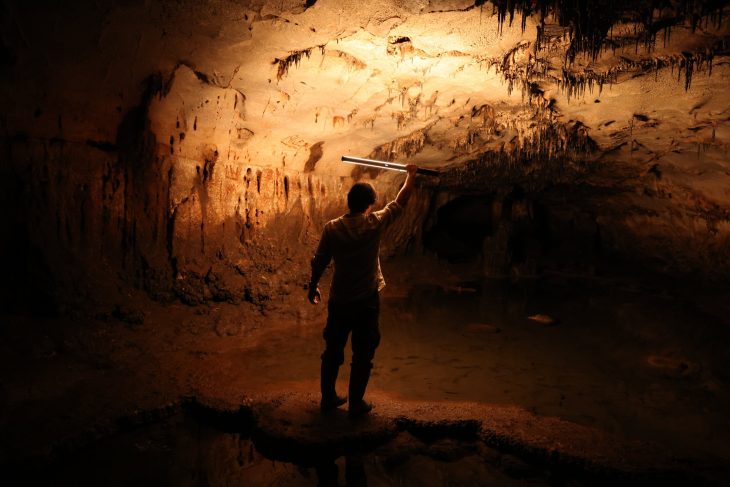
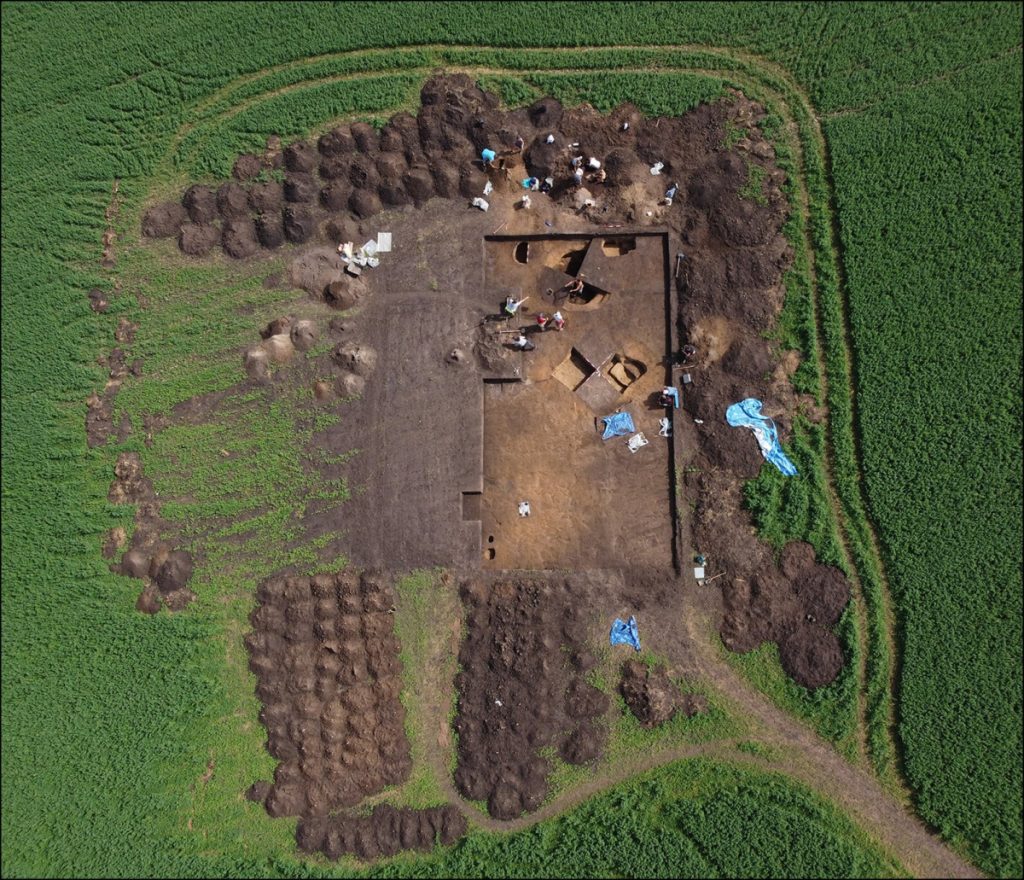
Archaeologists excavated the famous Iron Age site Němčice and uncovered the earliest glass workshop north of the Alps.
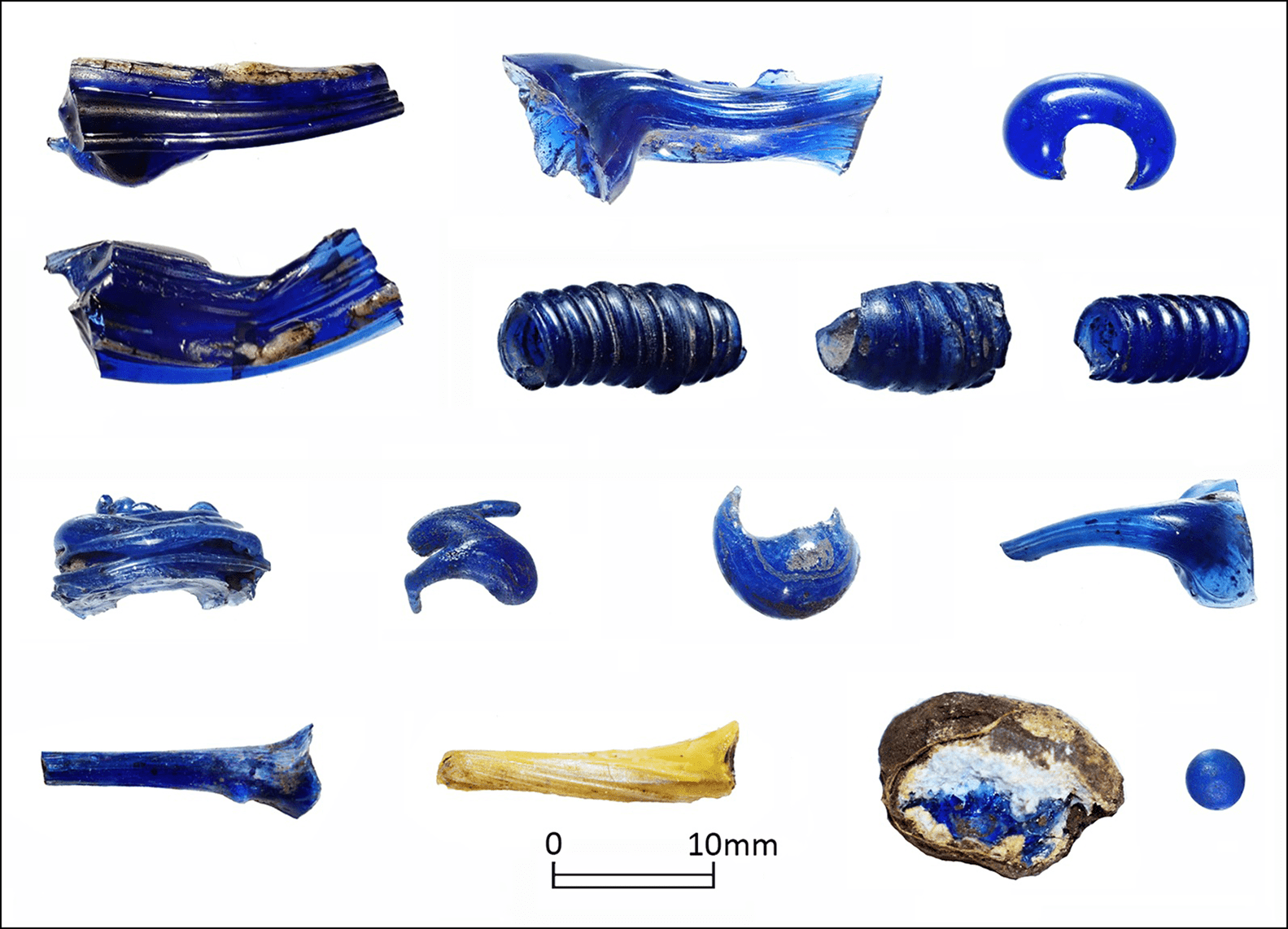
Numerous beautiful glass bracelets and beads have also been found at the site. As a result, it was thought that Němčice was a center of glass production, but only these excavations have confirmed this fact.
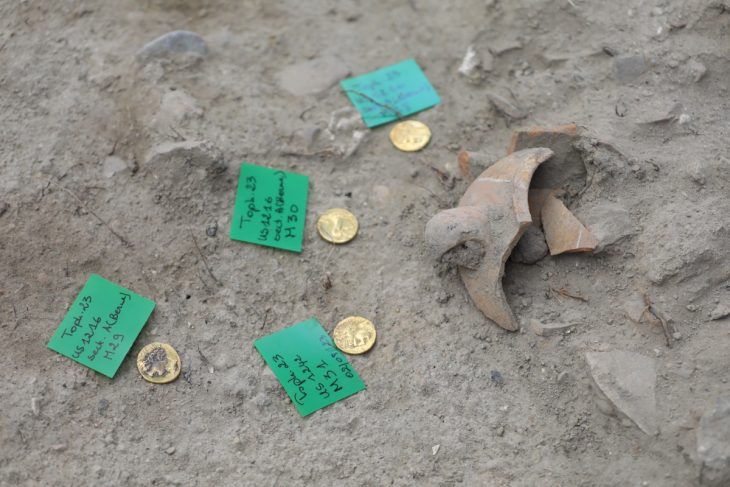
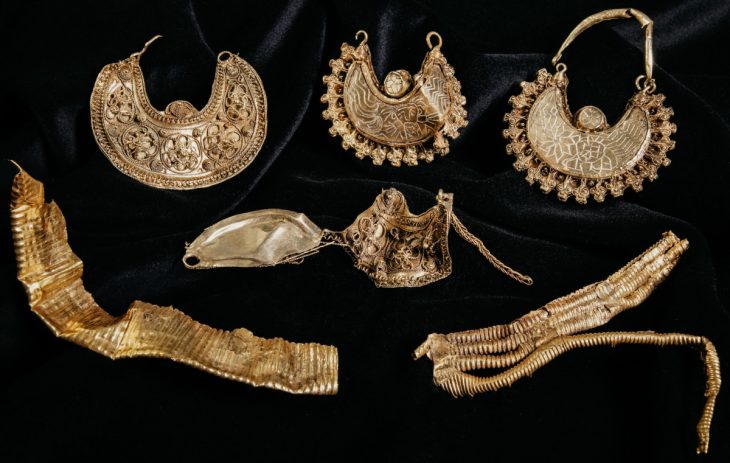
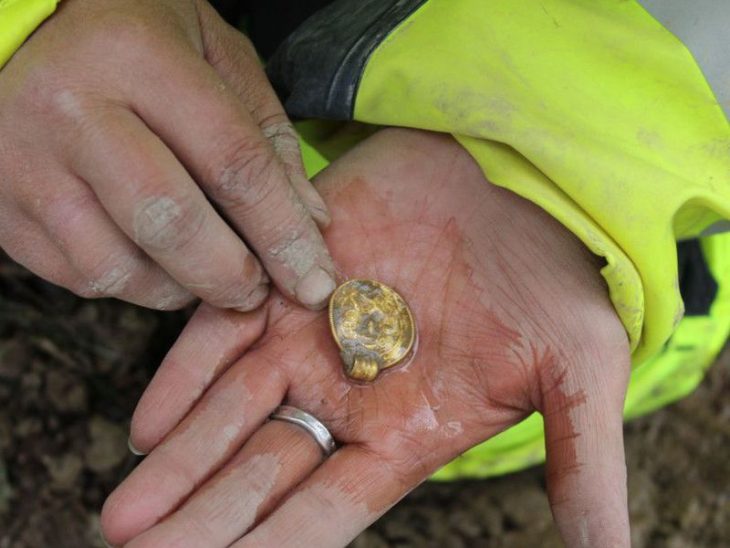
The central agglomeration of Němčice in Moravia was one of the most important archaeological sites of the La Tène period (MÖ 3. – 2. yüzyıl) in Central Europe. Němčice is also famous for its unprecedented amount of gold and silver coins which number over 2,000.
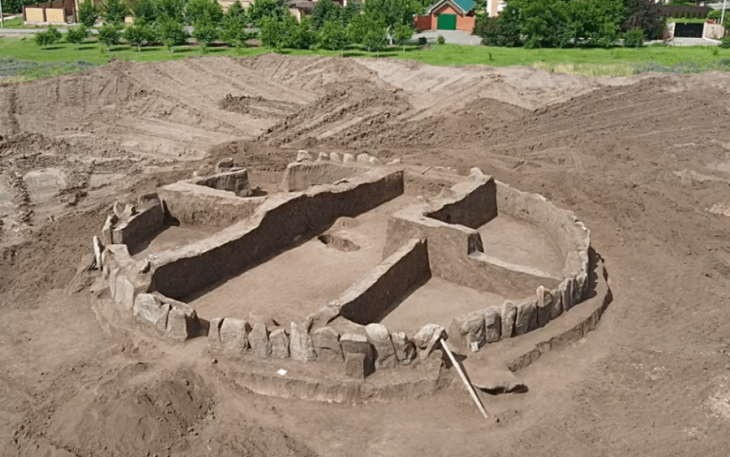
According to a study published on June 29 in the journal Antiquity, the team also discovered a possible sanctuary, suggesting that Iron Age people performed rituals there.
While conducting excavations in 2002, researchers made the discovery of Němčice. Subsequent surveys led to the discovery of sunken huts, bronze amulets, and coins dispersed throughout the site. The coins are clues that Němčice was likely part of the “Amber Road,” a large central European network that linked the Baltic coast to the Mediterranean region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

While glassmaking tools were not found on site, a mixture of complete and partially complete glass products was discovered. This indicates that glass was produced at Němčice.
“No one yet knows how exactly the Celts made glass bracelets,” lead author Ivan Čižmář, an archaeologist at the Institute of Archaeological Heritage Brno in the Czech Republic, said in the statement. “Therefore, we were interested in anything that tells us something about the technology of production.”
During the excavation, pieces of amber that were also in various stages of completion were discovered in addition to glass beads and bracelets. This confirms that the complex was associated with multiple manufacturing materials, making it even more regionally significant.
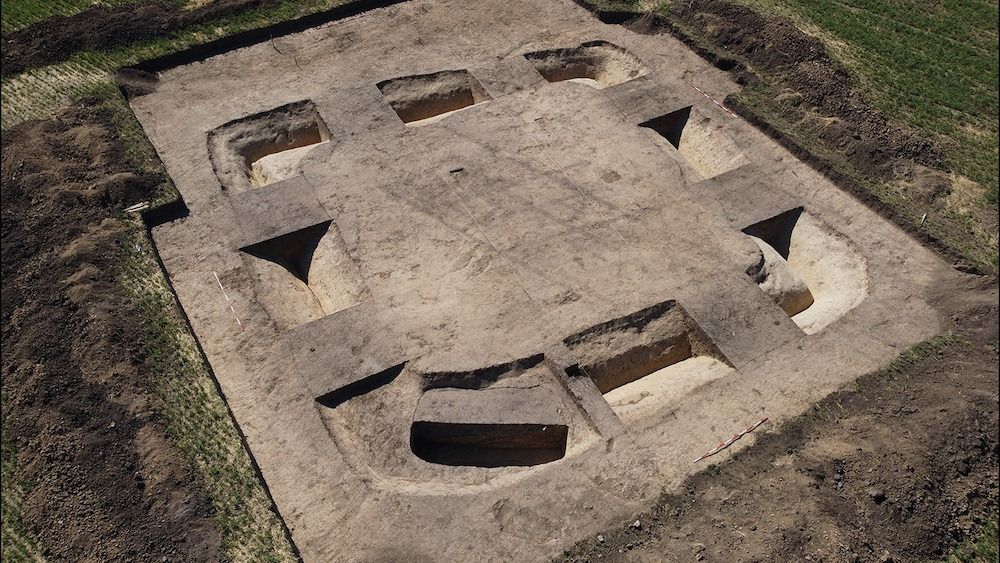

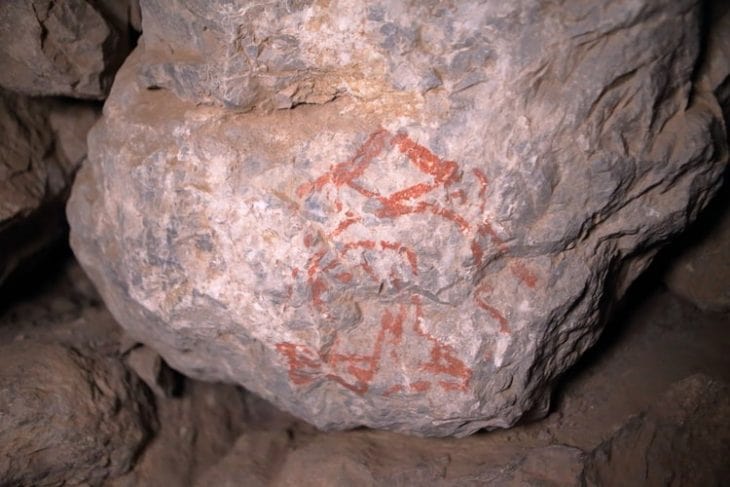
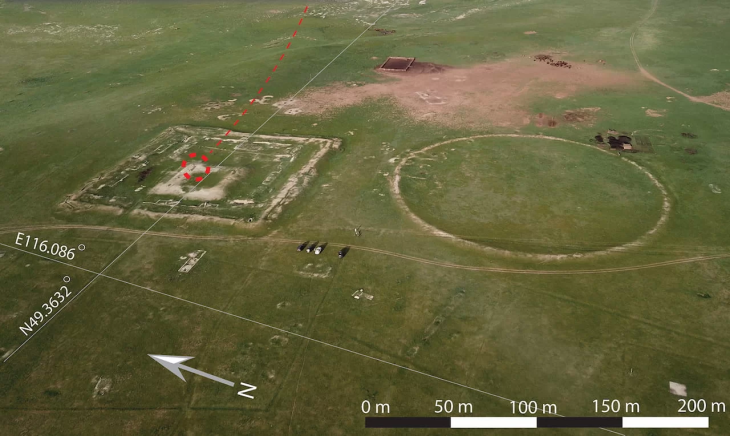
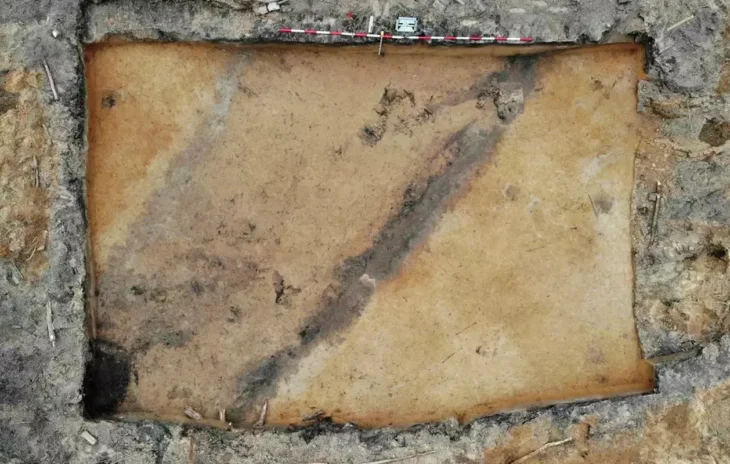
Also at the site’s highest point, a square area of Němčice that had been geophysically surveyed was excavated. It has many similarities with possible ritual structures from Austria, implying shared beliefs in Central Europe.
“The presence of these likely sacred features at Němčice indicates the character of the site not only as a trade and production center,” Dr. Čižmář said, “but also as a seat of an elite and ritual center.”
The study is published in the journal Antiquity.