Researchers have presented their findings after discovering the remnants of an ancient Mayan city on a building site in Mexico. The site hosts an array of palaces and other buildings.
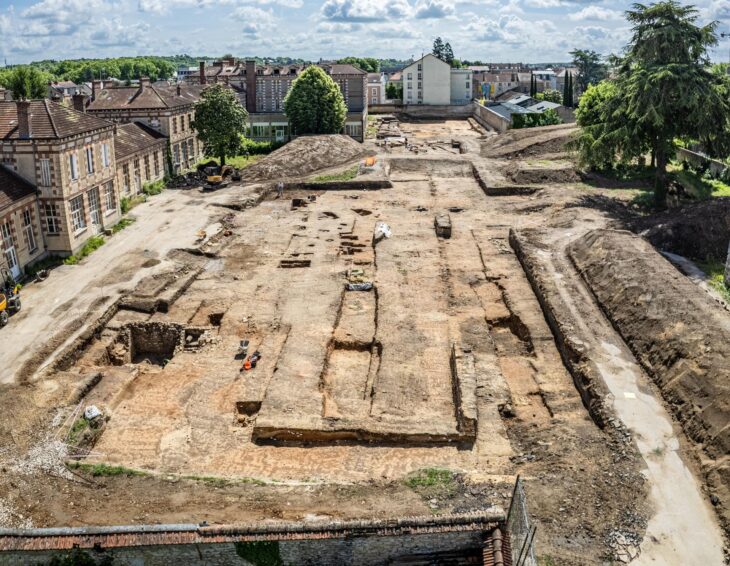
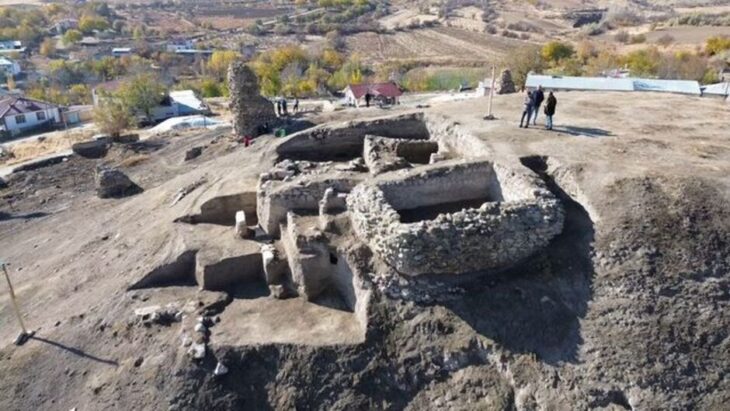
Archaeologists working in the Yucatan region of Mexico have revealed the remains of a 1500 years old Mayan city, local media reported on Friday.
The discovery was made by archaeologists from the Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia (INAH) near Merida in Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula.
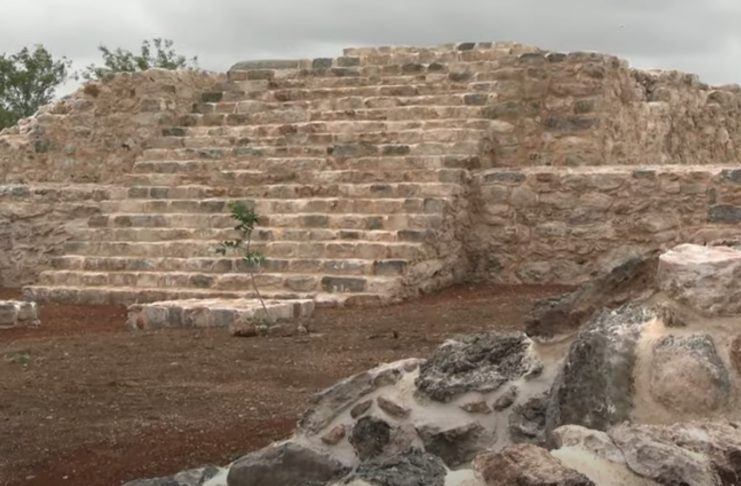
The city of Xiol — which means “the spirit of man” in Mayan — is believed to have been the home of some 4,000 people between 600 and 900 CE, during the late classic period. During the 9th century, many Maya polities collapsed, leading to the abandonment of cities, the ending of dynasties, and a northward shift in inactivity.
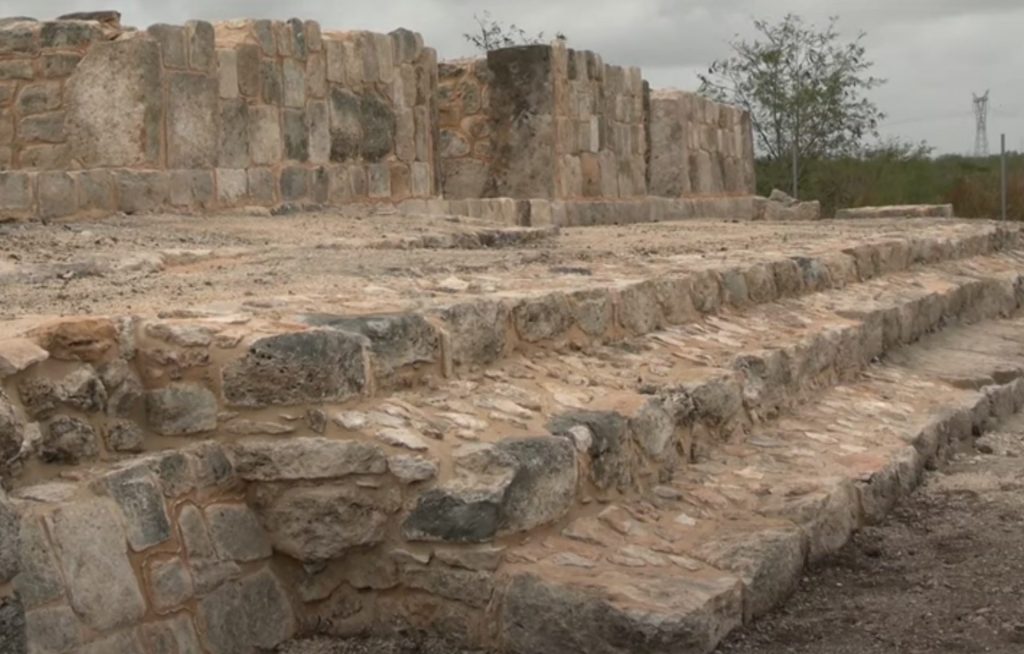

Archaeologists first found the site in 2015, but the results of the excavations and restoration work are only now being made public as the Sky Park industrial site nears completion.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The discovery of this Mayan city is important for its monumental architecture and because it has been restored despite being located on private land,” delegate for the INAH center in Yucatan, Arturo Chab Cardenas, told news agency EFE.
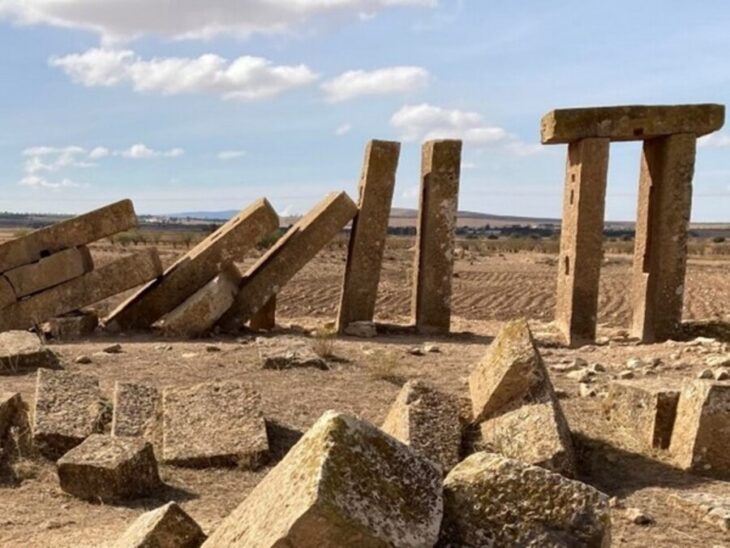
The site is of particular interest due to its Puuc style architecture — famously used for the Chichen Itza pyramid — which is more typically found in the southern part of the Yucatan region. The ceremonial complex consists of a platform and a small pyramid.
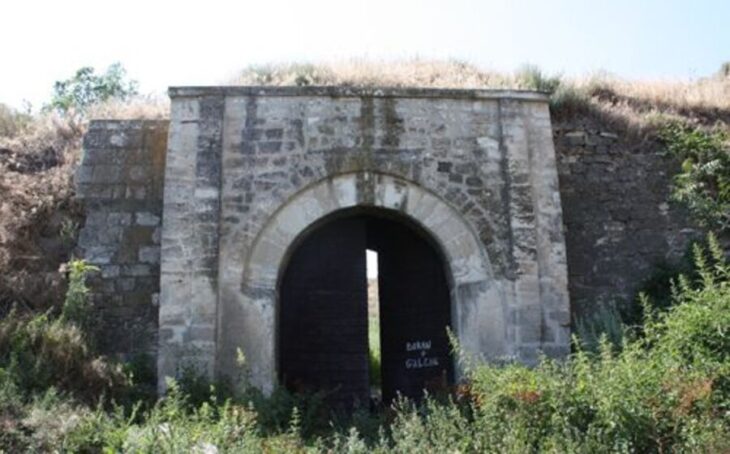
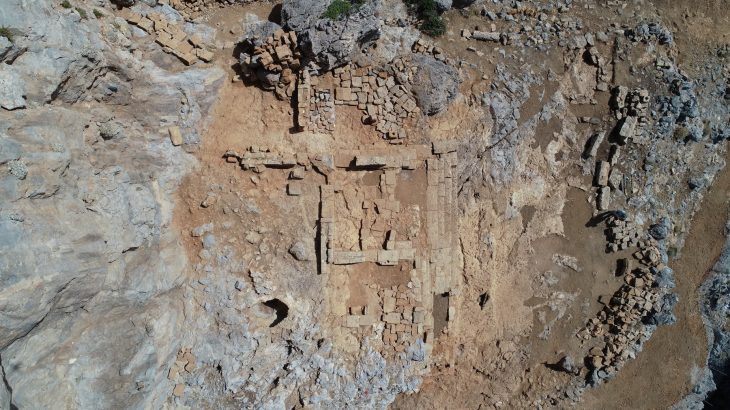
Researchers also uncovered palace ruins, plazas, elevated platforms, carved stone heads, and stone altars, as well as a cenote that was most likely utilized for ritual offerings to the Maya gods.
Alongside the finds, archaeologists highlighted evidence of the various social classes that lived here.
“There were people from different social classes … priests, scribes, who lived in these great palaces, and there were also the common people who lived in small buildings,” Carlos Peraza, one of the archaeologists leading the excavations, said.
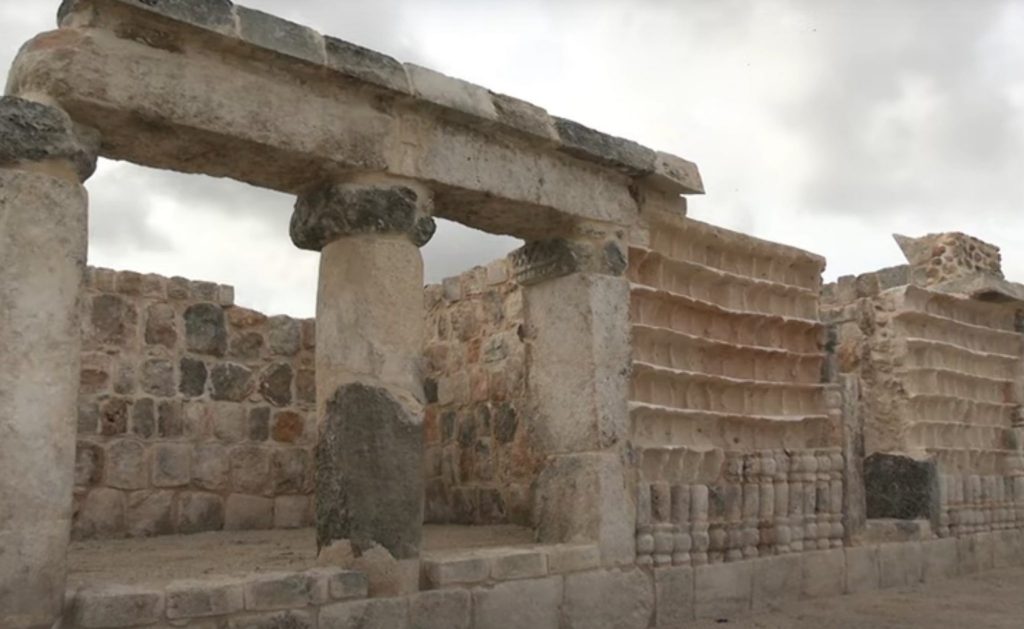

“With time, urban sprawl (in the area) has grown and many of the archaeological remains have been destroyed … but even we as archaeologists are surprised, because we did not expect to find a site so well preserved,” Peraza added.
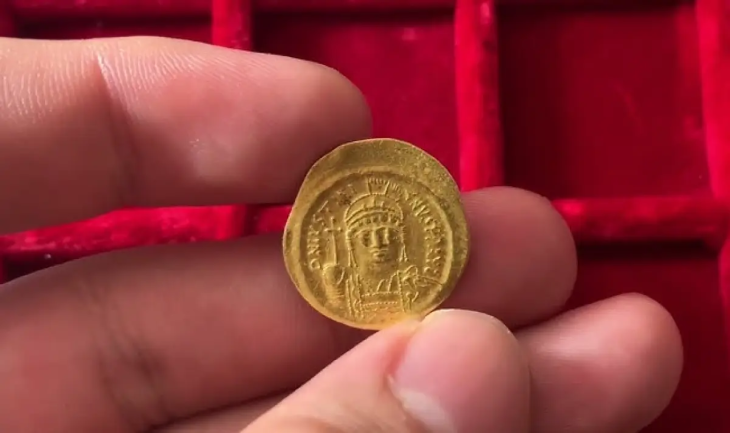
38 funerary deposits containing offerings of ceramics, jewelry, obsidian, and flint tools were exhumed by archaeologists, revealing new anthropological data on the inhabitants of Xiol and their burial customs. Remains of marine life suggest that the inhabitants complemented their agricultural-based diets by fishing.
The team has so far identified and restored 12 structures, with further evidence of wider archaeological remains in the surrounding fields and low-lying jungle.
Several tools and ceramics dating back as far as the pre-classic period (700-350 BCE) were also displayed by the researchers.
Cover Photo: INAH