A system of ancient ceramic water pipes, the oldest ever unearthed in China, shows that neolithic people were capable of complex engineering feats without the need for centralized state authority, finds a new study by University College London (UCL) and Peking University researchers.
The findings are described in a study published August 14 in the journal Nature Water.
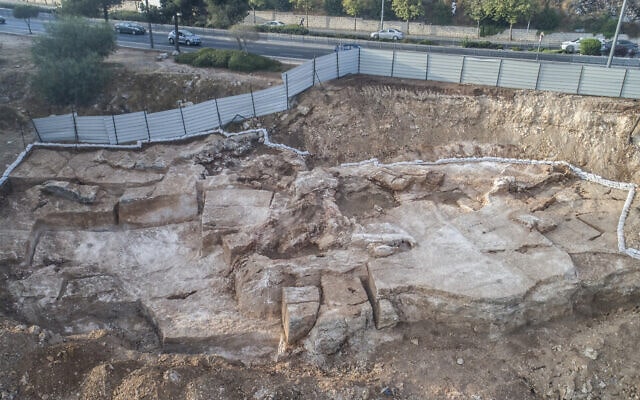
In the study, the archaeological team describes a network of ceramic water pipes and drainage ditches at the Chinese walled site of Pingliangtai dating back 4,000 years to a time known as the Longshan period (from about 2600 to 2000 BCE).
The Pingliangtai town was home to roughly 500 people during Neolithic times and had protective walls and a surrounding moat. It sits on the Upper Huai River Plain on the vast Huanghuaihai Plain, and the climate 4,000 years ago saw large seasonal climate shifts. Summer monsoons could dump a foot and a half of rain on the region every month.
With all this rain, it was critical for the region to manage floodwaters. The people of Pingliangtai appear to have built and operated a two-tier drainage system to help mitigate the rainy season’s excessive rainfall. Simple but coordinated lines of drainage ditches ran parallel to the rows of houses to divert water from the residential area to a series of ceramic water pipes that carried the water into the surrounding moat, and away from the village.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The team suggests that this network of pipes shows that the community cooperated with one another to build and maintain this drainage system.
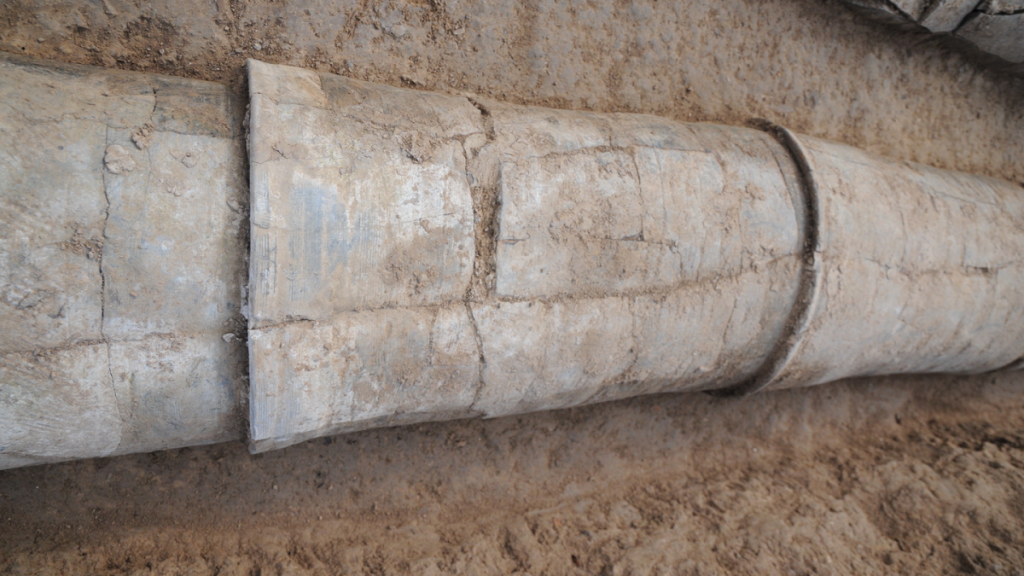

Dr Yijie Zhuang (UCL Institute of Archaeology), senior and corresponding author on the paper, said: “The discovery of this ceramic water pipe network is remarkable because the people of Pingliangtai were able to build and maintain this advanced water management system with stone age tools and without the organisation of a central power structure. This system would have required a significant level of community-wide planning and coordination, and it was all done communally.”
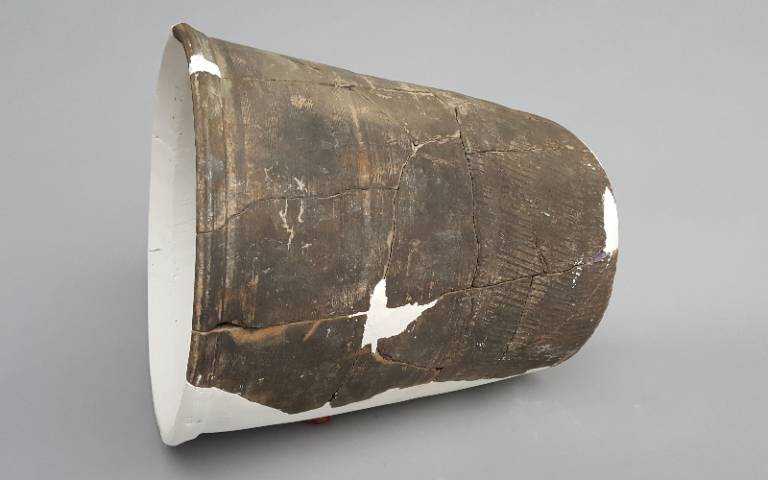
The ceramic water pipes make up a drainage system which is the oldest complete system ever discovered in China. Made by interconnecting individual segments, the water pipes run along roads and walls to divert rainwater and show an advanced level of central planning at the neolithic site.
What’s surprising to researchers is that the settlement of Pingliangtai shows little evidence of social hierarchy. Its houses were uniformly small and show no signs of social stratification or significant inequality amongst the population. Excavations at the town’s cemetery likewise found no evidence of a social hierarchy in burials, a marked difference from excavations at other nearby towns of the same era.
But, despite the apparent lack of a centralised authority, the town’s population came together and undertook the careful coordination needed to produce the ceramic pipes, plan their layout, install and maintain them, a project which likely took a great deal of effort from much of the community.
The level of complexity associated with these pipes refutes an earlier understanding in archaeological fields that holds that only a centralized state power with governing elites would be able to muster the organization and resources to build a complex water management system. While other ancient societies with advanced water systems tended to have a stronger, more centralized governance, or even despotism, Pingliangtai demonstrates that was not always needed, and more egalitarian and communal societies were capable of these kinds of engineering feats as well.

Co-author Dr Hai Zhang of Peking University said: “Pingliangtai is an extraordinary site. The network of water pipes shows an advanced understanding of engineering and hydrology that was previously only thought possible in more hierarchical societies.”
These ceramic water pipes represented an advanced level of technology for the time. While there was some variety in decoration and styles, each pipe segment was about 20 to 30 centimeters in diameter and about 30 to 40 centimeters long. Numerous segments were slotted into each other to transport water over long distances.
Researchers cannot say specifically how the people of Pingliangtai organized and divided the labour amongst themselves to build and maintain this type of infrastructure. This kind of communal coordination would also have been necessary to build the earthen walls and moat surrounding the village as well.
The Pingliangtai drainage system is unique from water systems elsewhere in the world at the time. Its purpose to drain rain and flood water from monsoons differs from other neolithic systems in the world, many of which were used for sewerage water drainage or other purposes.