The Birkleyn Caves were known as “the place where the world ends” and as “the place where the water of immortality flows”.
Located 15 kilometers from the Diyarbakır city center, Lice is home to the Birkleyn Caves, where Assyrian inscriptions, reliefs, and remains of the Byzantine era can be found.
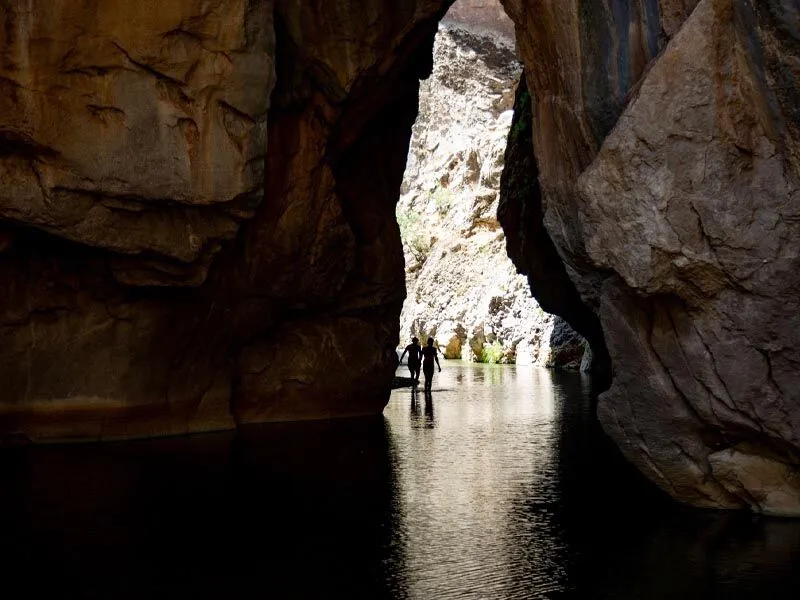
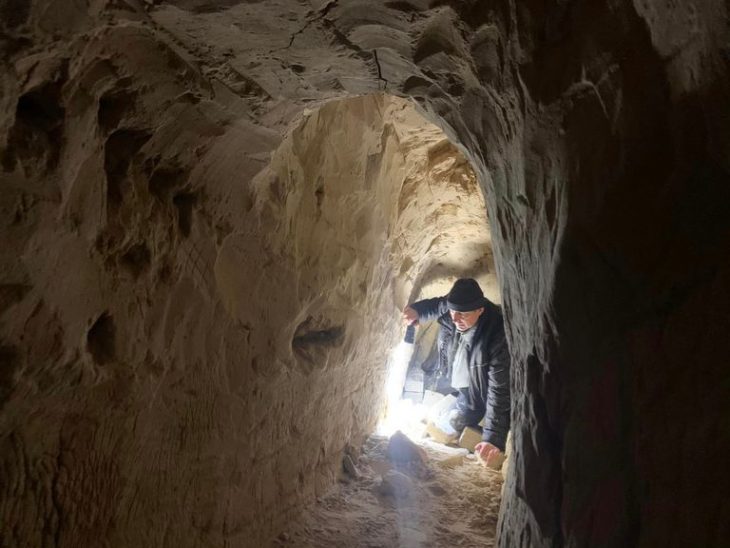
Five sections of a partially eroded cave system make up the Bırkleyn Mağarası (Birkleyn Caves). Both passages have a cave river because the main branch is a river cave, and since they are through caves, they are not usually regarded as springs. However, Bırkleyn Cave was considered to be the source of the Tigris River by the Assyrian kings who conquered this region and left behind several inscriptions and reliefs, the oldest of which are over 3000 years old.
The place where the Birkleyn waters flows underground through a natural tunnel before surfacing is called Birkleyn, or the Tigris Tunnel. In the ancient times, the place where the water disappears to flow underground was dubbed “end of the world.”
Lake Hazar, located 100 kilometers to the west of Gölardı, is the Tigris River’s official spring. This is one of the well-known river’s principal eastern tributaries. Although the Bırkleyn Mağarası is not a spring, it was long believed to be the spring of the Sebeneh-su. There are three springs in the through-cave, and the three rivers combine to form the Kara River, which is swallowed by the cave and only resurfaces 750 meters down the valley.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
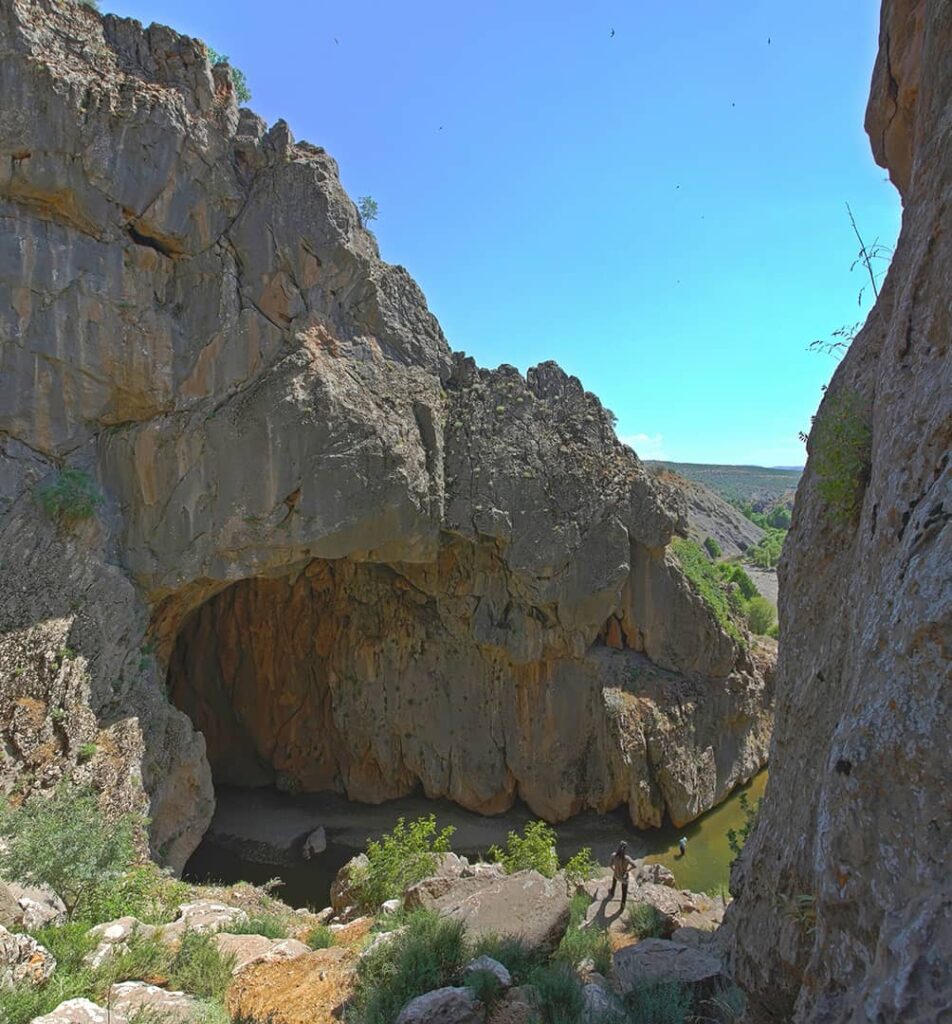

In 852, King Salmanassar III of Assyria sent an expedition to the Tigris River’s headwaters. He ordered his army to detour on its way back to Assyria from inner Anatolia in order to accomplish this. He also took the resurgence to be the real spring because it appears that he never ventured inside or outside the cave. The Bırkleyn Mağarası is the source he located, and he positioned inscriptions at the spring. This is considered the first hydrogeologic excursion made by man.
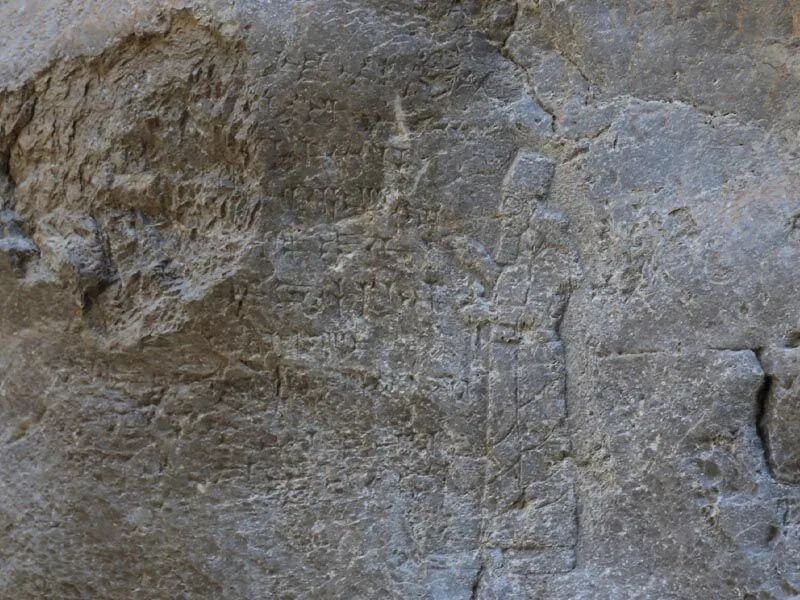
The lower entrance of the cave has reliefs and inscriptions of Tiglatpileser I (1114–1076 BC) and Shalmaneser III (858–824 BC). There are 3 reliefs and 5 cuneiform inscriptions belonging to Assyrian King Tiglatpileser I (1114-1076 BC) and Salmanassar III (859-828 BC) in the cave.
Shalmaneser III’s bronze bands at Tell Balawat also featured a detailed representation of this significant commemorative event. They are probably the world’s oldest cave images, dating to 850 BC. It is currently on exhibit at London’s British Museum. Additionally, his visit to the location was recounted in his annalistic texts on public monuments in Assyrian cities.
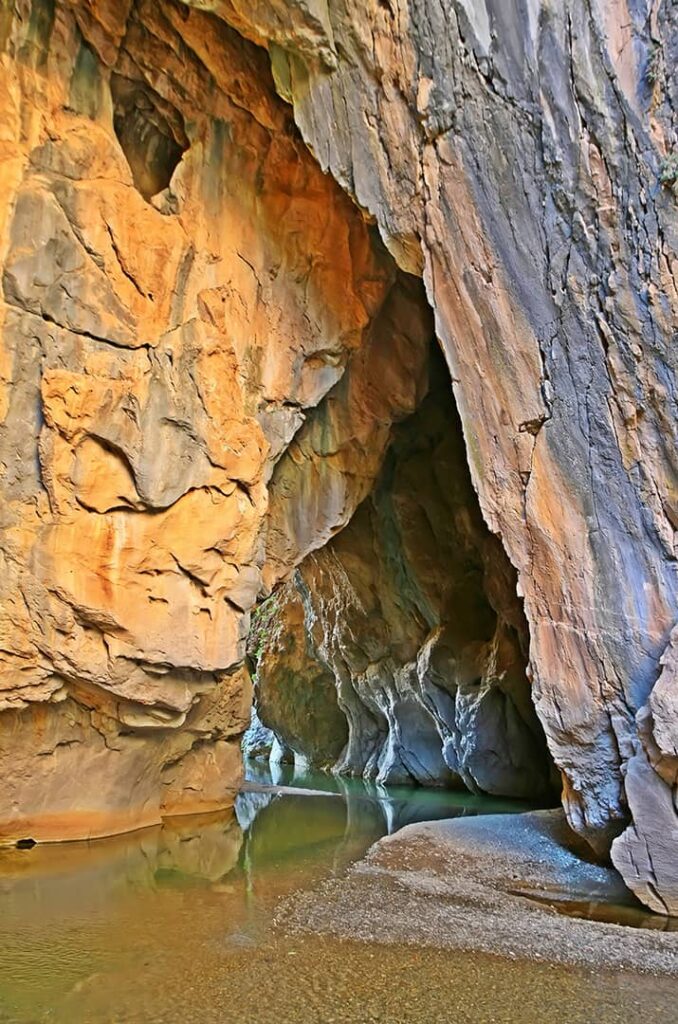

The first information obtained from research is based on the visit of C. Lehmann-Haupt in 1862 and W. Bleck in 1898-99. In 2004, a team led by Dr. Andreas Schachner from the University of Munich visited two of the caves documented Assyrian reliefs and inscriptions, and examined all the archaeological remains in the vicinity. The survey conducted by Dr. Schachner revealed that caves were used since the Late Neolithic Age.
Bırkleyn has been the subject of legends with its history and nature and is also mentioned in the holy books. According to the legend, which is told among the people but is not based on any historical documents; Alexander the Great, King of Macedonia, stayed here with his army of 15 thousand people on his way to the Persian campaign. Pliny thought it was one of the passages into the underworld.
In the same way, it is told among the people that Zülkarneyn, who is described in Surah Kehf in the Qur’an, spent a period of his life here. For this reason, the local people refer to this legend as Iskender-i Zülkarneyn. It is believed that Alexander and Zülkarneyn are the same person.
İskender’i Zülkarneyn (Alexander Dhu al-Qarnayn), lit. “The Two-Horned One”, appears in the Quran, Surah al-Kahf (18), Ayahs 83–101 as one who travels to east and west Some think he is Alexander the Great. It is as well interpreted as the horns of the ram-god Zeus-Ammon, as it may mean that he traveled to the east and the west, from one extremity (“horn”) of the world to the other. There are about half a dozen historic people which could be Zülkarneyn.

İskender’i Zülkarneyn was embarking on an expedition, according to this legend. His head developed two horn-like tumors that started to hurt a lot. In a dream, Alexander was informed that his horns would vanish if he washed in the water of the Birkleyn caves in Lice. İskender-i Zülkarneyn came and conquered Lice. When he drank the water emerging from the caves and washed his head with the water, one of his horns immediately disappeared.
Today, the spot is a major tourist attraction where nature lovers can trek and explore the area’s natural wonders.
Cover Image Credit: Serhat Uçar- Güneydoğu Ekspress