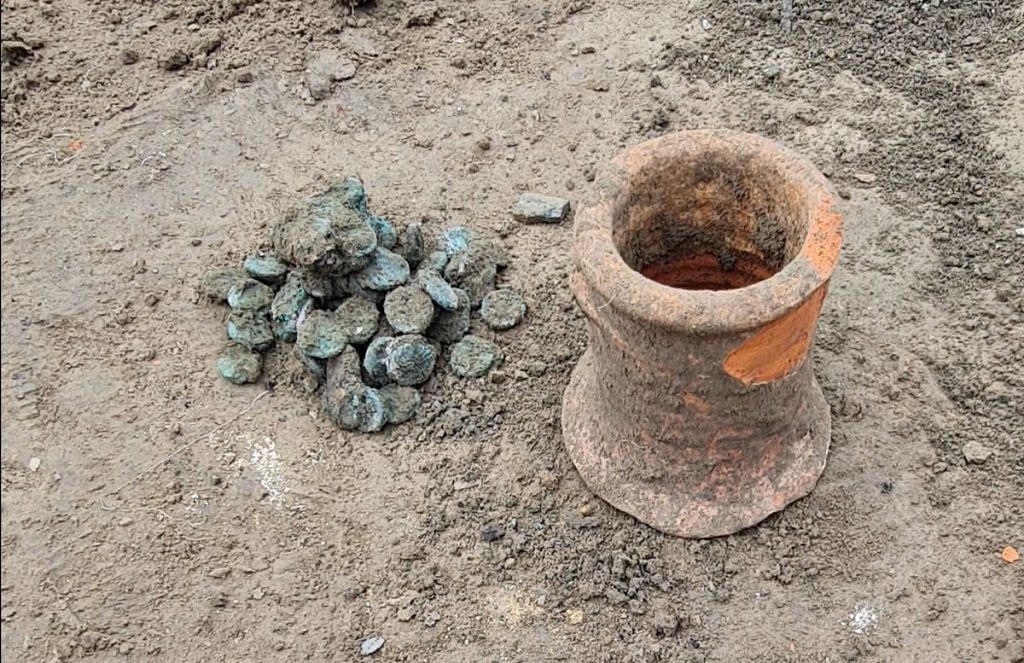
Archaeologists have discovered 80 coins known as Copper staters dating back to the sixth century at Phanagoria on the Black Sea coast.
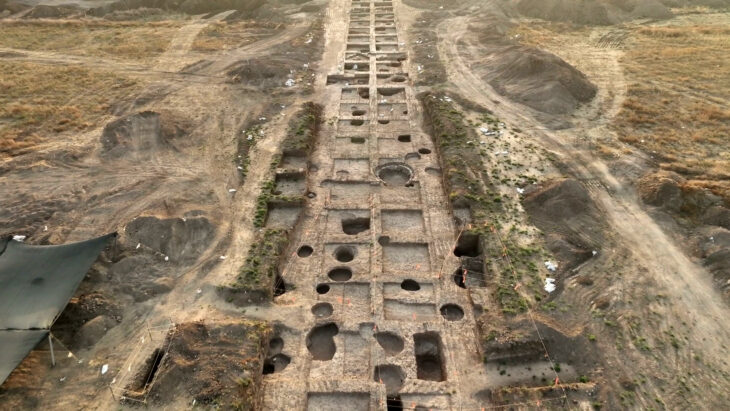
The discovery took place when Russian archaeologists found an amphora whilst researching evidence of a destruction layer caused by fire.
Phanagoria was built in 543 BC by Teian immigrants and grew into a Greek trading center between the Maeotian coast and the nations on the southern side of the Caucasus.
This was the third season of the Phanagoria expedition of the Institute of Archeology of the Russian Academy of Sciences. A gold coin of the Byzantine emperor Justinian I (527–565) was discovered in the stratum of fire in previous years. It allowed the date of the disaster to be determined: the second or third decades of the sixth century. A trove of copper coins from the 2021 season was discovered not distant from this discovery, in a layer of conflagration.
“Treasures are not often found,” explains Vladimir Kuznetsov, head of the Phanagoria archaeological expedition of the Institute of Archeology of the Russian Academy of Sciences. “As a rule, they are evidence of catastrophic events in people’s lives, as a result of which the one who hid money or valuable items was unable to return and use their savings,” told Medievalists.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Archaeologists think the burying of the treasure was linked to a series of Hun or Turk assaults that destroyed major sections of the city.
Residential buildings, wineries, public buildings perished in the fire, and a large amount of ash, soot, fragments of burnt wooden floors of buildings, broken dishes, and the remains of burnt grain in amphoras speak of a significant scale of the disaster. Finds include a broken marble countertop and a baptismal font, which bear witness to the destruction of an early Christian basilica nearby.
Researchers believe that these unique discoveries are related to the turbulent historical events in the Bosphorus Strait when the cities of the Bosphorus voluntarily became part of the Byzantine Empire in the 6th century. The transition from nomadic Huns to Byzantine rule in the Bosphorus Strait occurred during the reign of Emperor Justin I in 518-527. Perhaps it was mentioned for the first time in 519 that the Duomo of Fanagoria was related to this incident: Bishop John of Fanagoria signed the documents of the Patriarchal Synod of Constantinople, and the Diocese of Fanagoria Directly affiliated to the synod of bishops.
Vladimir Kuznetsov of the Russian Academy of Sciences said: “According to the composition of the treasure, one can determine what money was in use in the internal market of the Bosporus in the 6th century.”
A closer look at the coins indicates that they are mostly copper staters of Bosporan rulers from the late third to early fourth centuries AD. The final minting of Bosporan coins occurred about AD 341, but a large number of staters made of inexpensive copper-lead alloy remained to circulate around the Bosporus for several decades, whilst the role of “expensive” money was played by Byzantine gold.
Top Image: Photo courtesy Institute of Archeology of the Russian Academy of Sciences