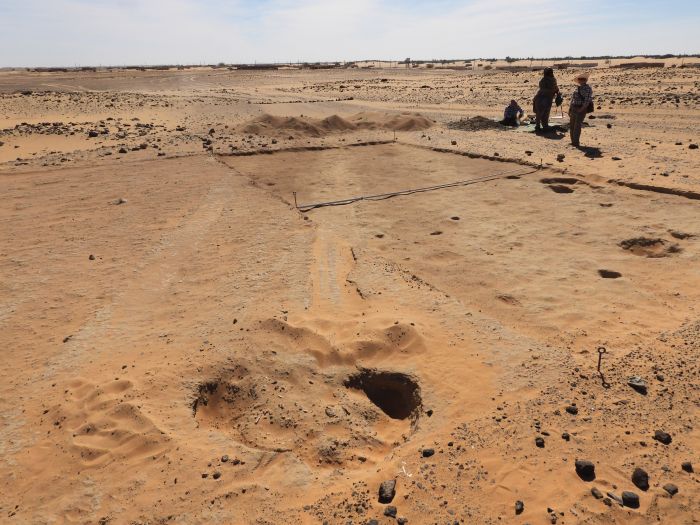
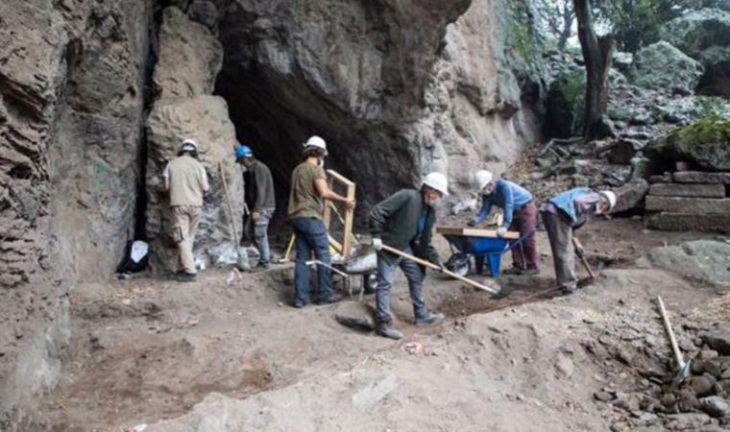
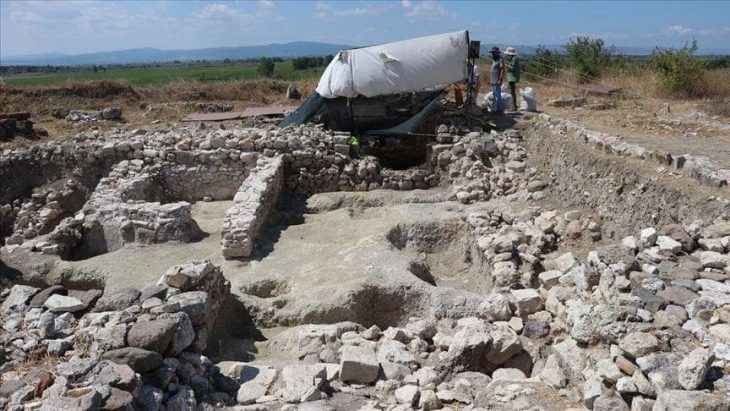
During excavations in the Letti basin in northern Sudan, archaeologists have unearthed 7,000-year-old bone tools used to bleed cows. Explorers believe this may be the earliest evidence of such a practice.
7,000-year-old burials were discovered during the excavation of a cemetery in the Letti Basin, including the remains of an elderly man and animal skin fragments that had been dyed red by the mineral ochre. The burials belonged to some of the region’s first cattle breeders.
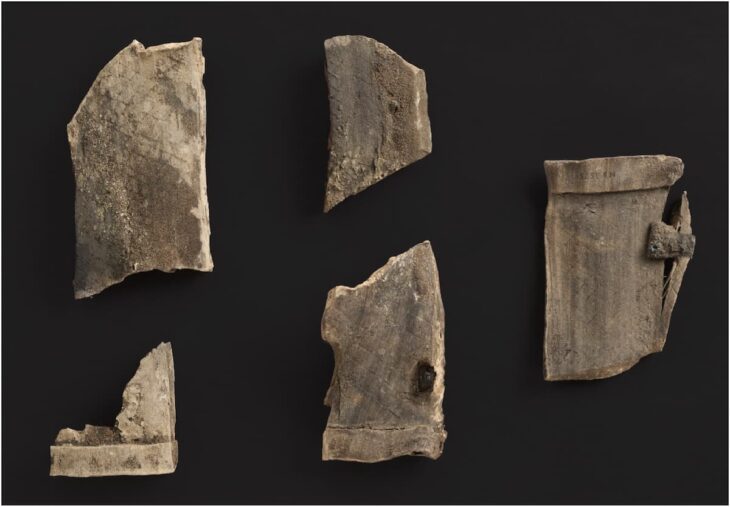
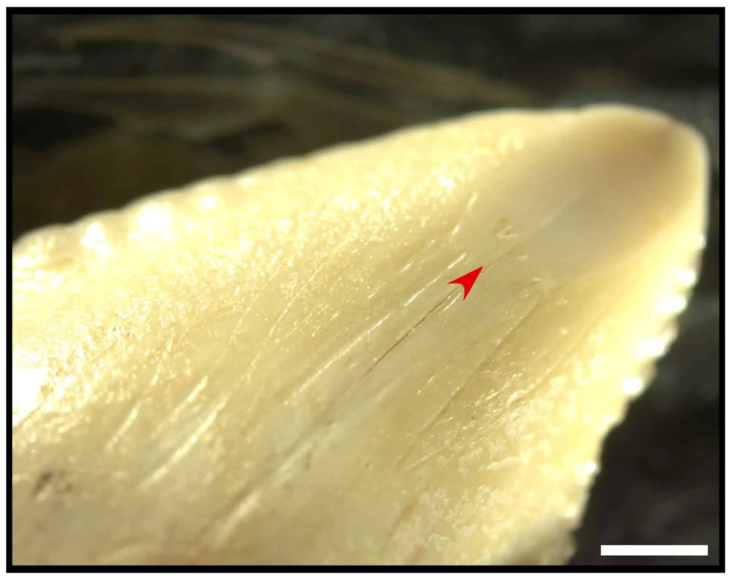
Along with five bone blades probably made from cattle bones, the burial pit also contained a small bowl with ochre traces. The bone blades had a funnel-like or gutter-like shape and were still razor-sharp, as revealed by a closer inspection.
The tools immediately drew the attention of researchers, Piotr Osypiński, one of the excavations’ lead archaeologists, told Science in Poland.
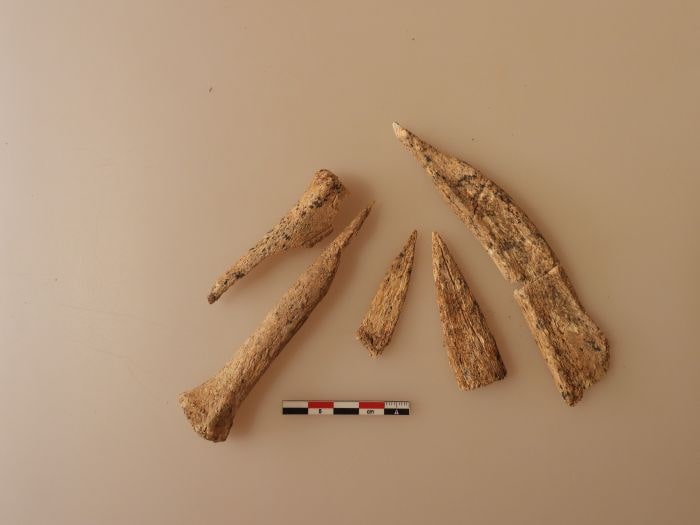

Experts believe these tools were used for cattle bloodletting, the release said. The custom of bleeding cows is still practiced today by the Maasai people of Kenya and Tanzania, Osypiński said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dr. Piotr Osypiński, said: “Given the characteristic shape of the blades, they could have been used to bleed cows, similar to modern African shepherds, such as the Maasai. Without any harm to the animals, cows’ blood is drunk on special occasions, usually mixed with milk. It would be the oldest known record of this type of practice”.
For the Maasai people, cow’s blood is “both ordinary and sacred food,” and is “considered beneficial for people with weakened immune systems” with its high amount of protein. Blood can be consumed on its own, mixed with milk, or mixed into other cooked dishes. Cattle bleeding entails nicking the animal’s neck, collecting the blood in a bowl, and then clotting the wound to ensure proper healing.
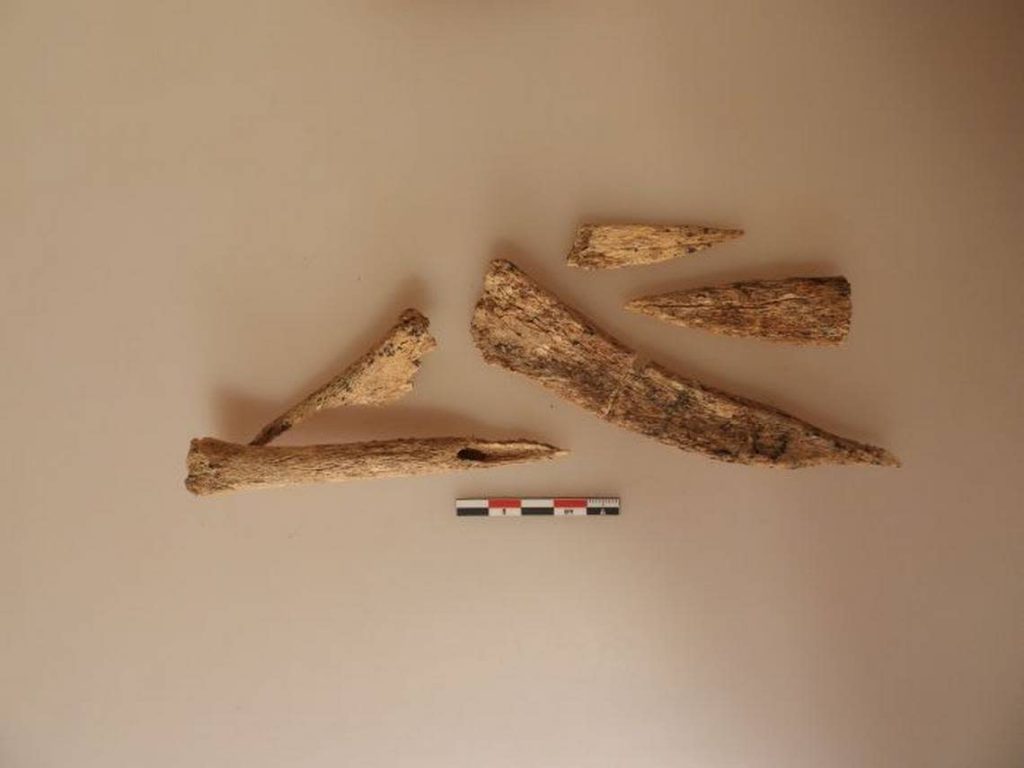

At a different cemetery burial, more bone blades were discovered. The remains of a young man were curled up in a fetal position in this tiny oval grave. The deceased, with a small, precisely cut hole in his skull, was covered with animal skin dyed in ochre.
According to the press release, the man’s skull hole may have contributed to his demise. It’s unclear whether this hole was made during surgery or as part of a ritual.
Cover Photo: M.Osypinska