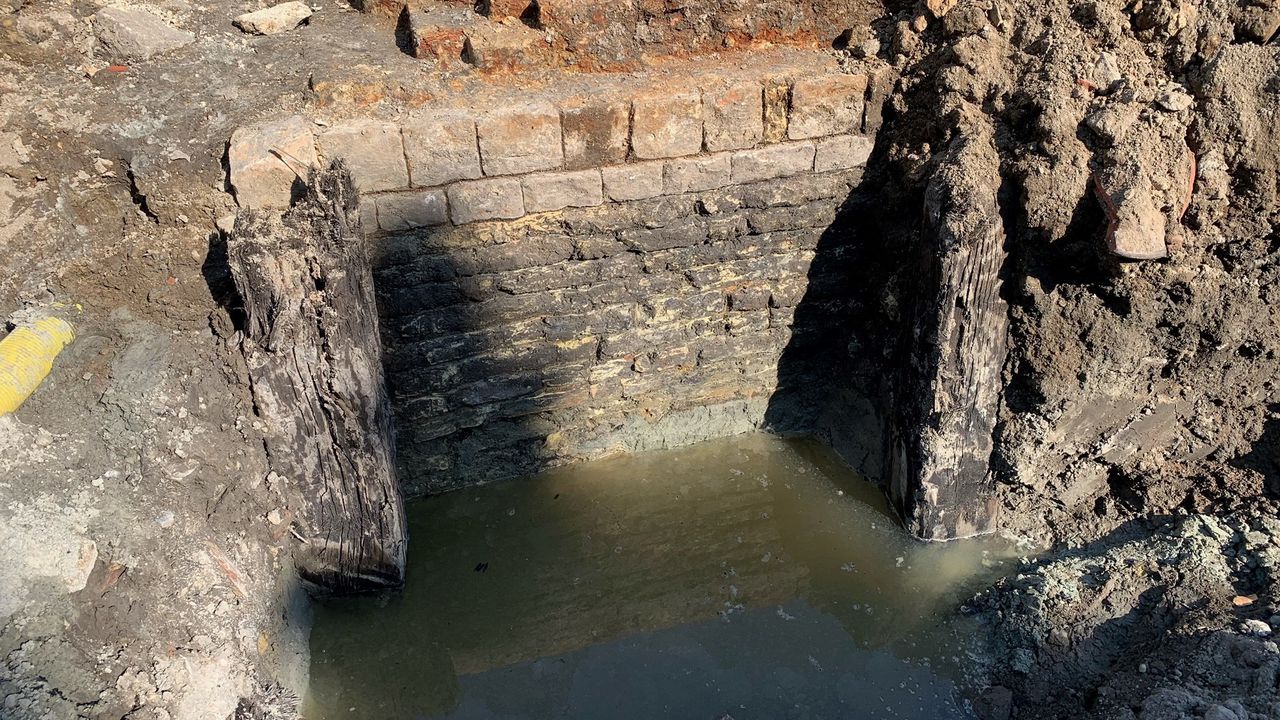
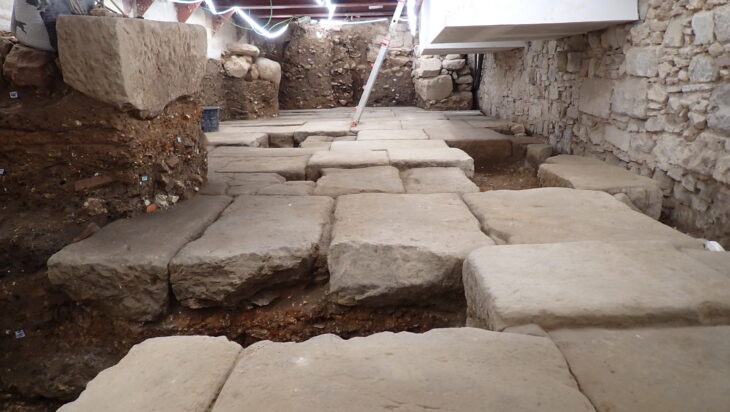
Excavations at Leper (Ypres), located in the West Flanders province of Belgium, have uncovered a 16th-century quayside. The find was made in a place where the old river Ieperlee flows.
Boats could go directly to the Grote Markt via this river to trade. The River Ieperlee has meanwhile disappeared from the city center, but the excavations have revealed its former quayside and several mooring posts, all in good condition even after 375 years under the ground.
Water was important for a medieval town. Goods were shipped into the city center, right up to the cloth hall, and could also be transported out in the same way. However, when in the 17th century a new port was built parts of the Ieperlee river fell into disuse. It was partially filled in or covered over.
The Vandepeereboomplein, built on top of the old Ieperlee, is opening these days for Aquafin’s sewer works. Archaeologists hoped that the remains of the quay wall would be uncovered, and that hope came true. Wooden mooring posts that were used to prevent ships from hitting the quay wall have also come to light.
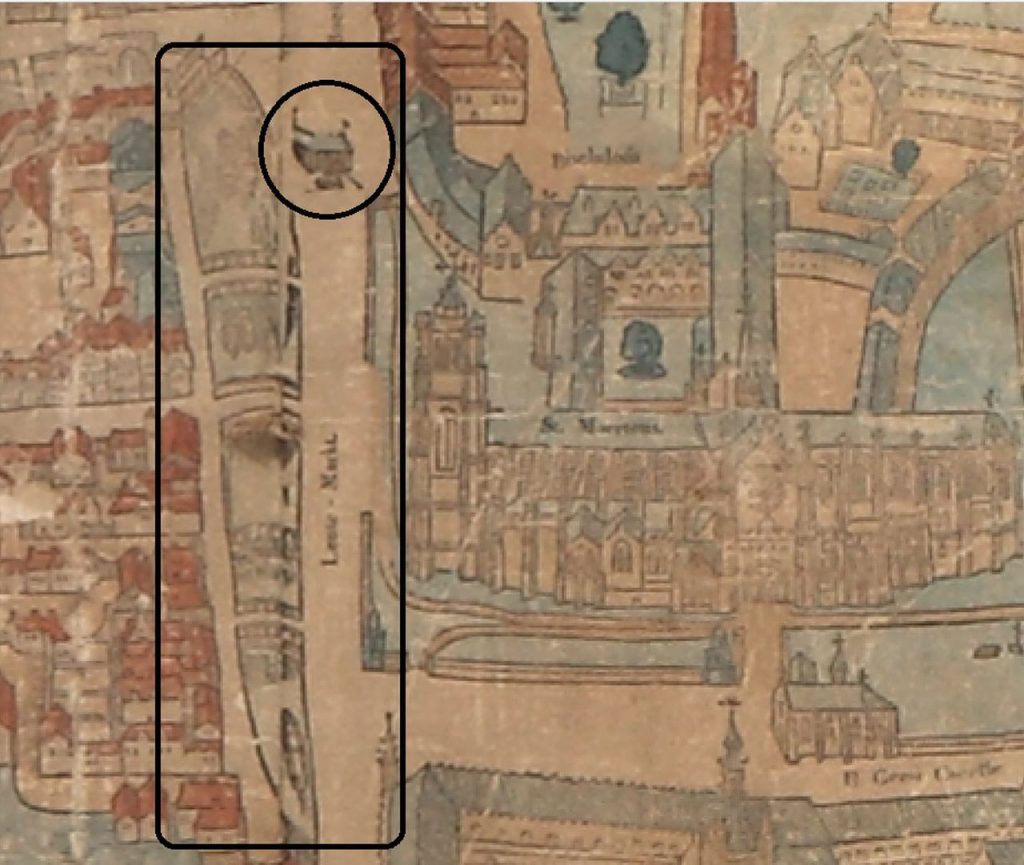
The dig yielded the foundations of a wooden crane used to load and unload ships too. The crane is familiar to historians as it is also pictured on medieval maps of the West Flemish city. Rings in the wood should allow scientists to establish a clear date for the crane.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
People in Ieper are pretty surprised an intact quayside probably stretching for 50 meters has been uncovered. Archaeologists had hoped that during the renovation of the square part of the quayside could still be preserved and remain visible e.g. under a sheet of glass. The Ieper city authorities are now examining what can be done as this wasn’t part of the original intention.
Archaeologists are taking loads of pictures that will allow the quayside to be reconstructed in 3D on computers. It remains to be seen whether the real quayside will be preserved for posterity.
Source: VRT
















