Amateur archaeologists have unearthed a striking Roman dodecahedron in the serene countryside of Norton Disney, England, a mysterious class of objects that have baffled experts for centuries.
A volunteer with the Norton Disney History and Archaeology Group discovered the dodecahedron in the Lincolnshire village of Norton Disney.
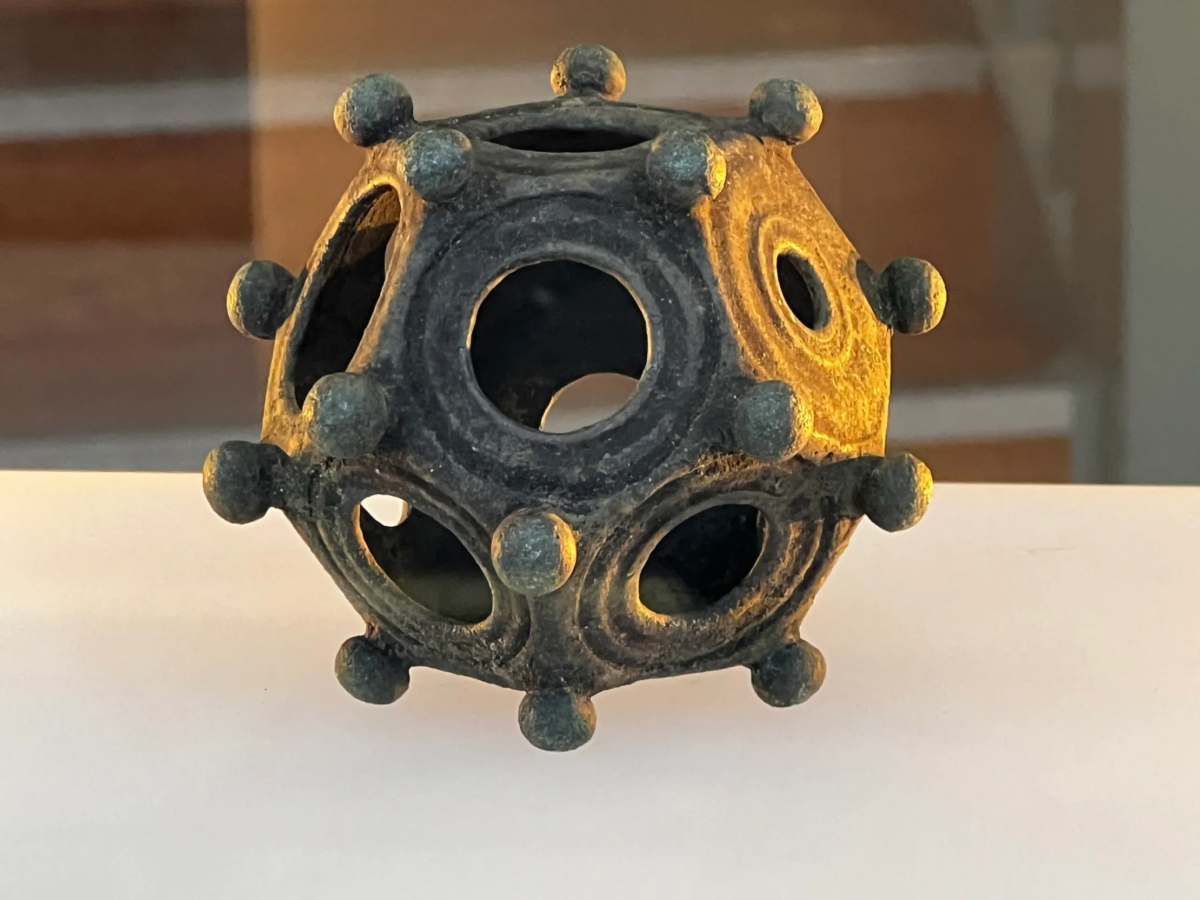
The object’s purpose is unknown to modern archaeologists because the 12-sided metal shell lacks markings and no mention of them can be found in contemporary literature.
About thirty-two examples, complete or in part, from Roman Britain are known to exist. The Norton Disney example now makes 33. Throughout the Roman world, there are about 130 known examples. which are located in the Roman provinces of the northwest.
The Norton Disney dodecahedron is an exceptionally good example and the only one in the Midlands. It’s beautifully crafted, undamaged, and in perfect shape. It exhibits exquisite craftsmanship and a superior level of finishing. It is a prime example of expertly crafted and superbly finished work.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
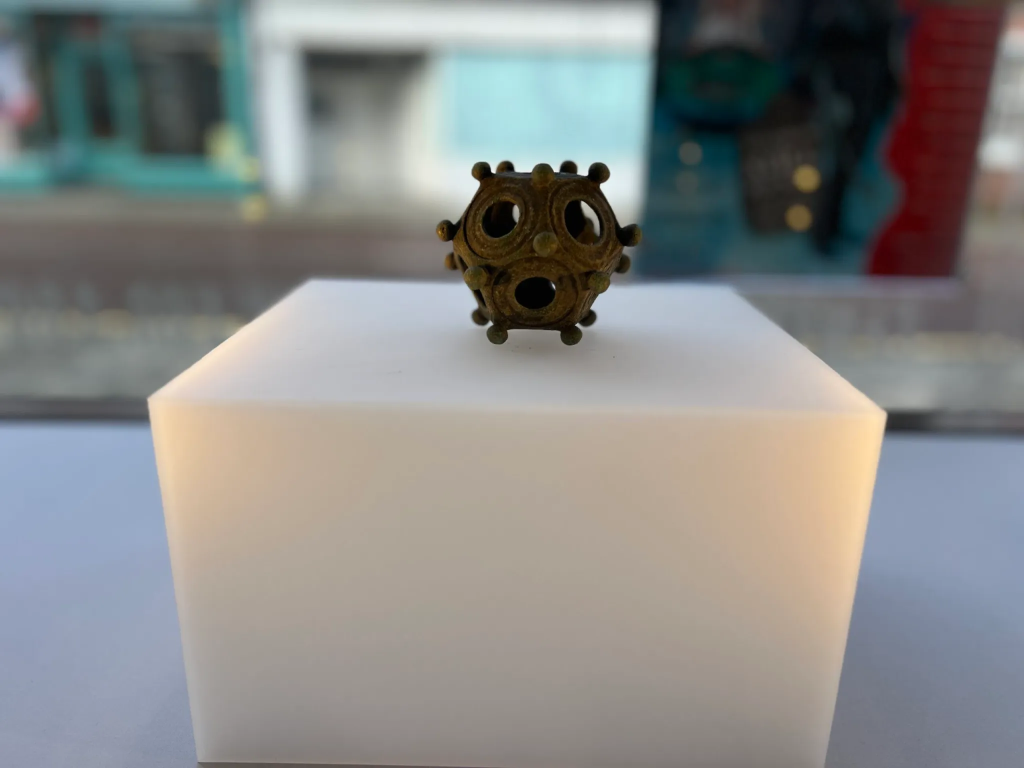

Richard Parker, the secretary of the Norton Disney History and Archaeology Group, said they dug up the object, which is the size of a grapefruit, about 35 miles southeast of Sheffield in one of the trenches the group made at the site for the two-week dig.
The Norton Disney dodecahedron is a copper alloy object. 75% copper, 7% tin and 18 % lead. It’s overall height is 8cm. Its overall width is 8.6cm and weighs 254g.
It is also an important find in that it was found “in situ”, where it was deliberately placed some 1700 years before with 4th-century Roman pottery in some sort of excavated hole or quarry pit.
The purpose of dodecahedra is still very unclear because there are no known descriptions of them in Roman literature. They won’t be measuring devices because they aren’t a standard size. They are not a tool because they don’t exhibit any wear. They’re also not knitting machines. Dodecahedron took a great deal of time, effort, and skill to construct, so it wasn’t used for everyday tasks, especially since there are other materials that could have served the same function. It is believed that ritual and religious uses are the most likely uses.
The remarkable metal shell is now on display in the National Civil War Centre, Newark Museum.
Cover Photo: Norton Disney History and Archaeology Group