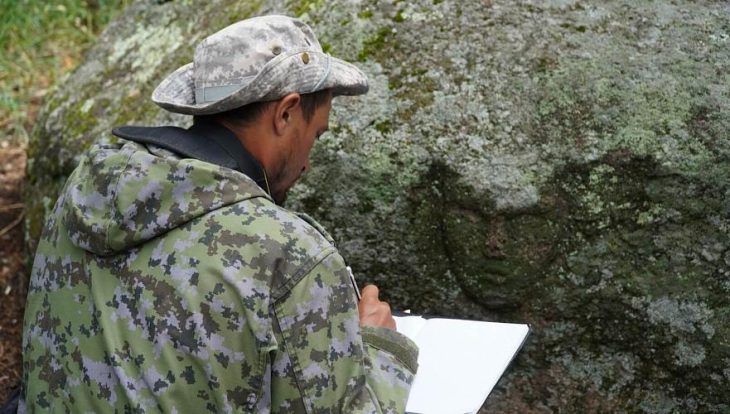
In the hills near the Andalusian town of Jódar, Spain, archaeologists have uncovered a monumental solstice sanctuary where the sun itself played a role in ancient Iberian rituals. The discovery, published in the journal Complutum, reveals a 2,500-year-old stone complex that may have served as a temple of the cosmos, designed to capture the drama of the winter solstice.
A Monument to the Sun
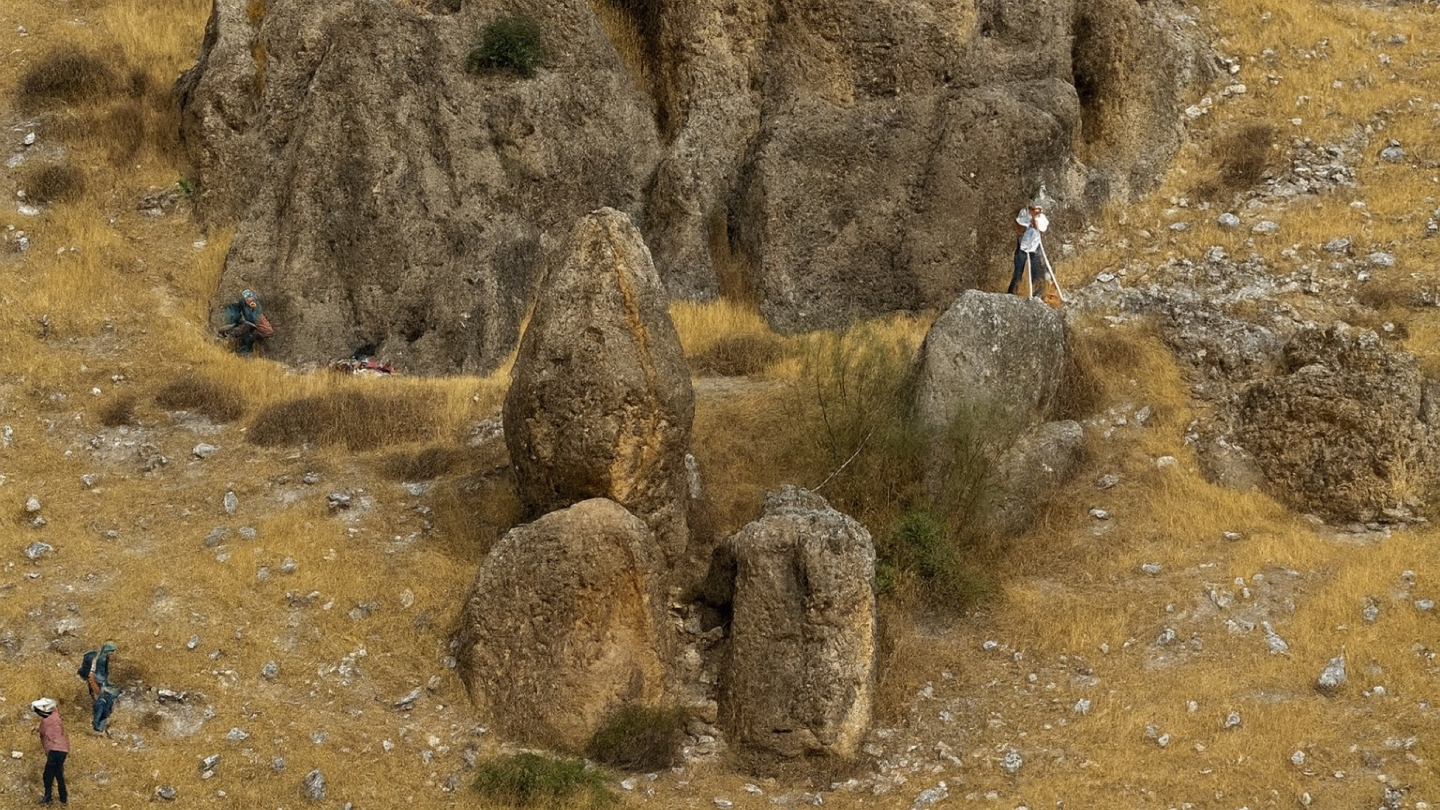
The centerpiece of the site, known as El Fontanar, is a towering monolith more than five meters high. Its elongated, upright form faces the point where the sun rises on the shortest day of the year. At dawn on the winter solstice, a ray of sunlight pierces the tip of the stone and projects toward a nearby rock shelter.
This shelter, nearly seven meters tall, has a V-shaped entrance that archaeologists interpret as a powerful symbol of femininity. A massive boulder above the opening resembles fallopian tubes, while the lower stones mark the contours of female anatomy. At the moment of the solstice sunrise, the shadow of the “male” stone stretches across the ground and touches the lower recess of the shelter, where the rock surface evokes a vulva-like form.
Researchers describe the scene as a deliberate recreation of hierogamy—a sacred union between male and female forces. It represents not only a cosmic marriage but also a mythic ritual of fertility and rebirth, connecting the solar hero to a goddess of the earth.
Linking Myth and Stone
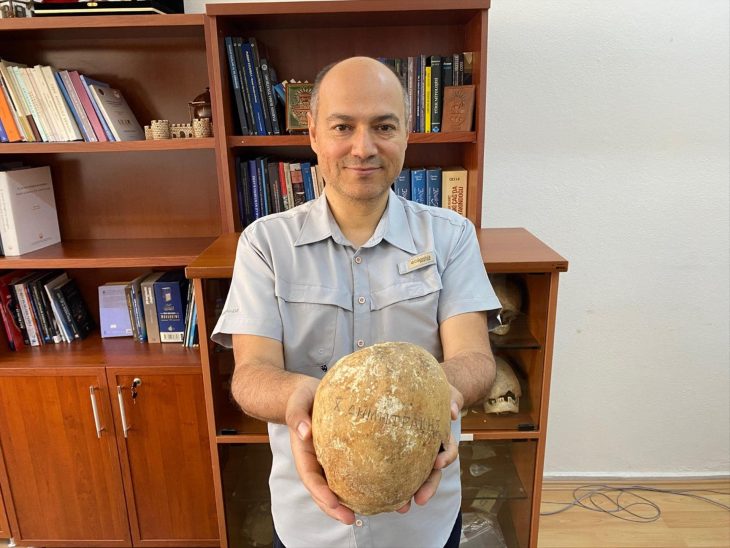
Lead archaeologist Arturo Ruiz explains that such imagery echoes religious traditions across the Mediterranean, from Egypt to Greece. Yet in Iberian culture, these were not abstract symbols. They were carved into the landscape itself, timed with the movements of the sun and experienced through ritual.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The sanctuary’s construction is dated to the 5th–4th centuries BCE, predating many of the region’s major Iberian settlements. This suggests that the site was a focal point of religious life long before urban centers flourished.
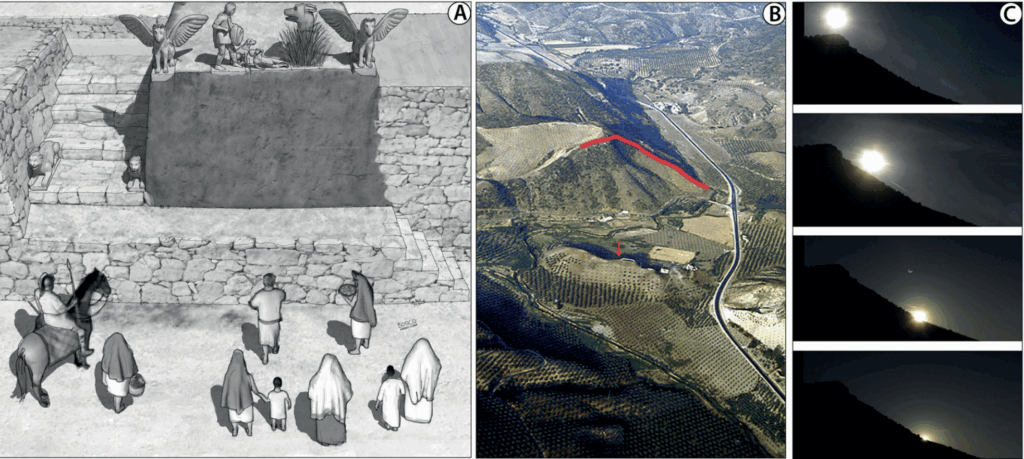
The Hero’s Journey and the Goddess
The discovery ties into broader Iberian mythology centered on Iltiraka (ancient Úbeda la Vieja) and Puente Tablas. In these traditions, a solar deity or hero descends into the underworld in autumn, only to be reborn by the winter solstice. The alignment of El Fontanar’s stones appears to dramatize this myth: the death of light, the sacred union, and the promise of renewal.
“This monument is extraordinary for its scale and intention,” notes Ruiz. “It was designed to unite heaven and earth, to affirm the sacred connection between masculine and feminine principles.”
A Cosmic Theater
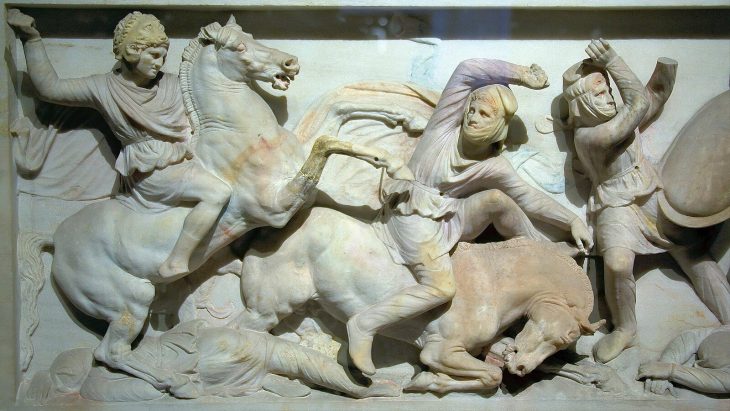
The findings also align with earlier studies at El Pajarillo, another Iberian site in the Jandulilla valley. There, sculpted scenes depict a hero battling a wolf, a symbolic passage to the underworld. Together, El Pajarillo and El Fontanar form a ritual landscape—a sacred path where myth, astronomy, and territory converge.
For the Iberians, the land itself became a stage for the hero’s journey. The cycle of descent, union, and resurrection was not merely told in stories but played out in the shifting light of the solstice sun.
Global Significance
The sanctuary of El Fontanar underscores how ancient peoples integrated astronomy, architecture, and spirituality. Across cultures, the solstice marked a turning point, a triumph of light over darkness. In Iberia, this moment was immortalized in stone, blending myth with cosmic reality.
For modern archaeology, the discovery highlights the sophistication of Iberian ritual and the depth of their symbolic connection to the natural world. More than a ruin, El Fontanar is a timeless reminder that humanity has always sought to bridge earth and sky, body and cosmos.
Ruiz, A., Molinos, M., Esteban, C., Yanes, M., & Lechuga, M. Á. (2025). Paisaje, camino y liturgia en el mito del héroe de Iltiraka. Complutum, 36(1), Estudios en Homenaje a Teresa Chapa Brunet. https://doi.org/10.5209/cmpl.102416
Cover Image Credit: Institute for Iberian Archaeology (IAI)
















