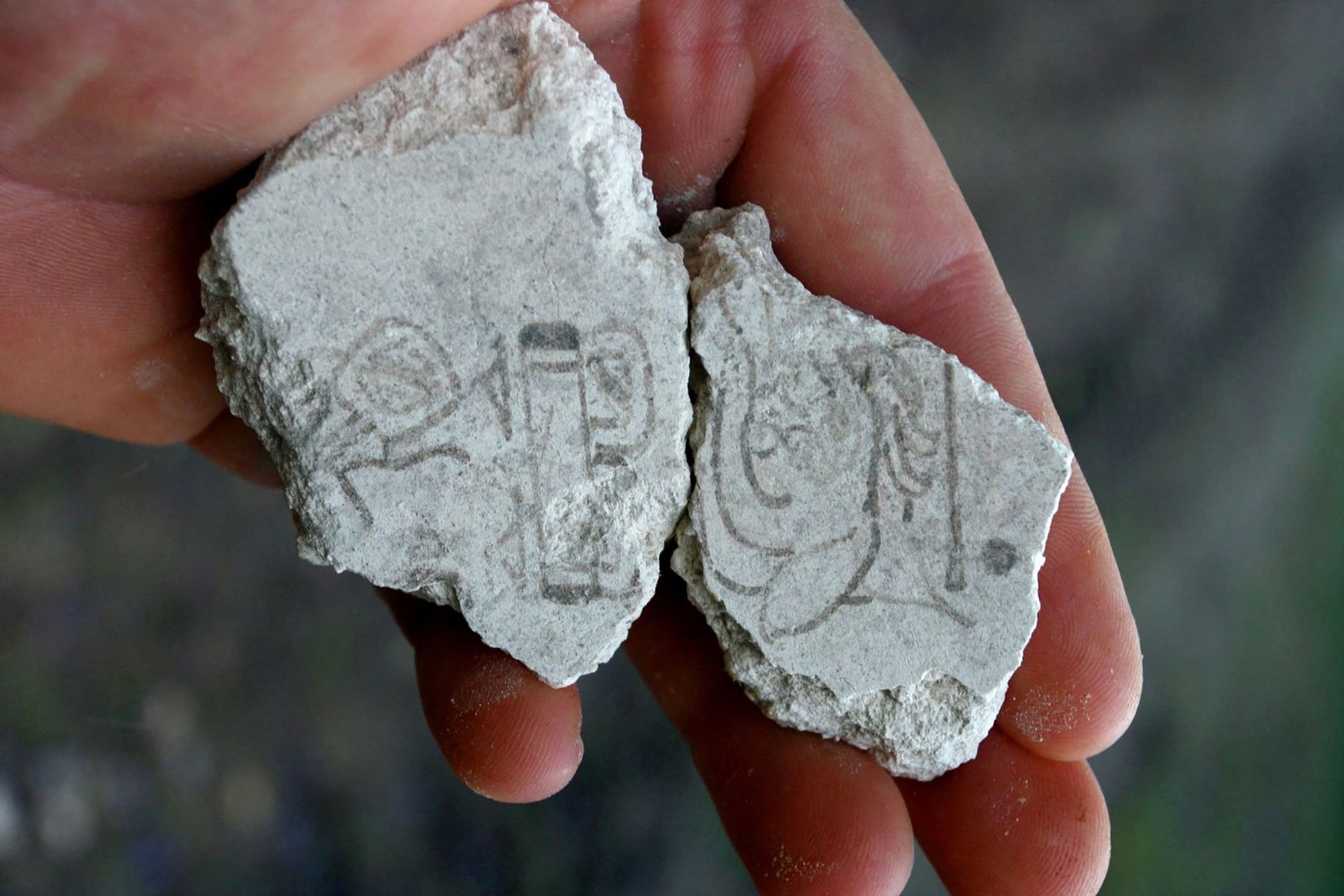
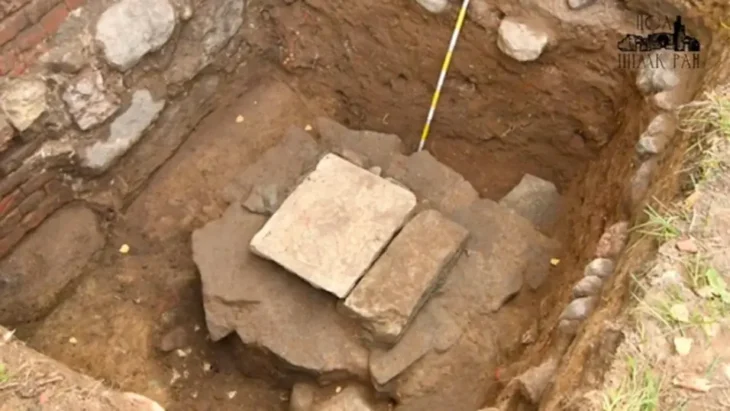
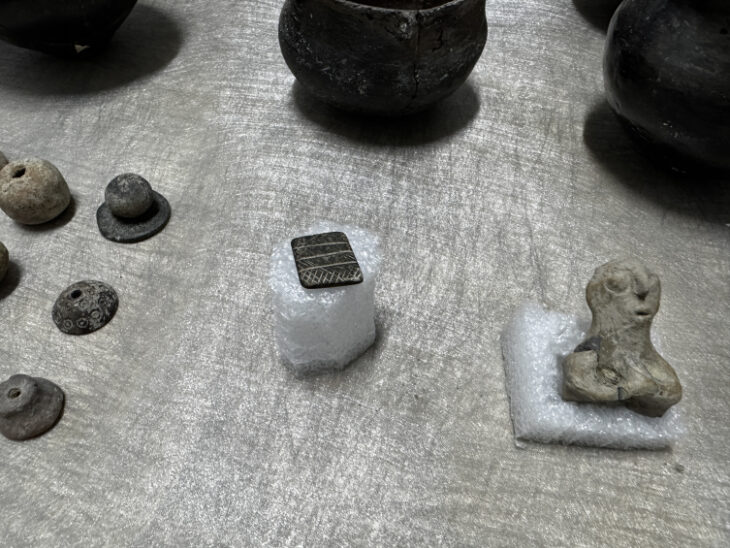
Archaeologists identified two plaster fragments depicting a date that the Maya civilization called ‘7 deer’ and was part of the 260-day calendar cycle.
The Maya calendar dates back further than previously recognized, a mural more than 2,220 years old reveals. The finding probably indicates other aspects of Maya culture also originated at least 150 years earlier than has been acknowledged.
The fragments were found at the San Bartolo archeological site in the jungles of northern Guatemala, which gained fame with the 2001 discovery of a buried chamber with elaborate and colorful murals dating to about 100 B.C. depicting Maya ceremonial and mythological scenes, researchers said on Wednesday.
Research has shown construction at the site began 2,300 to 2,200 years ago and that the pyramids at the site were built in multiple phases. The pieces with the “7 Deer” glyph were unearthed inside the same Las Pinturas pyramid where the still-intact later murals were located. As was the case with this structure, the Maya often built what initially were modest-sized temples, then constructed ever-larger versions atop the earlier ones. This pyramid eventually reached about 30 meters (100 feet) tall.
Dating of charcoal fragments—found in the same layer of debris as the wall fragments—showed them to be from approximately 300 and 200 BCE, making them the oldest known samples of a Maya sacred calendar.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The glyph found on the mural fragments for “7 Deer,” one of the calendar’s 260 named days, consisted of the ancient Maya writing for the number seven over the outline of a deer’s head.
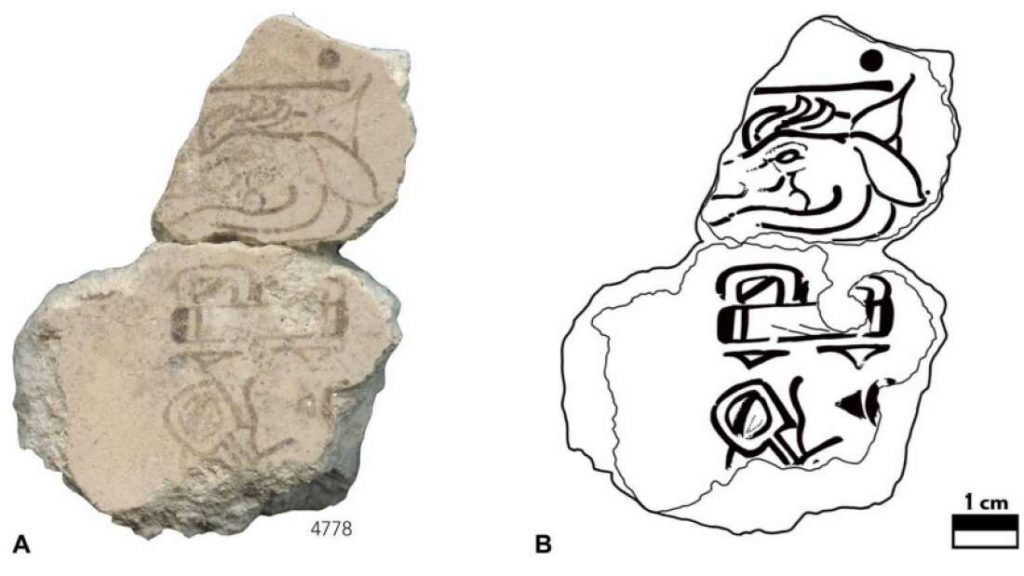
“The wall was intentionally destroyed by the ancient Maya when they were rebuilding their ceremonial spaces – it eventually grew into a pyramid. The two pieces fit together and have black painted calligraphy, opening with the date ‘7 Deer.’ The rest is hard to read,” Stuart added.
“The paintings from this phase are all badly fragmented, unlike any from the later, more famous chamber,” Stuart said.
Until now, the earliest definitive Maya calendar notation dated to the first century B.C.
The calendar, rooted upon observations of the movements of the sun, moon and planets, was based on a ritual cycle of 260 named days. The 260-day calendar, called the tzolk’in, was one of several inter-related Maya systems of reckoning time, also including a solar year of 365 days, a larger system called the “Long Count” and a lunar system.
The calendar was among the achievements of a culture that also developed a writing system encompassing 800 glyphs, with the earliest examples also from San Bartolo. The Maya built temples, pyramids, palaces and observatories and engaged in sophisticated farming without using metal tools or the wheel.
San Bartolo was a regional center during the Maya Preclassic period, spanning from about 400 B.C. to 250 A.D. This age set the foundation for the blossoming of Maya culture during the subsequent Classic period, known for cities including Tikal in Guatemala, Palenque in Mexico and Copan in Honduras.
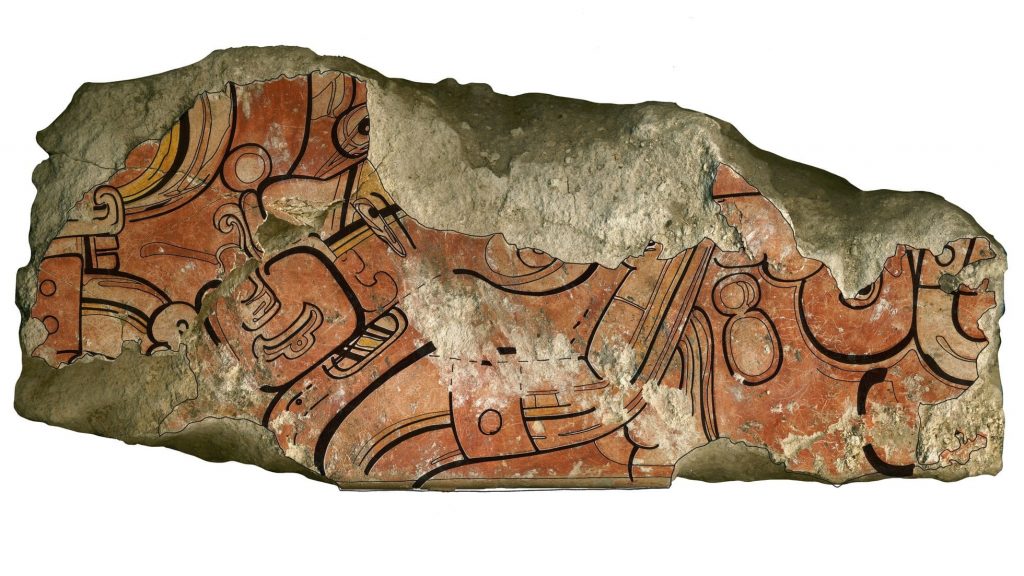

About 7,000 mural fragments – some as small as a fingernail and others up to 20-by-40 centimeters (8-by-16 inches) – have been found at San Bartolo, amounting to what anthropology professor and study co-author Heather Hurst of Skidmore College in New York state called “a giant jigsaw puzzle.”
The “7 Deer” and other notations seen on 11 San Bartolo mural fragments examined in the study hint at mature artistic and writing conventions in the region at the time, suggesting the calendar already had been in use for many years.
“Other sites will likely find other examples, perhaps even earlier examples,” Hurst said.
“Second, the scribal tradition represented in these 11 fragments is diverse, expressive, their technology for paint preparation and calligraphic fluidity is impressive – this was a well-established tradition of writing and art,” Hurst added.
Some Maya communities today still use the ancient calendar.
“This calendar system has lasted for at least 2,200 years, maintained by the Maya during times of incredible change, stress and tragedy,” Stuart said.
The article was published in the journal Science Advances.
Cover Photo: Archaeologists find the earliest Maya calendar in the Guatemalan pyramid. BY REUTERS
















