Researchers have suggested compelling evidence that Anglo-Saxon warriors from late sixth-century Britain participated in Byzantine military campaigns in the eastern Mediterranean and northern Syria.
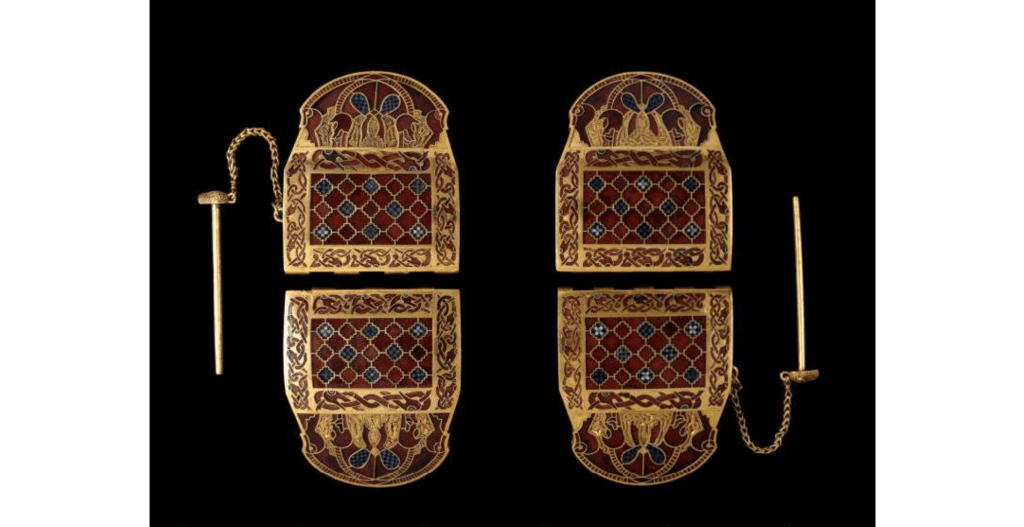
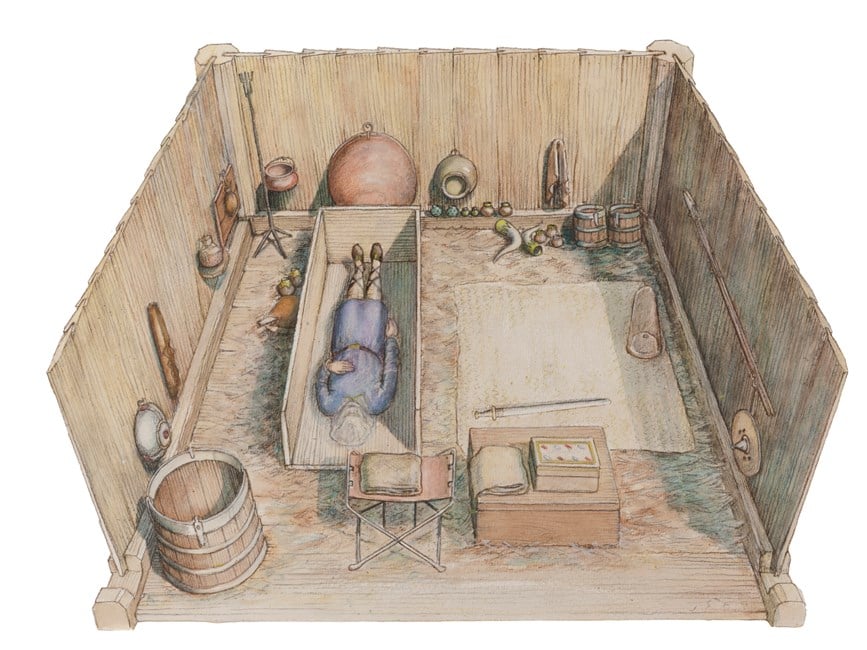
The findings, supported by artifacts from prominent Anglo-Saxon burial sites (Sutton Hoo, Taplow, and Prittlewell, among other sites), suggest a previously unrecognized international dimension to their history.
Dr. St John Simpson, a senior curator at the British Museum, said there was compelling evidence that Anglo-Saxon princes also fought for the Byzantine Empire in the eastern Mediterranean against the Iranian Sassanids, due to items found at burial sites in Sutton Hoo, Taplow, and Prittlewell in England.
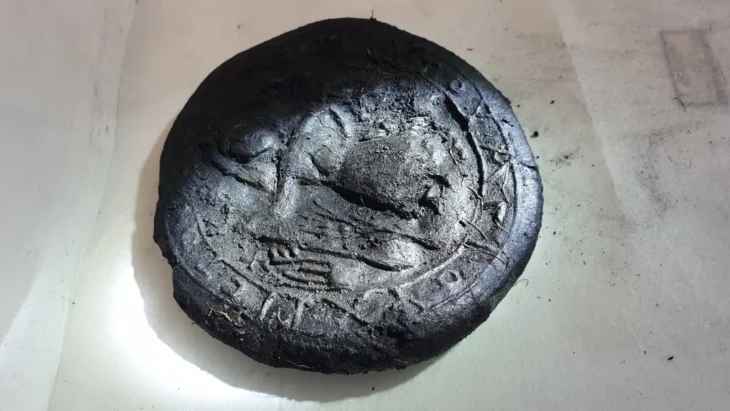
“The pearl roundel on the Prittlewell flagon is unique and puts its iconography firmly within a Sasanian design language, suggesting that it was made farther east, in a Sasanian workshop,” Simpson said, according to The Guardian.
Dr. Simpson has worked closely with Oxford University medieval historian Helen Gittos to carefully examine the unusual objects unearthed at Sutton Hoo, Taplow, and Prittlewell. They have come to the conclusion that the eastern Mediterranean and northern Syria are most likely the origins of these artifacts. These artifacts suggest that Anglo-Saxon warriors had been involved in Byzantine military campaigns against the Sasanian Empire, a powerful Iranian dynasty controlling vast territories.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Simpson said, according to The Guardian, “The eastern connections of the warrior tunics at Prittlewell and Taplow, coupled with the design of the shoulder clasps from Sutton Hoo, strengthen the idea that these individuals returned from Syria aligned even more closely with the late antique fashions of Byzantine-Sasanian elite warrior society.”

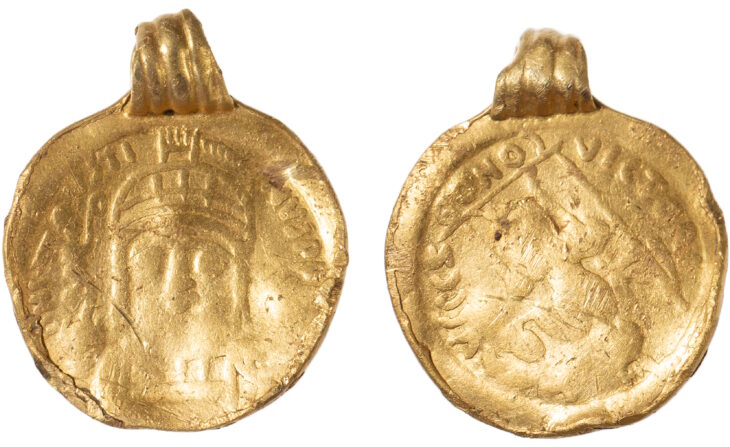
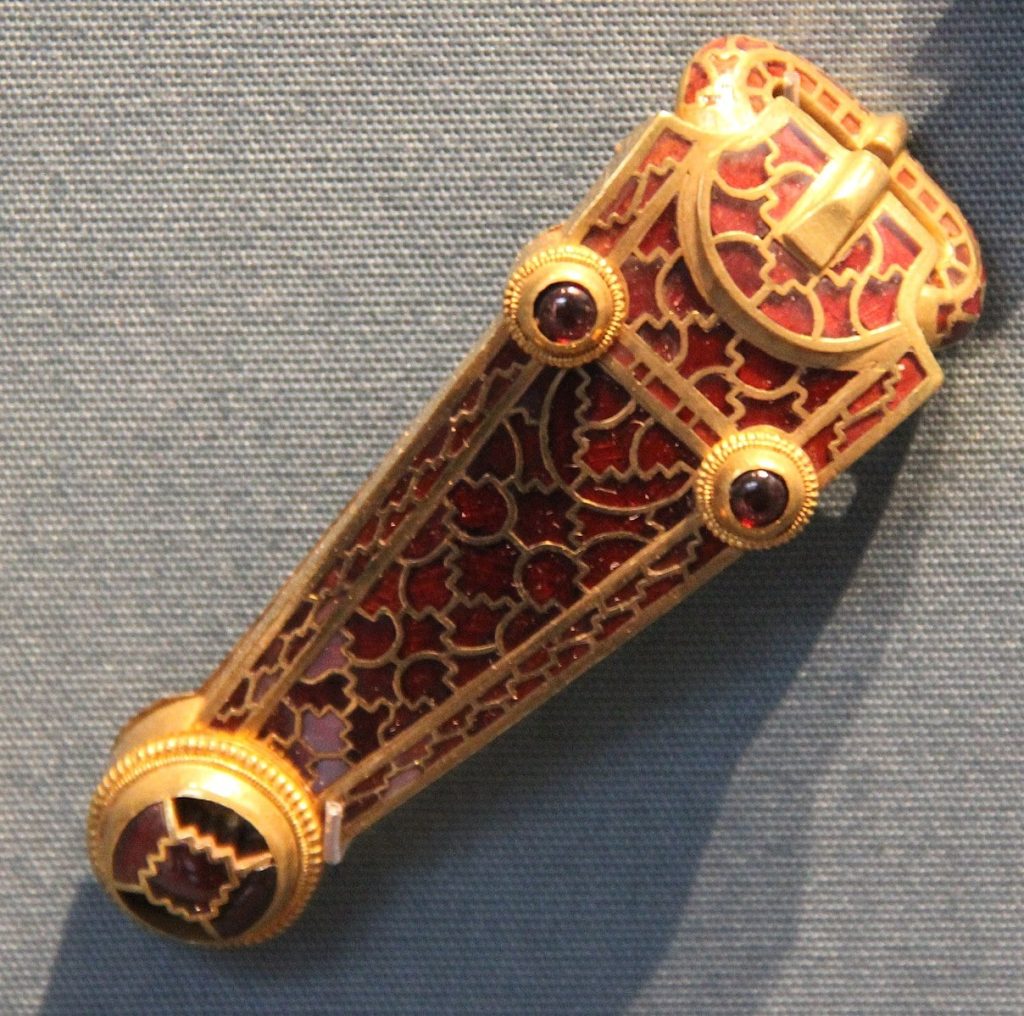
Archaeologists have uncovered the remains of a man at Taplow in Buckinghamshire who was dressed in an unusual and distinctive Eurasian-style riding jacket. In the meantime, a copper flagon bearing a unique pearl roundel picturing St. Sergius in a Sasanian-style roundel was discovered in the Prittlewell burial chamber in Essex. This iconography suggests that the flagon was made in a Sasanian workshop and firmly situates it within a Sasanian design language.
After centuries of Roman rule, the early Anglo-Saxon period of English history was generally seen as a violent, insular, and relatively backward time.
Simpson said that the number of items found at the burial sites, including the armor of Eurasian design, flies in the face of the “simplistic” view that non-local goods found on the isles arrived via trade and could help us rethink life in Anglo-Saxon England.
“These finds put the Anglo-Saxon princes and their followers center-stage in one of the last great wars of late antiquity. It takes them out of insular England into the plains of Syria and Iraq in a world of conflict and competition between the Byzantines and the Sasanians and gave those Anglo-Saxons literally a taste for something much more global than they probably could have imagined,” Simpson said.

The discovery of bitumen lumps at Sutton Hoo, which were previously thought to be related to the ship’s caulking, was another fascinating discovery. However scientific examination has revealed that these bitumen lumps came from a particular source in northeastern Syria. The Sasanians believed bitumen had therapeutic benefits and used it to line their ceramic vessels.
Simpson suggested, “I think that’s another item that’s been brought back with perceived or real curative power by superstitious warriors who’ve possibly even converted to Christianity on effectively Byzantine crusades against the Sasanians.”
The evidence gathered by Simpson and Gittos points to Anglo-Saxon warriors serving under Byzantine emperors Tiberius II and Maurice, who recorded in his military handbook that “Britons” were skilled fighters in wooded areas.
The Byzantines, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, ruled a vast territory in southeastern Europe and northwestern Asia until their defeat by Muslim Arabs and later Ottoman armies.
This involvement likely stemmed from a combination of adventure and the prospect of pay, as the Byzantines were known to recruit mercenaries from across Western Europe to bolster their mobile armies. They frequently hired mercenaries from elsewhere in Europe to handle waves of attacks from Sassanid and other forces, with potentially rich rewards for foreign fighters.
Gittos, a fellow and tutor in medieval history at the University of Oxford, said: “This opens up a startlingly new view on to early medieval British history.” The discoveries suggest that the Anglo-Saxon elite were not only aware of but actively participated in the broader geopolitical and military conflicts of their time, far beyond the shores of Britain.
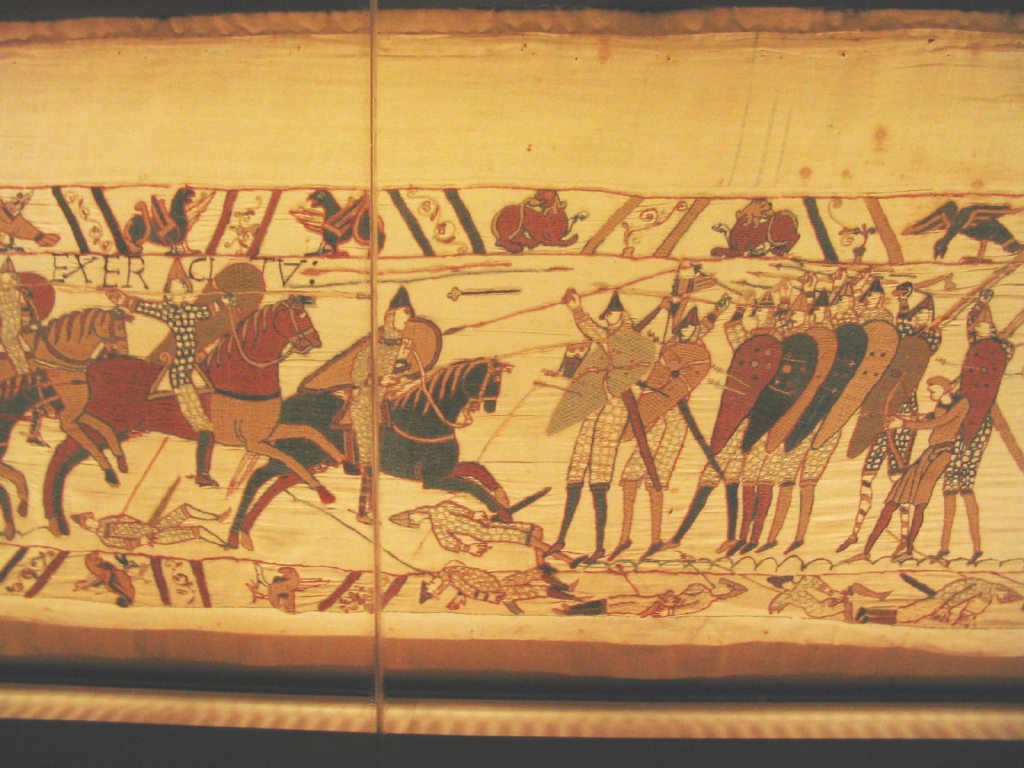
Cover Photo: Bayeux Tapestry. Anglo-Saxon shield wall against Norman cavalry in the Battle of Hastings. Photo: Gabriel Seah
















