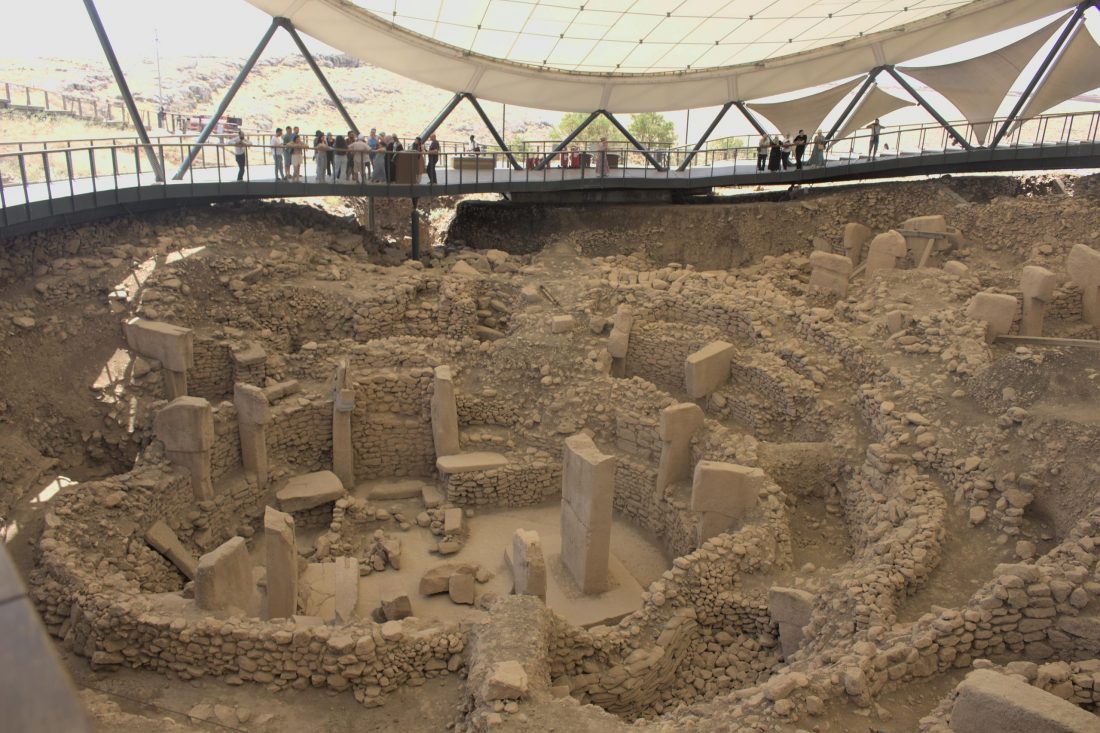
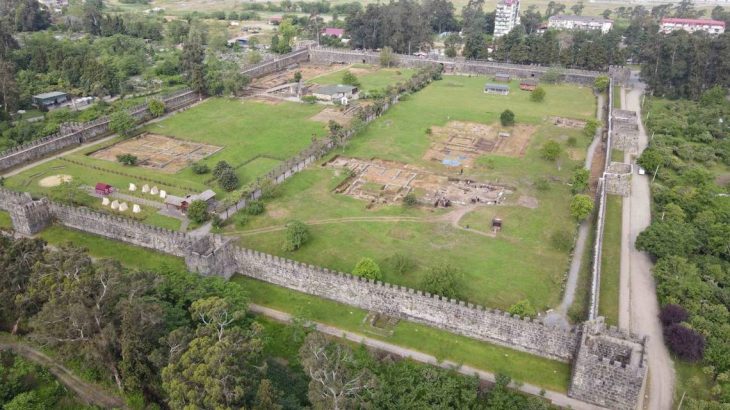
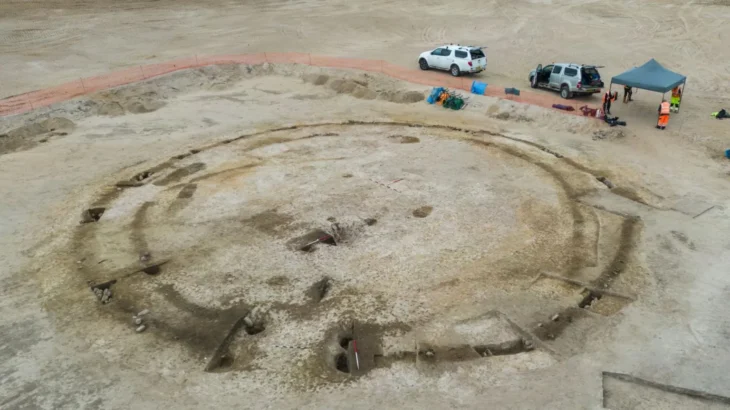
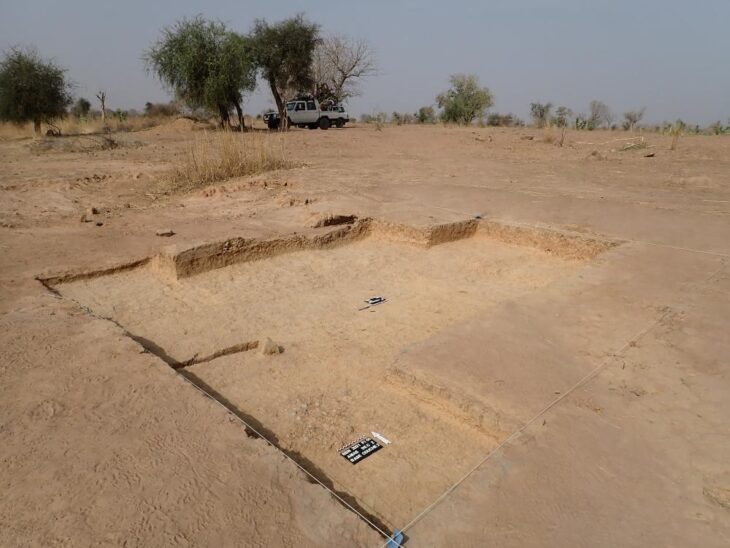
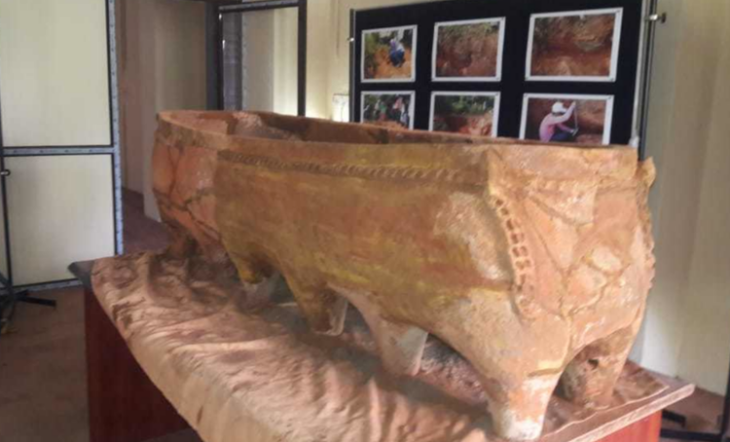
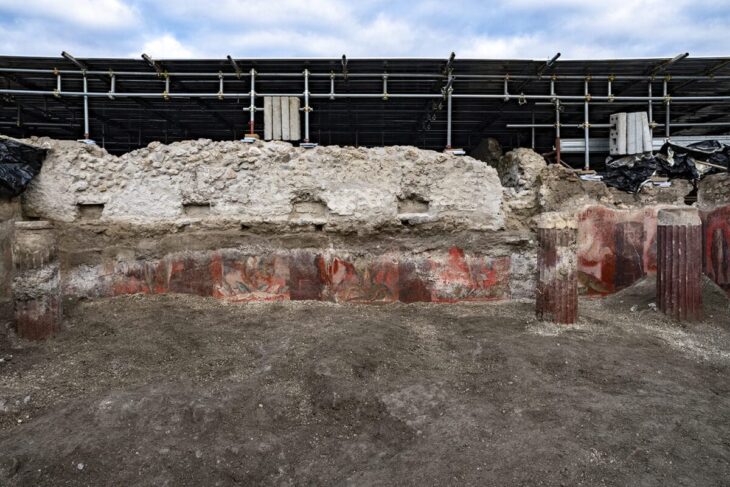
A recent discovery at Göbeklitepe, the oldest known Mesolithic temple complex, has revealed grinding stones, new finds expected to shed light on human history.
“During this year’s work we made a large number of findings such as grinding stones and hammerstones indicating daily use in these places,” Necmi Karul, an archeologist at the Istanbul University and leader of the excavation team, according to the news reported by Anadolu Agency.
Karul stated that the information obtained in archaeological excavations changes as new studies are conducted and data analysis is made. He said that while some of the generally accepted views on Göbeklitepe are still valid, some are likely incorrect in light of new findings from excavations.
Grinding stones were frequently used in ancient times to crush or pulp plants or animals for use in cooking. “Analysis of these findings will give us an idea of what these activities were,” he said, adding that they plan to do this during the winter.
As the team began to consider other possibilities about the ancient site, he said: “One of the prominent ones is that although it has been suggested that there were only public buildings in Göbeklitepe, called temples by some, it was known that there were places in the form of dwellings and shelters.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
He went on to say: “More of these (dwellings and shelters) have been found. So this has fueled debate over whether this was a gathering center or a settlement where people live at the same time.”
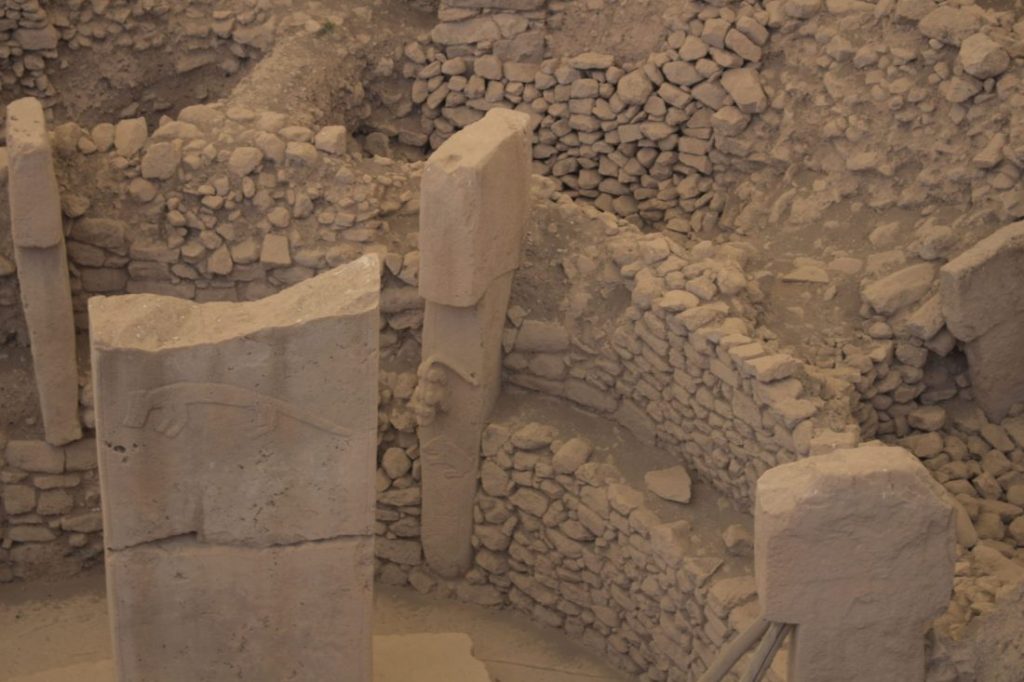

The discovery of residences in Karahantepe and other stone hills that were in existence at the same time as Göbeklitepe, according to Karul, increased the likelihood that these locations were settlements with public structures.
He stated that Göbeklitepe and other sites known as Taş Tepeler “Stone Hills” in Turkish were contemporaneous and spanned a period of about 1,500 years, emphasizing that all findings from these sites reflect the culture of the time. He added that according to those findings, the first agricultural experiments were carried out in this region.
In 2016, German Archaeological Institute archaeologist Laura Dietrich began analyzing thousands of stone grinding tools that had been excavated at Göbekli Tepe over the course of nearly two decades. Using a combination of use-wear studies, experimental archaeology, and microscopy, Dietrich analyzed the way in which the stones had been worn down over time and showed that they had been used to process grains and legumes. She identified chemical residues on many of the vessels that provided evidence they had been used to cook vats of porridge or perhaps the occasional batch of prehistoric beer. “Most probably,” Dietrich’s study says, “these people were cultivators, or at least had strategies to gather large quantities of wild grain.”
“The existence of tools pointing to agricultural experiments shows us that when the first settlements began to appear at the site, there was no agricultural activity, but wild grains were collected, and that this collection process evolved into the cultivation of plants over time,” Karul said. While the layers at nearby Cakmaktepe are “possibly older” than Gobeklitepe and Karahantepe, architectural remains pointing to the presence of complex societies in Sayburc from the beginning of the Neolithic period were unearthed last year.

The team also found the remains of a rectangular-planned building from the end of the Neolithic period, which would demonstrate a complex character at the Sefertepe site, adding that findings from the pre-Neolithic period were also unearthed in the Söğüt field.
“It is a fact that both Göbeklitepe and other settlements are sites that were part of an interacting social organization in a wide region about 11,000-11,500 years ago.”
While Karul described the period as the beginning of settled life and living together in larger groups for the first time, he stressed that this brought a new social order, new relationships and a division of labor.
On the presence of a developed workforce organization, Karul said that public buildings are among the best indicators of this and that the figures in these structures and the scenes depicted on the figures are the products of a communal memory based on a distant past.
“When we put all this together, we see the construction of a new society that we have never encountered before.”
Southeast Turkey’s Göbeklitepe is a UNESCO World Heritage site that dates back to 11.7 ka BCE. It consists of circular, doorless rooms that are laterally aligned and supported by five-meter-tall limestone columns that are T-shaped on the interior and exterior. Most columns contain animal drawings.
According to studies, the location may have served a special purpose, such as serving as a temple. After about 2 ka of use, the site was deliberately filled in with stones. The site predates the start of the agricultural era, so it is unclear what civilization built such massive structures using only hand axes and what the figures on the columns represent.