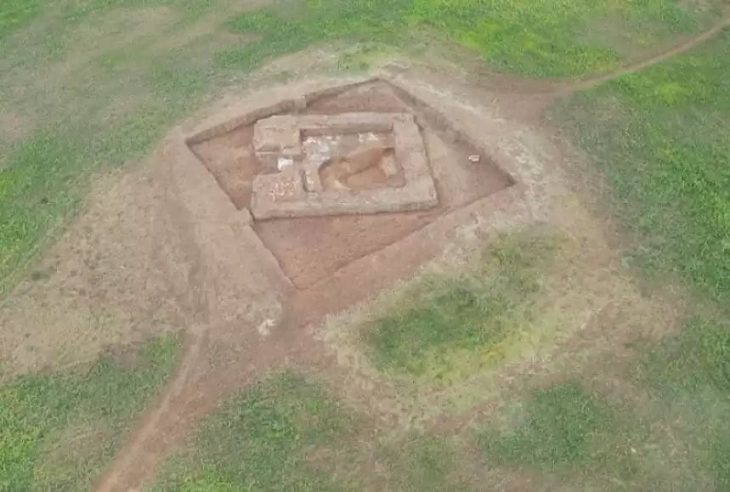
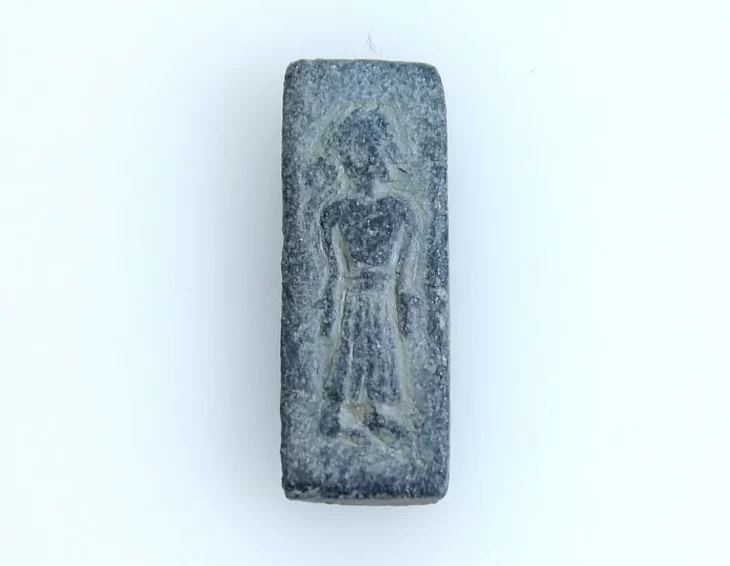
A groundbreaking discovery has been made in the Damjili Cave in Azerbaijan’s Gazakh district: the first human figurine from the Mesolithic era.
Dr. Yagub Mammadov, head of the Azerbaijani-Japanese Damjili International Archaeological Expedition at the Institute of Archaeology and Anthropology of the Azerbaijan National Academy of Sciences (ANAS), confirmed the finding, as reported by local media. This figurine marks a significant milestone in understanding the Neolithization of the South Caucasus, revealing that this transformative process occurred in stages rather than as a singular event.
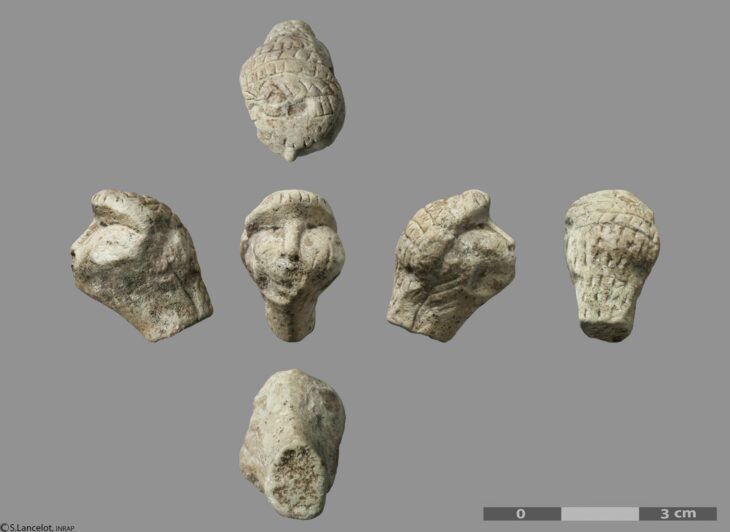
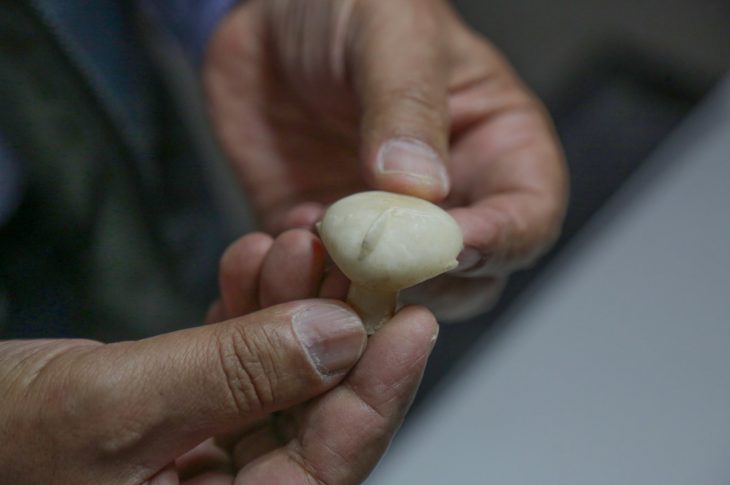
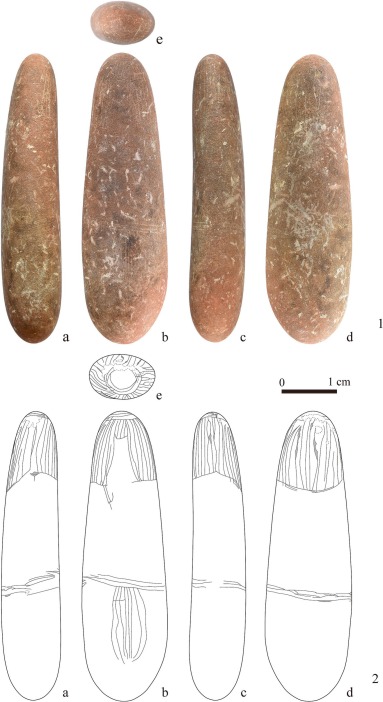
The figurine, which is unlike any other found in Mesolithic sites along the Kura River or throughout the Caucasus region, was unearthed during joint Azerbaijani-Japanese archaeological excavations in 2023. Mammadov noted that similar human figurines have not yet been found in the known Mesolithic sites on the Kura River and its environs, as well as in the Caucasus as a whole.
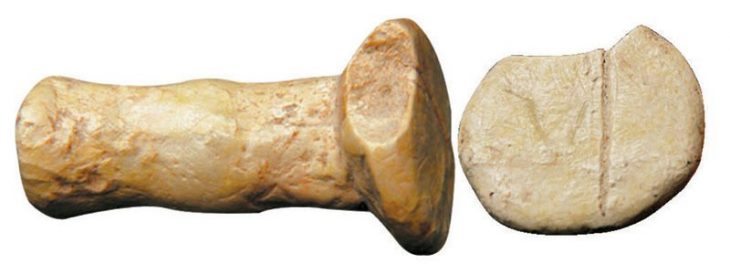
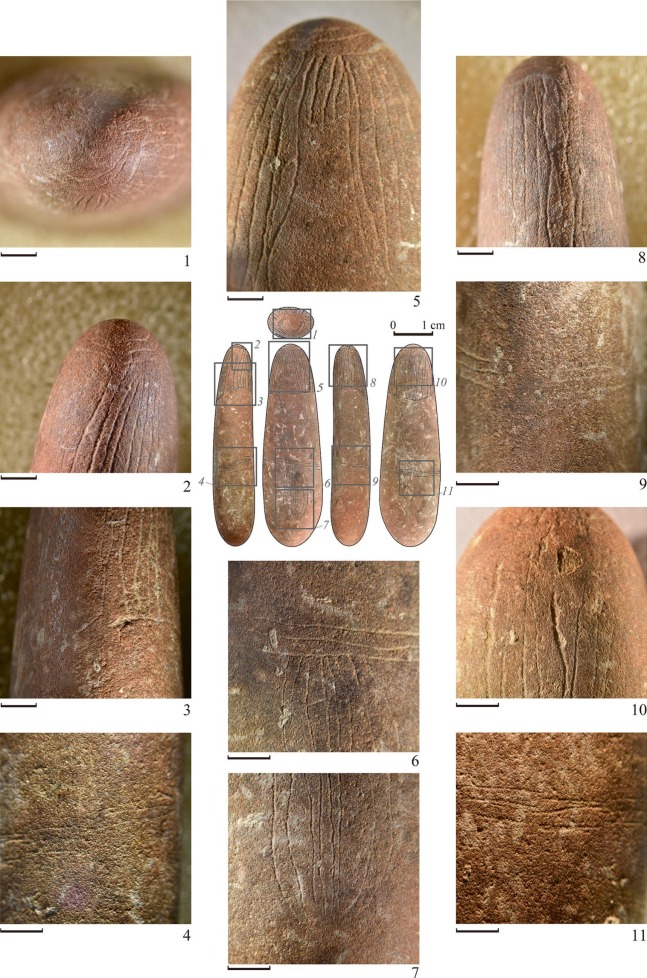
The newly discovered stone figurine, dated to the late 7th millennium BCE, is an elongated piece made from hard sandstone, featuring intricate engravings that depict a human figure. The stone figurine measures just 51 mm in length and 15 mm in width. It features intricate engravings that depict a human figure with a neat hairstyle and a belt with engraved lines, but notably lacks facial features. The question of whether this figurine symbolizes a man or a woman remains a subject of debate among researchers. The figurine was meticulously studied at a museum in Japan using modern laboratory techniques to gain further insights into its origins and significance.
The figurine’s design, which lacks facial features but includes detailed representations of hair and clothing, stands in stark contrast to Neolithic figurines, indicating a potential cultural divergence during this transitional period.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This discovery is particularly significant as no similar artifacts have been found in the surrounding area, highlighting the uniqueness of the Damjili find. The figurine was discovered by Ulviyya Safarova, a researcher at the Institute of Archaeology and Anthropology of ANAS, and has already captured academic attention, with the first official article about the figurine published in the 42nd issue of the journal Archaeological Research in Asia—a prestigious journal indexed in the Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus databases, holding a Q1 category ranking.
Recent archaeological research has indicated that the Neolithization in the South Caucasus was likely influenced by a combination of cultural exchanges and human migrations from the Fertile Crescent in Southwest Asia. While the timeline and mechanisms of these processes have remained ambiguous, recent multidisciplinary studies have shed light on the swift arrival of Neolithic culture in the region.
The Damjili Cave’s stratified sequence from the late Mesolithic to early Neolithic is of paramount importance, providing a unique dataset that highlights both continuity and discontinuity in local material culture. For instance, while pottery became prevalent in the Fertile Crescent during the 7th millennium BCE, the earliest Neolithic inhabitants of the Damjili Cave lived an almost aceramic lifestyle, reminiscent of their Mesolithic predecessors. This suggests that the transition was not merely a cultural replacement but involved the integration of indigenous communities.
Despite the significance of this find, the ideological and symbolic aspects of the Neolithization process remain underexplored. The figurine from the Damjili Cave provides a rare opportunity to investigate the continuity or discontinuity of portable art between the Mesolithic and Neolithic periods. The study emphasizes the need for further research into the symbolic changes accompanying the Neolithization process, not only in the South Caucasus but also in a broader context across Southwest Asia.
As researchers continue to analyze the implications of the Damjili figurine, it becomes increasingly clear that the Neolithization of the South Caucasus was a complex and multifaceted process. This discovery not only enriches our understanding of the region’s prehistoric cultural landscape but also highlights the importance of examining small artifacts that may hold the key to unraveling the intricate narratives of human development during this pivotal era.
Nishiaki, Y., Safarova, U., Ikeyama, F., Satake, W., & Mammadov, Y. (2025). Human figurines in the Mesolithic-Neolithic transition of the South Caucasus: New evidence from the Damjili cave, Azerbaijan. Archaeological Research in Asia, 42, 100611.