A team from Newcastle University and the University of Exeter have uncovered evidence that a house in England is the site of a lost residence of Harold, the last Anglo-Saxon King of England.
Harold Godwinson, also known as Harold II, was the last Anglo-Saxon King of England, reigning from January to October 1066. Harold became Earl of Wessex and played a significant role in defending England against Viking invasions. His claim to the throne was contested by William, Duke of Normandy, and Harald Hardrada, King of Norway. Harold famously defeated Hardrada at the Battle of Stamford Bridge in September 1066 but was subsequently defeated by William at the Battle of Hastings on October 14, 1066. His death marked the end of Anglo-Saxon rule in England and the beginning of Norman dominance.
The team has reinterpreted previous excavations and conducted new surveys, leading them to believe they have identified a power center associated with Harold Godwinson, who met his demise at the Battle of Hastings in 1066.
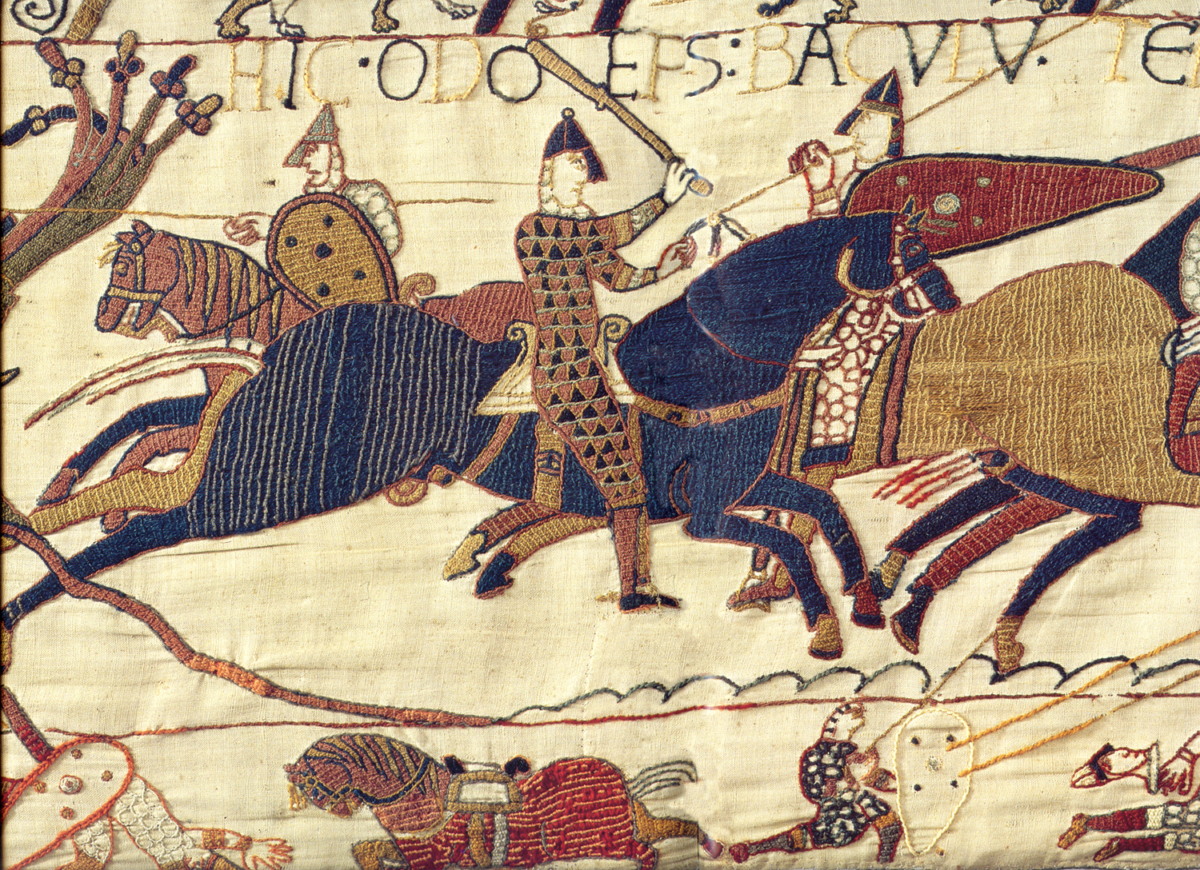
The coastal village of Bosham in West Sussex is prominently featured in the Bayeux Tapestry, which chronicles the Norman Conquest of England. Bosham is depicted twice in the Bayeux Tapestry. The Tapestry illustrates Harold’s feasting in an opulent hall at Bosham before his fateful journey to France, as well as his return, ultimately culminating in William, Duke of Normandy’s victory at Hastings.

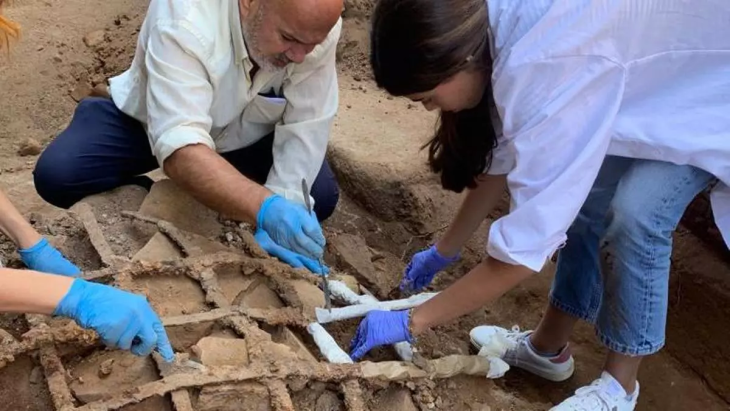
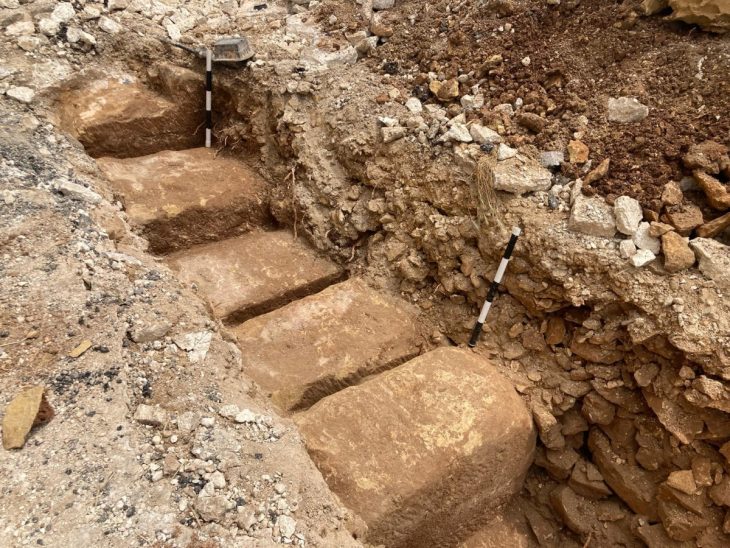
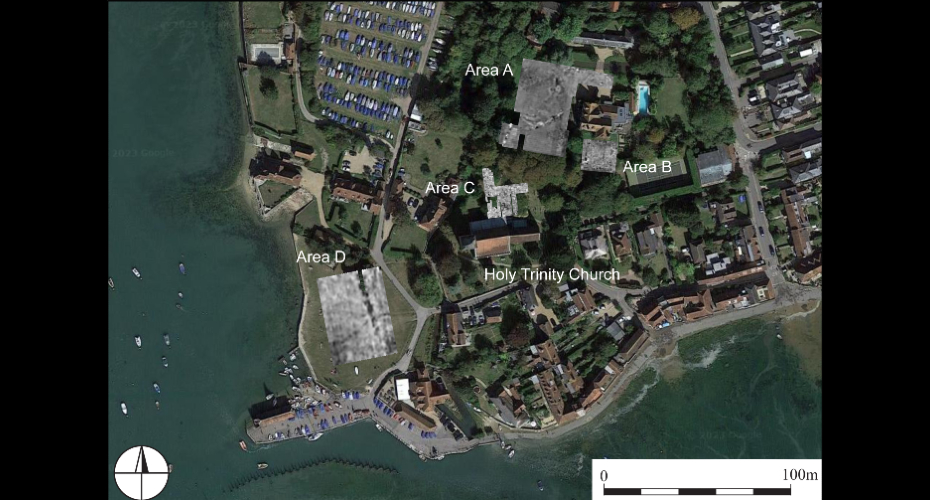
While the exact location of Harold’s residence in Bosham has remained unverified, it has been suggested that a manor house in the village—now a private residence—sits on the historical site. The archaeological team employed various methods to investigate the manor’s early history, including geophysical surveys, assessments of existing structures, and a thorough review of maps and records, alongside a re-examination of evidence from excavations conducted in 2006 by West Sussex Archaeology.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
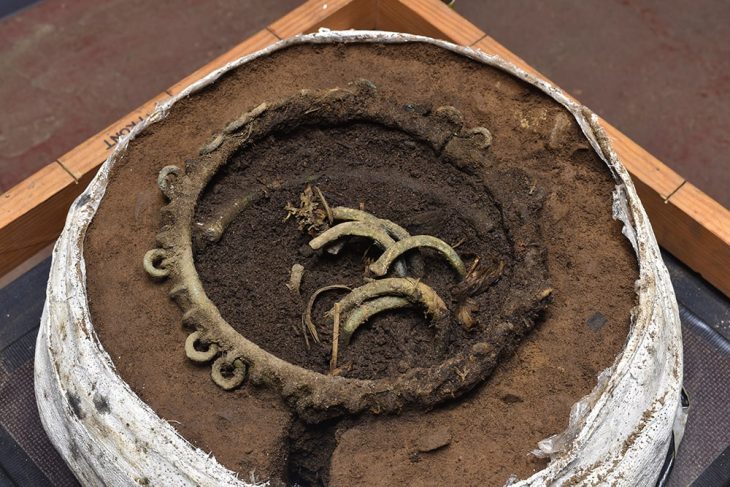
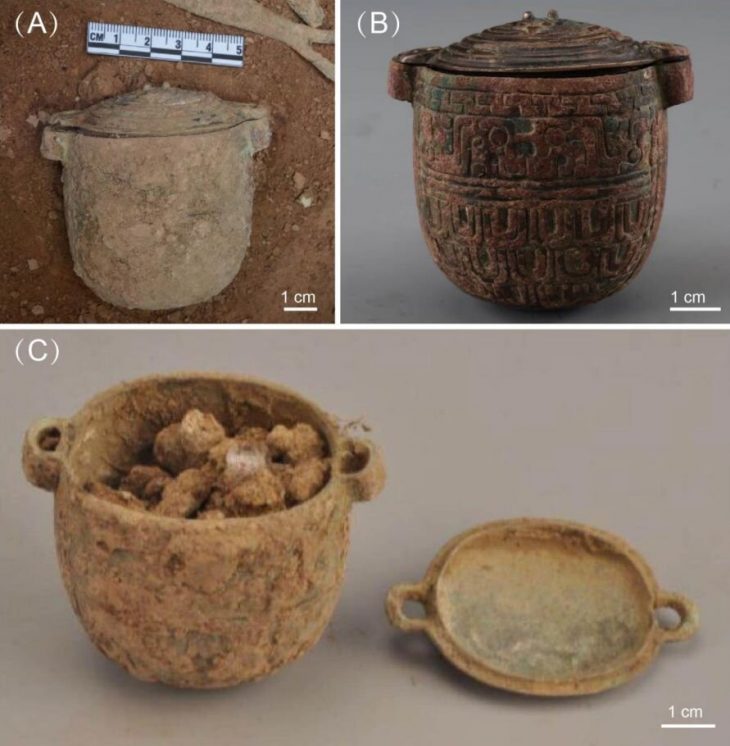
Their efforts confirmed the existence of two previously unidentified medieval buildings: one incorporated into the current house and another located in the garden. Notably, excavations from 2006 uncovered a latrine within a large timber structure, indicating the site’s elite status. This aligns with a trend observed over the past decade, where high-status houses in England began integrating toilets during the 10th century AD. The presence of the latrine suggests that the timber building was part of Harold’s residence depicted in the Tapestry, which was part of a larger complex that included a surviving church.
The findings, published in The Antiquaries Journal, were led by Dr. Duncan Wright, Senior Lecturer in Medieval Archaeology at Newcastle University. He stated, “The discovery of an Anglo-Saxon en-suite in the 2006 excavations confirms that this house is situated on the site of an elite residence predating the Norman Conquest. Considering this crucial evidence alongside other findings, it is beyond reasonable doubt that we have located Harold Godwinson’s private power center, famously illustrated in the Bayeux Tapestry.”
Professor Oliver Creighton, Co-Investigator from Exeter’s Department of Archaeology and History, emphasized the significance of the discovery, noting, “The Norman Conquest replaced the English aristocracy with a new ruling class that left few physical remnants. Thus, the findings at Bosham are immensely important—we have uncovered an Anglo-Saxon show-home.”
This research at Bosham is part of the broader Where Power Lies project, involving teams from Newcastle and Exeter, and funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council. The project aims to investigate the origins and early development of aristocratic centers like Bosham, providing a comprehensive assessment of the archaeological evidence for these sites across England.
Cover Image Credit: Public Domain
















