The western Baltic Sea may conceal far more prehistoric cultural heritage than previously believed — including monumental underwater structures created by Stone Age hunter-gatherers.
This possibility is at the heart of the newly launched SEASCAPE project, an interdisciplinary research initiative led by the Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW). The three-year project officially began today with a kickoff meeting at the IOW, bringing together experts from multiple institutions to explore submerged landscapes and their archaeological significance.
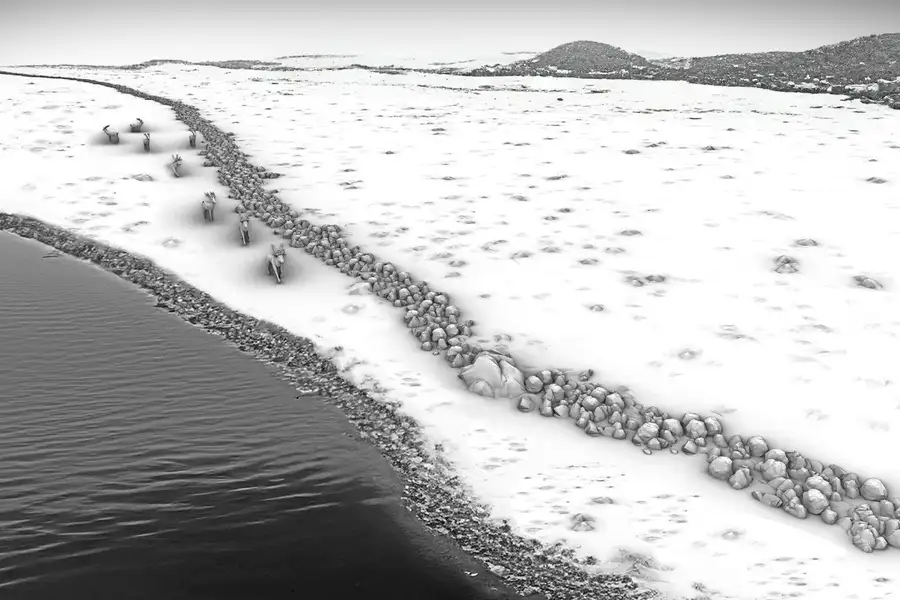
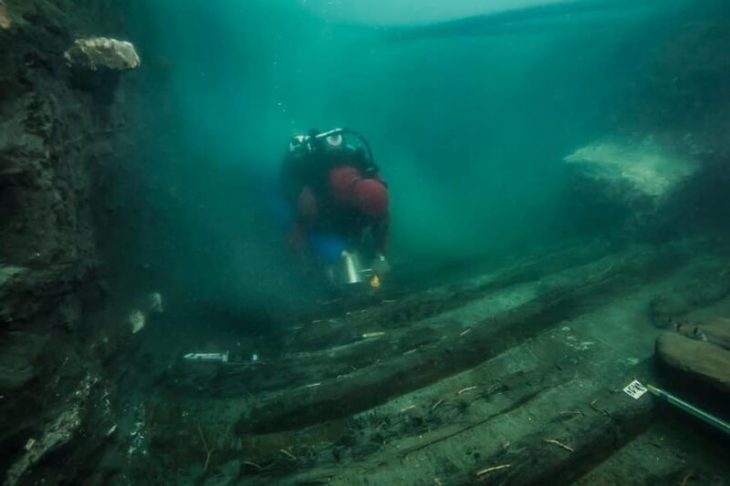
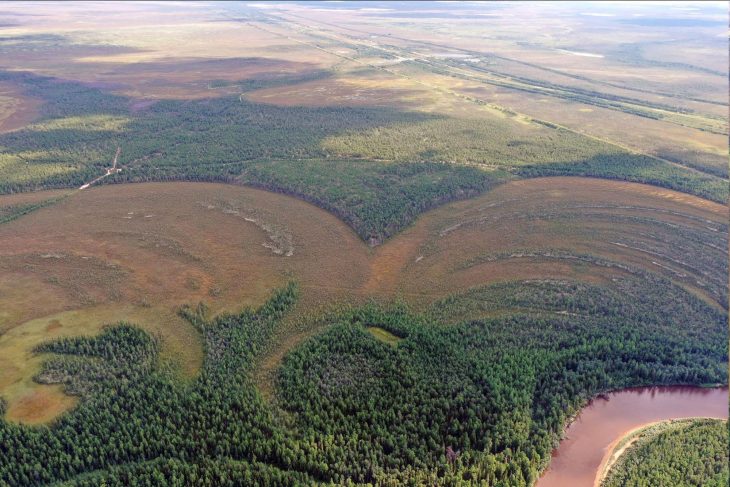
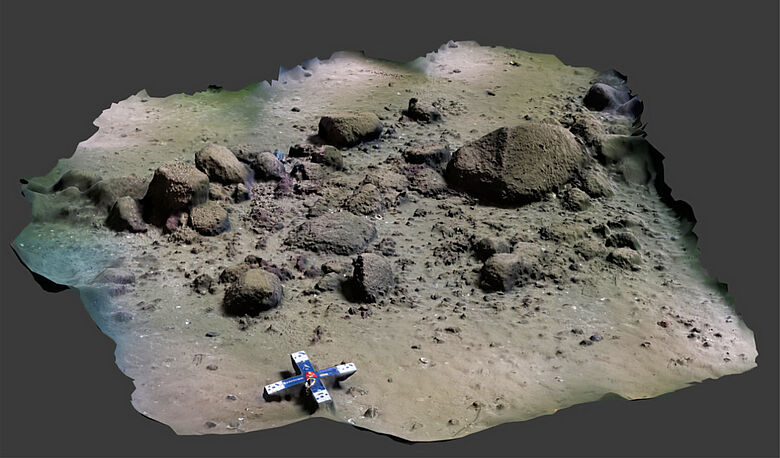
The starting point of SEASCAPE is a remarkable underwater discovery: a one-kilometre-long stone alignment located 21 metres beneath the surface of the Mecklenburg Bight, near Rerik, next to what was once a freshwater lake. Preliminary analysis suggests that this structure is a man-made hunting installation from the late Pleistocene, dating back around 11,000 years — before the Baltic Sea inundated the area. SEASCAPE will now investigate this hypothesis using a combination of geophysical surveys, geological analysis, and underwater archaeological methods.
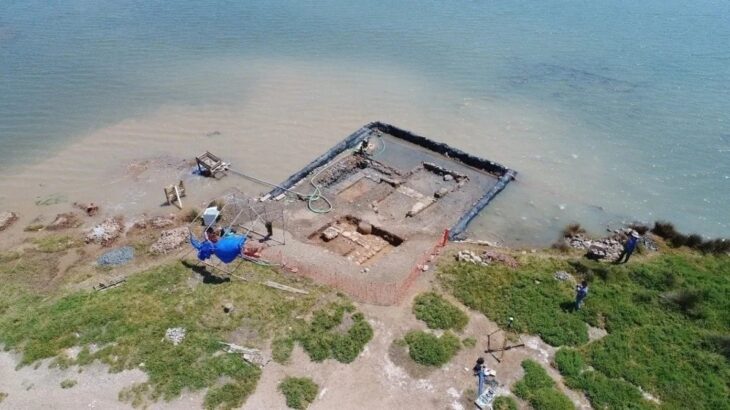
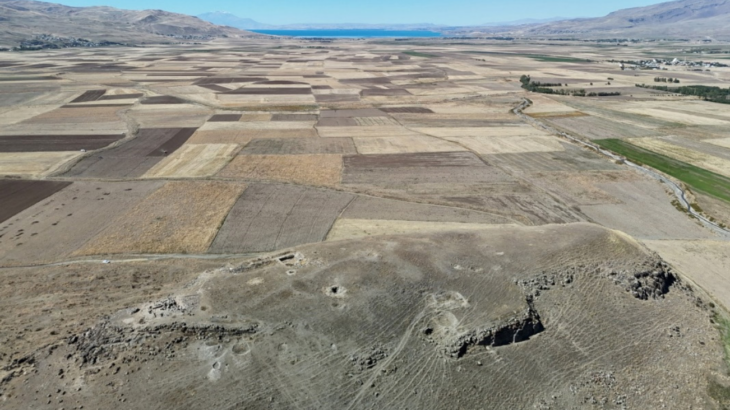
But the project’s scope extends beyond this single site. Historic hydroacoustic data from the Flensburg Fjord and Fehmarn Sound indicate the presence of additional large-scale structures, previously overlooked and now slated for high-resolution mapping and scientific analysis. Researchers also aim to reconstruct the paleoenvironmental conditions of these submerged sites and explore the origins, functions, and cultural significance of the discovered features.
The overarching goal of SEASCAPE is to develop a comprehensive reconstruction of prehistoric terrestrial landscapes now hidden beneath the Baltic Sea. By doing so, the project seeks to illuminate the lifeways of Mesolithic hunter-gatherer societies and offer new insights into early cultural development in Northern Europe.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“With SEASCAPE, we’re pioneering new scientific terrain — both literally, beneath the seafloor, and collaboratively, by integrating geophysics, archaeology, and palaeoenvironmental science,” says Dr. Jacob Geersen, marine geologist at IOW and project lead.
SEASCAPE represents a collaborative effort across leading research institutions, including the Leibniz Centre for Archaeology (LEIZA), University of Rostock, and Kiel University (CAU). The project is also supported by the State Office for Culture and Monument Preservation of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and the State Archaeology Department of Schleswig-Holstein, who oversee cultural heritage protection.
This initiative builds on previous foundational research conducted by the IOW in the early 2000s, during which geophysical surveys mapped sunken lakes and prehistoric shorelines on the Baltic Sea floor. These earlier studies form a vital scientific basis for SEASCAPE’s explorations.
Funded under the “Cooperative Excellence” program of the Leibniz Competition, SEASCAPE has secured nearly €1 million in support over its three-year term. The project has already earned recognition, receiving the North German Science Prize’s recognition award in December 2024 for its innovative approach combining marine geology, archaeology, and cultural landscape research.
Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW)
,Cover Image Credit: Graphical reconstruction of the stone wall as a hunting structure in a glacial landscape. Michał Grabowski