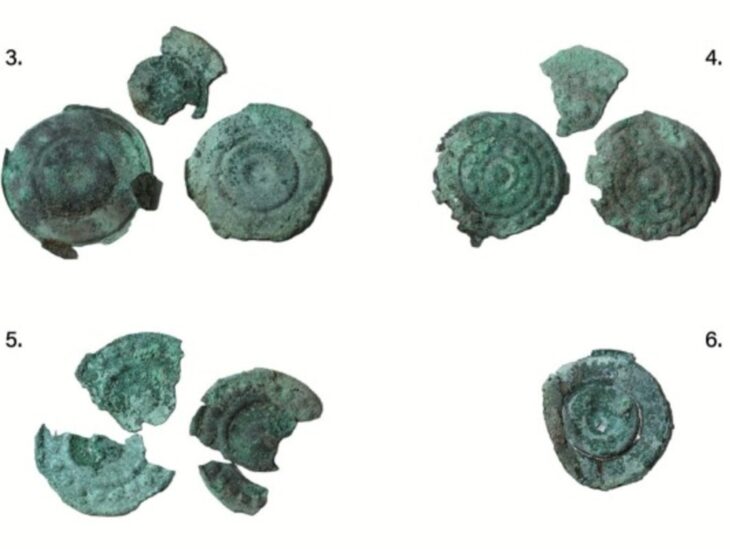
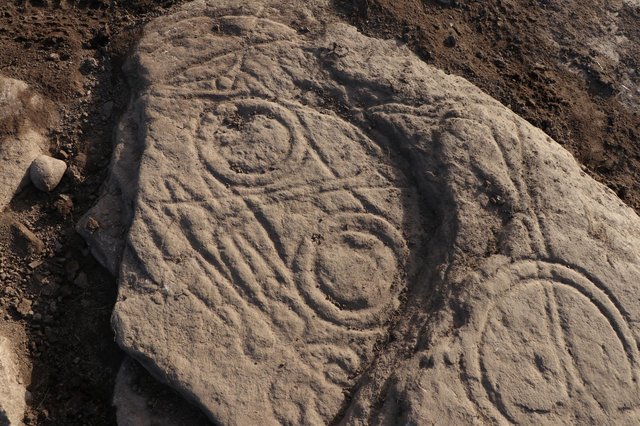
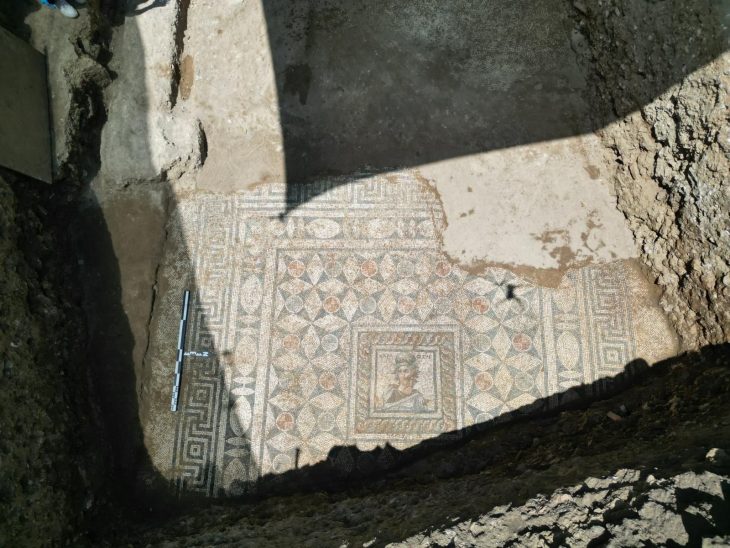
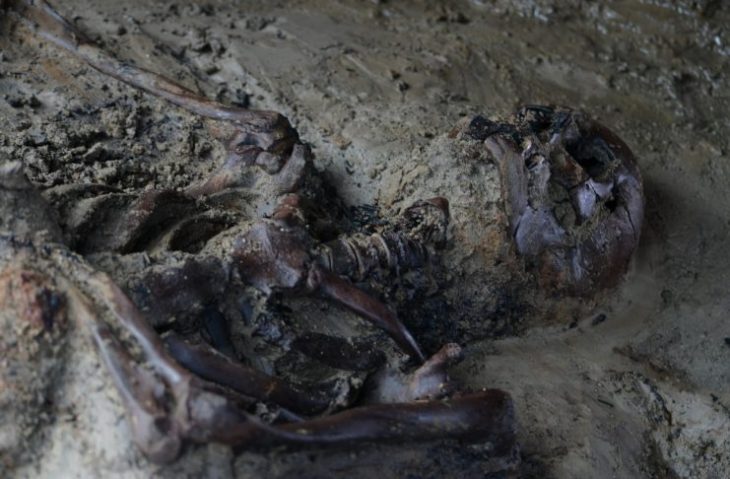
Archaeologists have uncovered significant remnants of the ancient Roman city of Metlosedum, now modern-day Melun, in a recent excavation revealing the urban sophistication and strategic importance of the site in the Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis.
Located approximately 40 kilometers southeast of Paris, Melun was a key settlement in Roman Gaul, sitting at the confluence of land and river trade routes between the Brie and Gâtinais plateaus. The site, situated within the territory of the Senones tribe—whose capital was in present-day Sens—held strategic value at the northwestern edge of their civitas, bordering other notable tribes like the Meldes, Parisii, and Carnutes.
Discoveries of Roman-Era Architecture
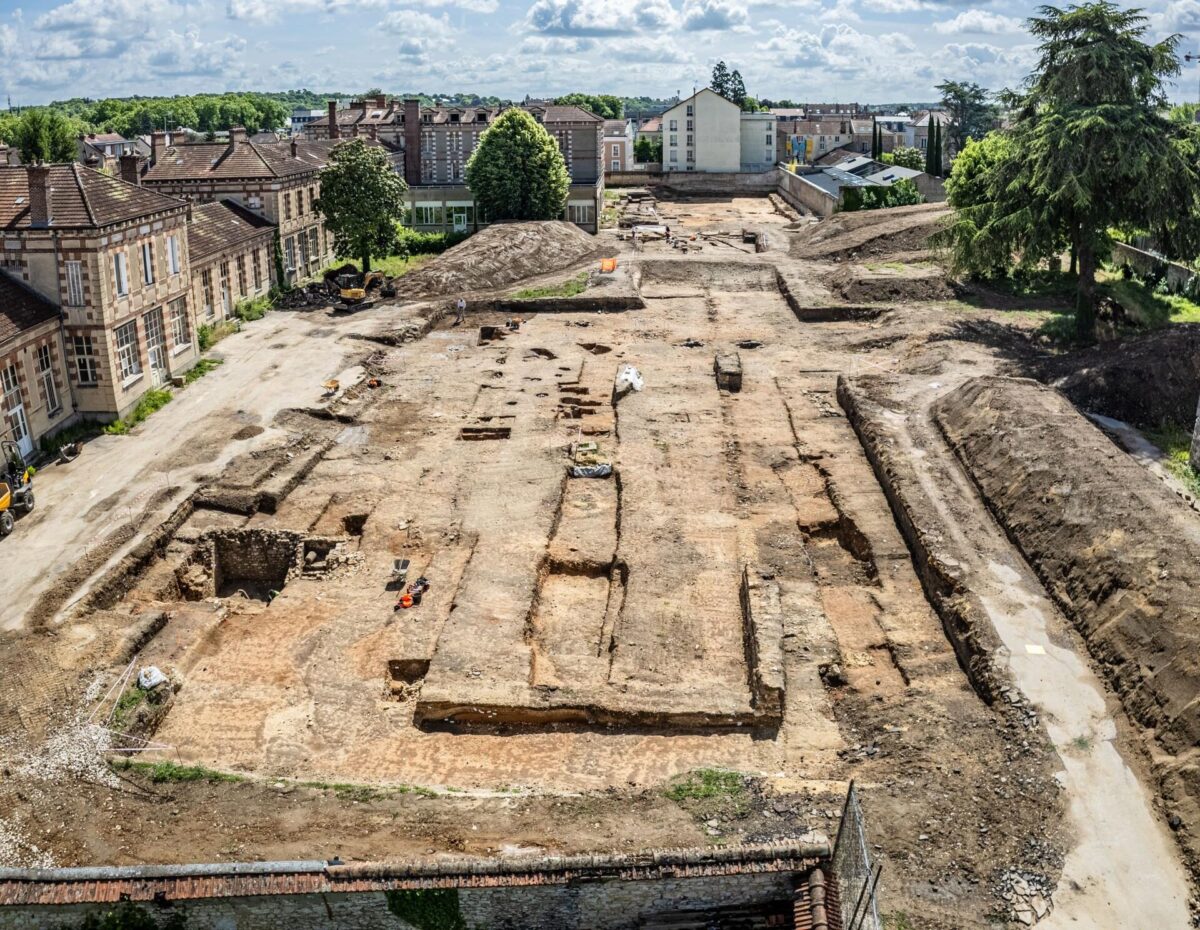
The excavation, led by the Service municipal de l’archéologie, SDASM, and Inrap, focuses on a 3,500 m² urban plot. It lies at the intersection of two major Roman roads: an east-west decumanus (beneath today’s rue de Belle Ombre) and a north-south cardo (aligned with rue de Dammarie). These thoroughfares outline the ancient street grid of Melun, confirming the city’s organized urban fabric.
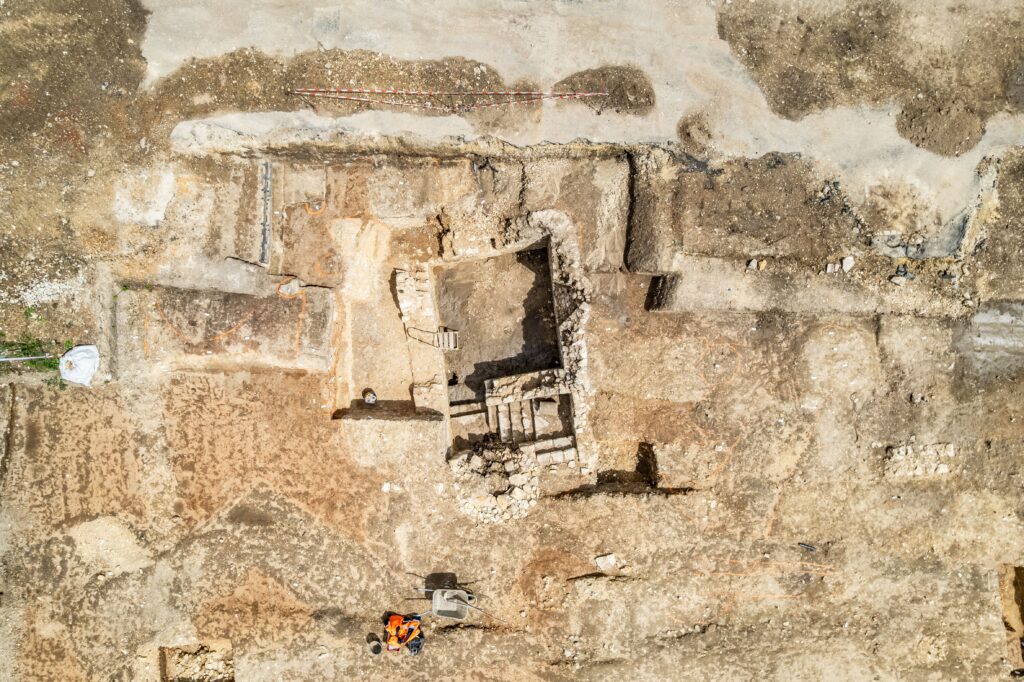

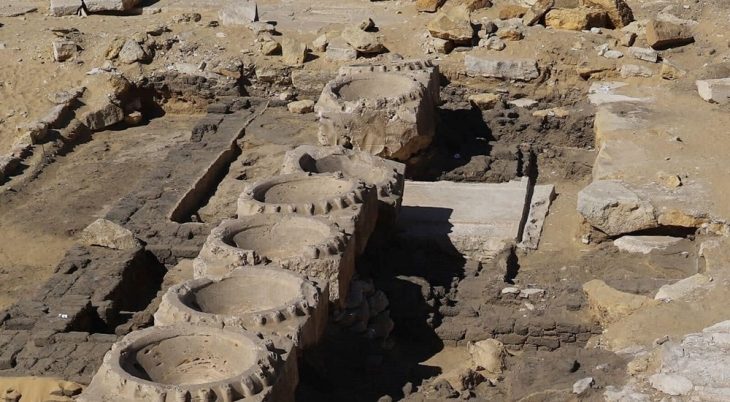
Two principal building sectors have been unearthed. To the west, archaeologists discovered a large rectangular Roman domus covering over 700 m². Despite partial dismantling in antiquity, several foundation segments made of stone bonded with lime mortar remain, outlining a complex with multiple rooms surrounding a central courtyard.
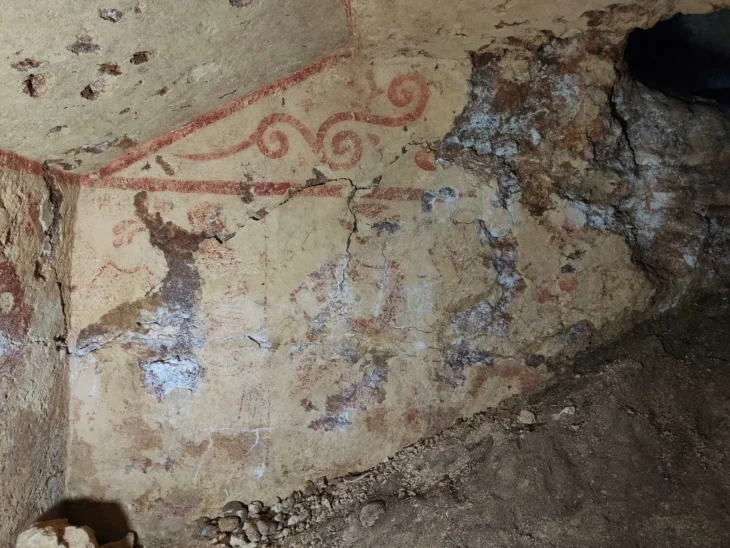
One highlight is a well-preserved cellar at the northwestern end of the building. Reaching a depth of 2.2 meters, the cellar boasts lime mortar walls, a ventilation shaft, and built-in niches, accessed via a three-flight staircase. A reused Roman column fragment was found embedded in the structure, a testament to adaptive reuse in Roman architecture.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Domestic Spaces and Urban Life
Roughly 40 meters east, a second building complex of around 600 m² has been partially exposed. Though heavily disturbed by modern utility works, it includes an excavated room, remnants of a possible kitchen area—such as a combustion structure built with tegulae (Roman roof tiles) and ceramic water conduits—suggesting daily domestic activities.
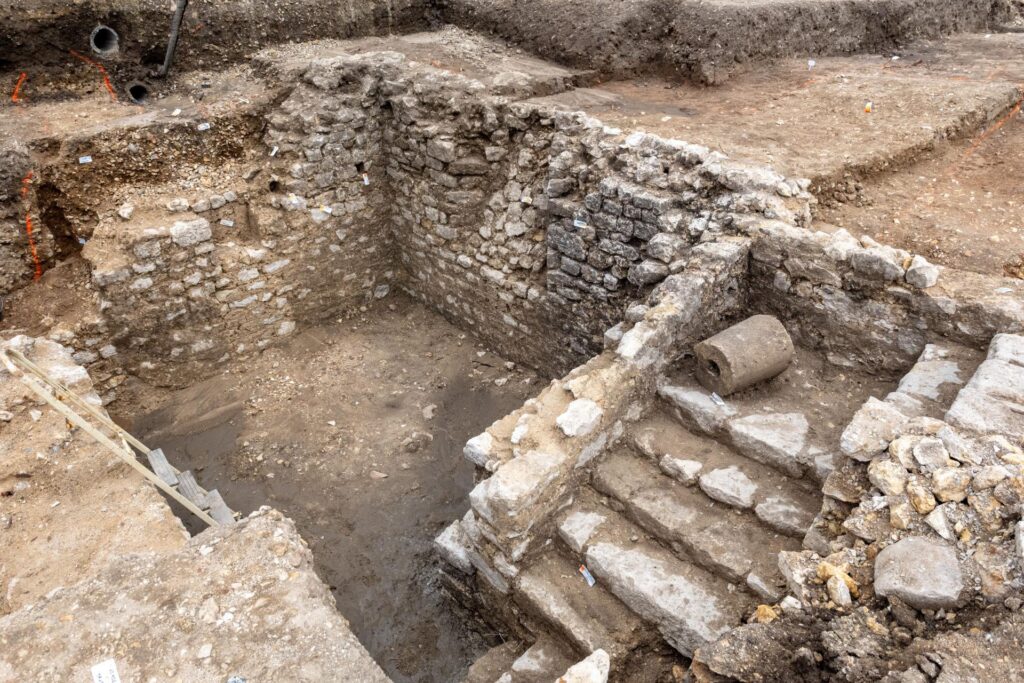

Between these zones lie open spaces containing storage pits, small unlined cellars, and eight ancient wells, built with unshaped limestone blocks. These features illustrate the integration of residential and service functions within the Roman cityscape, although no clear evidence of artisanal or industrial activity has yet been found.
Due to the incomplete nature of the remains, it is still unclear whether the western and eastern structures were two separate residences or parts of a single, expansive complex exceeding 2,000 m²—an unusually large footprint for Roman domestic architecture in the region.
Modern History Interwoven with the Ancient Past
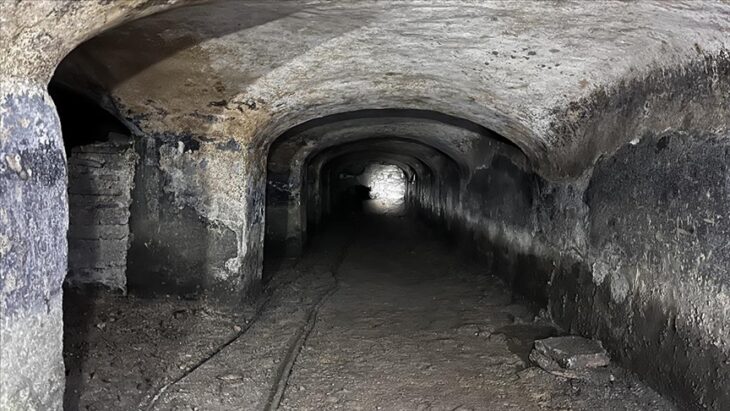
In a striking juxtaposition, archaeologists also discovered zigzagging World War II air raid trenches, part of a defensive installation built in a schoolyard to shelter civilians from aerial attacks. A French Adrian helmet (1926 model) was among the artifacts recovered from these features, highlighting Melun’s layered historical narrative.
Cover Image Credit: Drone view of the Melun (Metlosedum) excavation. Hamid AZMOUN, Inrap