An archaeological team from the Lyobaa project has confirmed the existence of a vast Zapotec underground complex in their study to explore the underground world of the Mitla archaeological site.
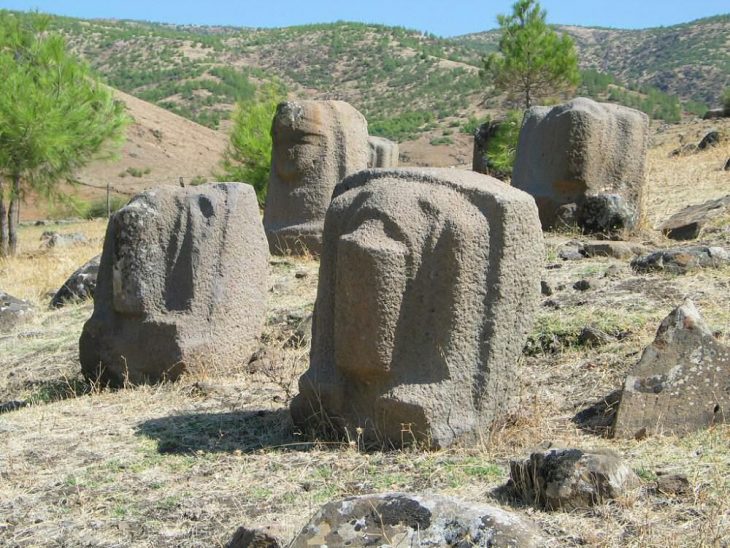
Mitla is an archaeological site associated with the Zapotec culture, located in the Oaxaca Valley in the present-day state of Oaxaca in southern Mexico. The Zapotec first inhabited it during the Classic Period (AD 100-650), having first developed from a fortified village into a large religious center.
The Zapotec believed that Mitla served as a gateway between the worlds of the living and the worlds of the dead for the burial of the Zapotec elite, hence the Nahuatl name Mictlán, which means “place of the dead” or “underworld.”
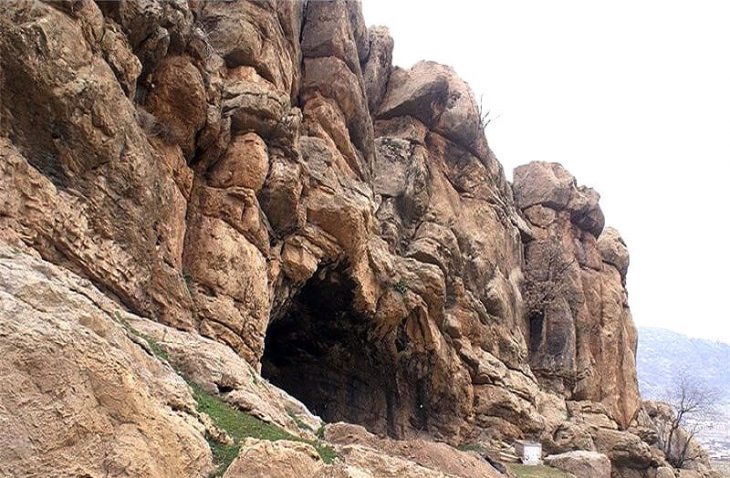
It has long been believed that the ancient Zapotec people constructed a massive and intricate labyrinth of chambers and passageways beneath monumental stone structures found at the Mitla archaeological site in the southern Mexican state of Oaxaca. The goal of this system of tunnels was to eventually lead to Lyobaa, the entrance to the Zapotecan underworld or Land of the Dead.
As part of a new study led by the Lyobaa Project with support from the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH), researchers launched an exploration project in Mitla in 2022.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
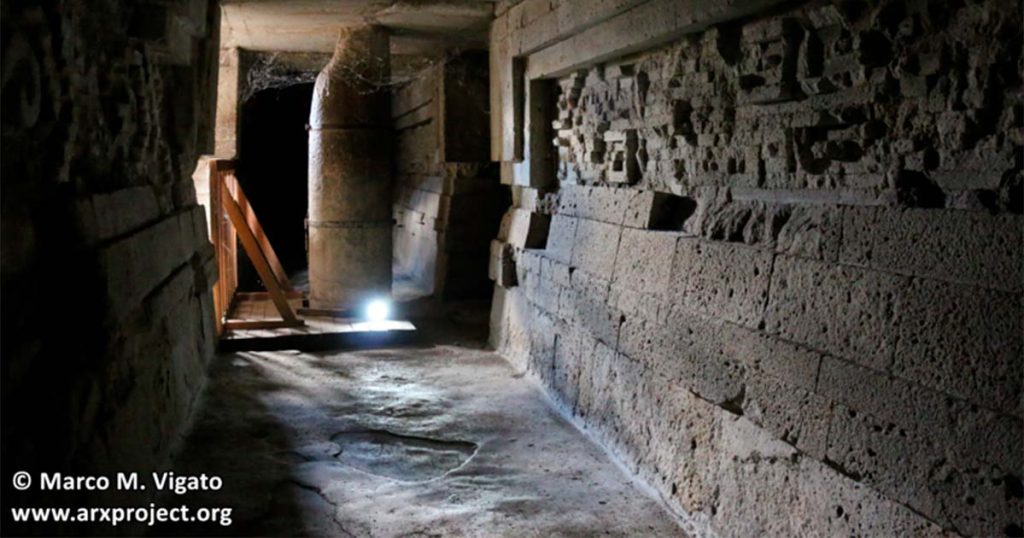

Their research has also revealed fascinating details about the various subterranean structures, revealing crucial information about a spiritual mecca built by and for the Zapotecan people who occupied southern Mexico during the pre-Columbian era.
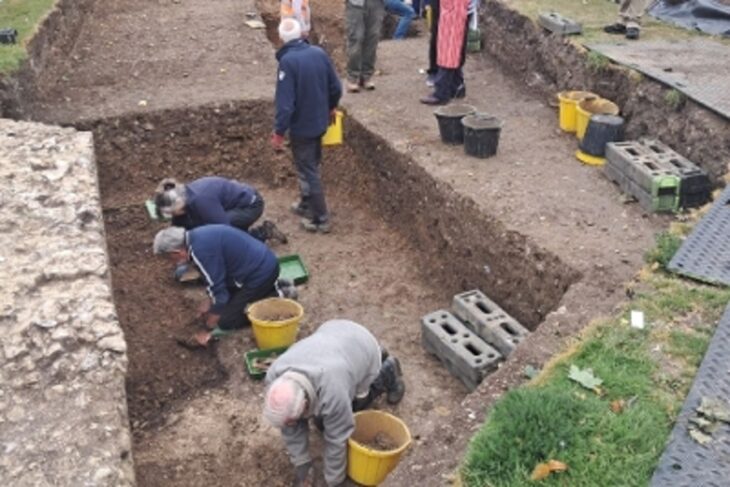
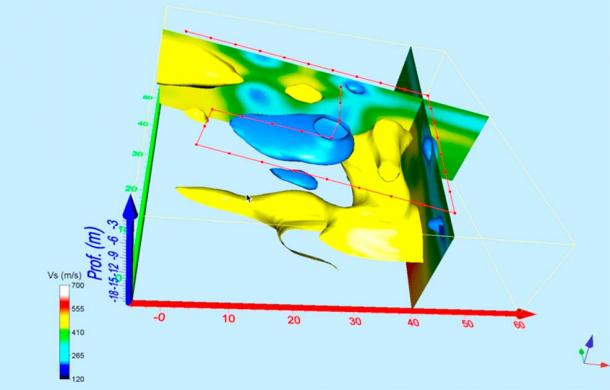
Researchers are using geophysical prospection techniques to confirm the existence of previously undetected underground chambers and passageways beneath Mitla.
The technologies deployed included Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR), Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT), and Seismic Noise Tomography, each of which uses electromagnetic emissions to penetrate the surface of the earth and generate images of what lies on the other side of that physical barrier.
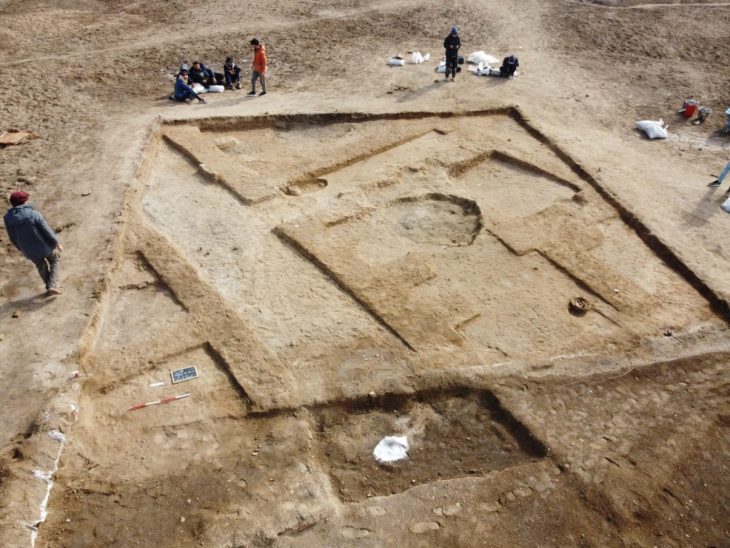
The researchers created composite 3D models of the subterranean world found just below the surface at Mitla by combining the results of their intensive scanning procedures.
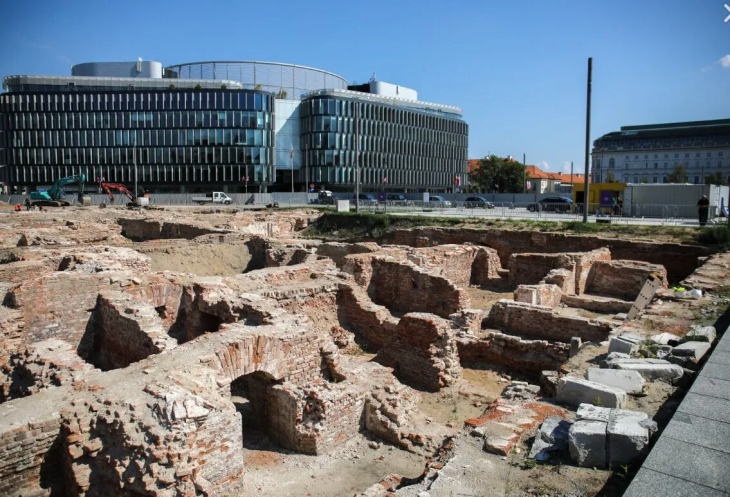
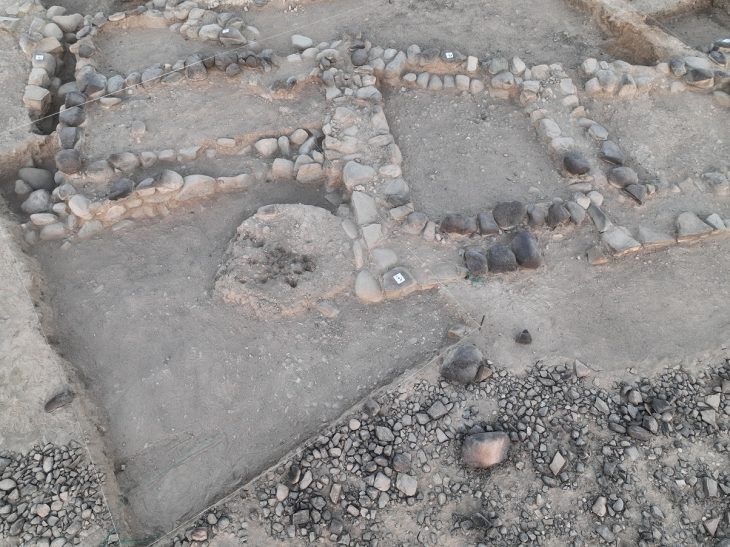
Most importantly, the geophysical survey findings unequivocally confirm the presence of multiple underground chambers and tunnels winding their way through the earth beneath a set of structures known as the Church Group (there are five sets of above-ground structures at Mitla, one of which features a Catholic church built in the late 16th century).
The surveys also looked into areas beneath the Palace of Columns, the site’s most elaborate building and a member of the so-called Columns Group of buildings. Here, the scans produced images that provided information on the building’s earliest stages of construction.
The researchers will continue to study the results of their initial explorations, looking for details that might have been missed during the first analysis.
Cover Photo: One of the 3D models of the spaces underneath Mitla. (©Marco M. Vigato / Arx Project )