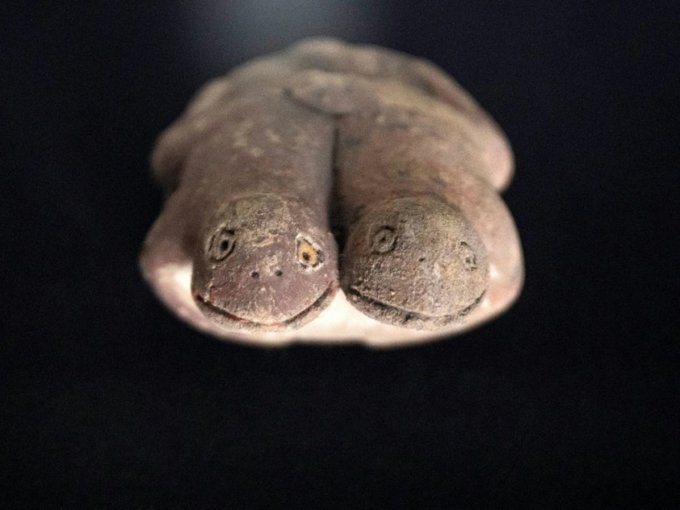
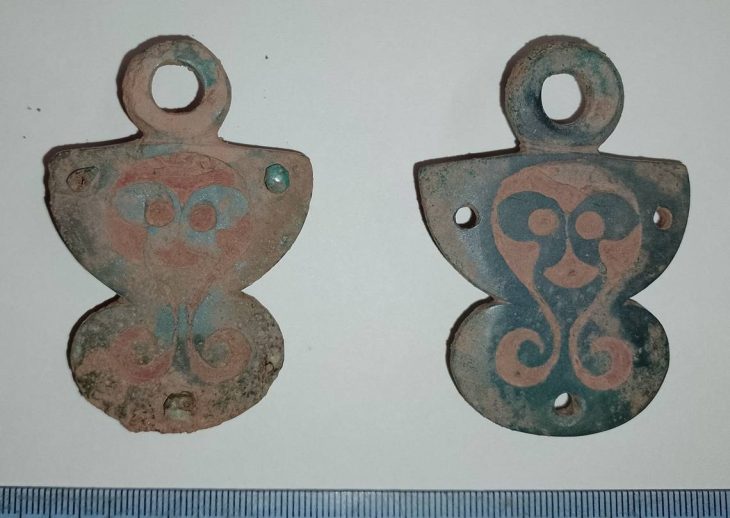
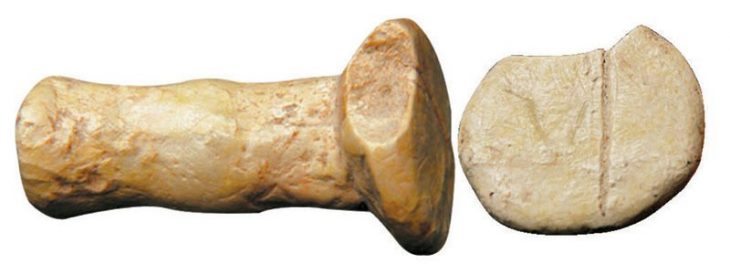
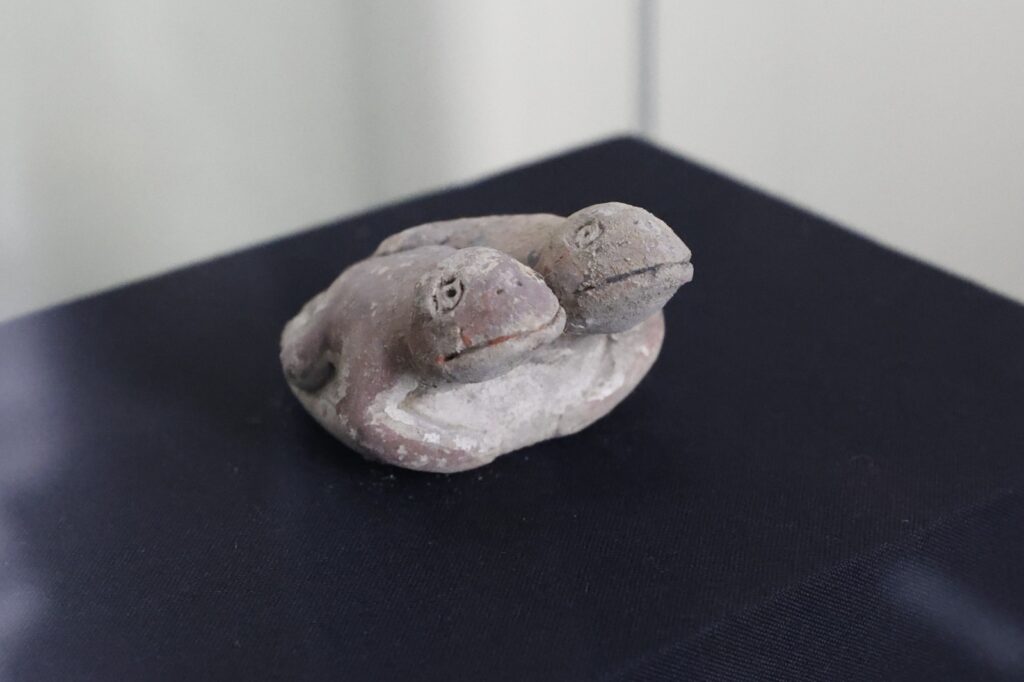
Archaeologists in Peru have announced a remarkable discovery: a 3,800-year-old Clay figurine depicting two frogs, unearthed at the Vichama archaeological site, part of the broader cultural sphere of the Caral civilization—the oldest known civilization in the Americas.
The finding was revealed by Peru’s Ministry of Culture and has drawn attention from researchers worldwide for its symbolic meaning and historical importance. Measuring about 12 centimeters in length, the clay figure represents two small frogs joined at their hind legs. According to experts, this is the first time a clay sculpture of this type has been discovered in Caral-related sites.
Symbolism of Frogs in Andean Culture
Tatiana Abad, lead archaeologist and director of excavations at Vichama, explained that frogs played a significant symbolic role in the Andean worldview.
“In the Andean cosmos, frogs are associated with water and rainfall, essential elements for agricultural cycles and survival in ancient societies,” she said during a press conference in Lima.
The sculpture’s imagery fits with other reliefs and carvings found at Vichama, which portray scenes of scarcity, fertility, and renewal. These artistic representations are believed to reflect the community’s response to environmental crises and climate change that the Caral civilization faced thousands of years ago.
Ruth Shady, director of the Caral Archaeological Zone and one of the most renowned researchers of this civilization, emphasized:
“This discovery reinforces the messages conveyed in the murals of Vichama. They narrate stories of shortages and hope in the face of climate shifts, demonstrating how ancient societies adapted to challenges that are still relevant today.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

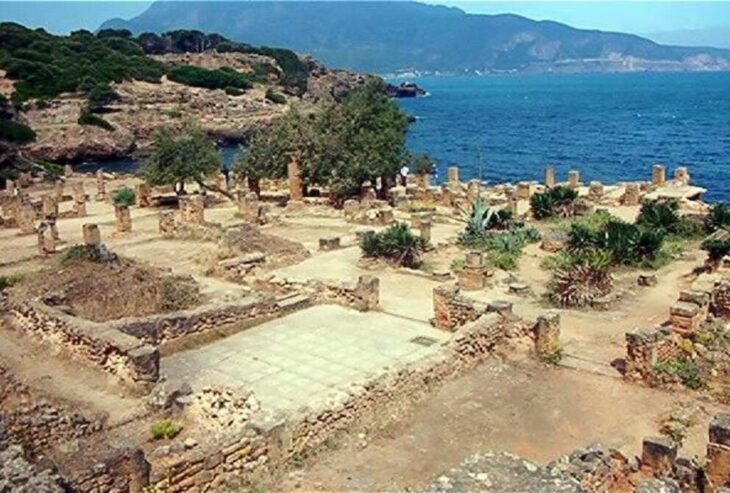
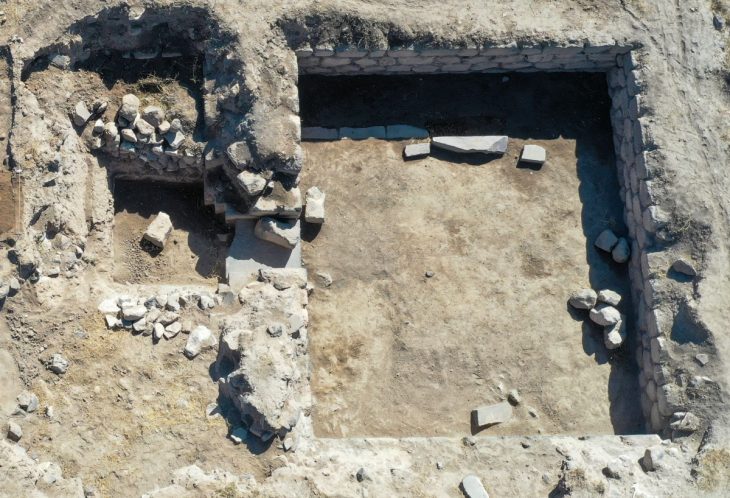
The Vichama Archaeological Site
Located about 110 kilometers north of Lima in the Huaura Valley, Vichama was an urban settlement that flourished during the later phases of the Caral civilization, around 1,800 BCE. Spread across 25 hectares, the site includes 28 major architectural structures, such as ceremonial plazas, public buildings, and residential areas.
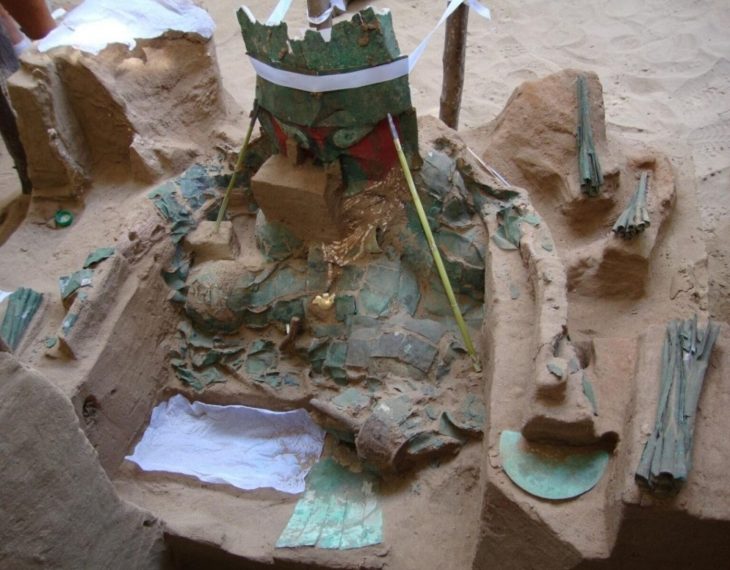
One of Vichama’s most striking features is its mud-brick relief murals, which depict human figures with emaciated bodies, pregnant women, and agricultural motifs—all interpreted as symbolic references to fertility, famine, and renewal. These reliefs, combined with the newly uncovered frog sculpture, provide a deeper understanding of how the people of Vichama connected spirituality, art, and survival strategies.
Excavations at Vichama began in 2007 and continue to reveal unique artifacts that distinguish the site from other Caral centers. Unlike the monumental stone pyramids of Caral itself, Vichama offers more insights into daily life and the symbolic world of its inhabitants.
Caral: The Oldest Civilization in the Americas
The Caral civilization, also known as Norte Chico, dates back nearly 5,000 years and is recognized as the earliest complex society in the Americas. Declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2009, Caral is often compared to the civilizations of Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley for its antiquity and achievements.
Caral society developed along the fertile valleys of Peru’s north-central coast, establishing around 30 major urban centers. Its largest city, the Sacred City of Caral-Supe, featured pyramids, circular plazas, amphitheaters, and residential complexes. Remarkably, Caral flourished without the use of ceramics or warfare—two characteristics often linked to early civilizations elsewhere. Instead, it relied heavily on agriculture, fishing, trade, and religious rituals.
The civilization’s sophisticated understanding of astronomy, architecture, and irrigation reflects a high degree of social organization. Its cultural legacy influenced later Andean societies, including the Chavín, Moche, and eventually the Inca Empire.
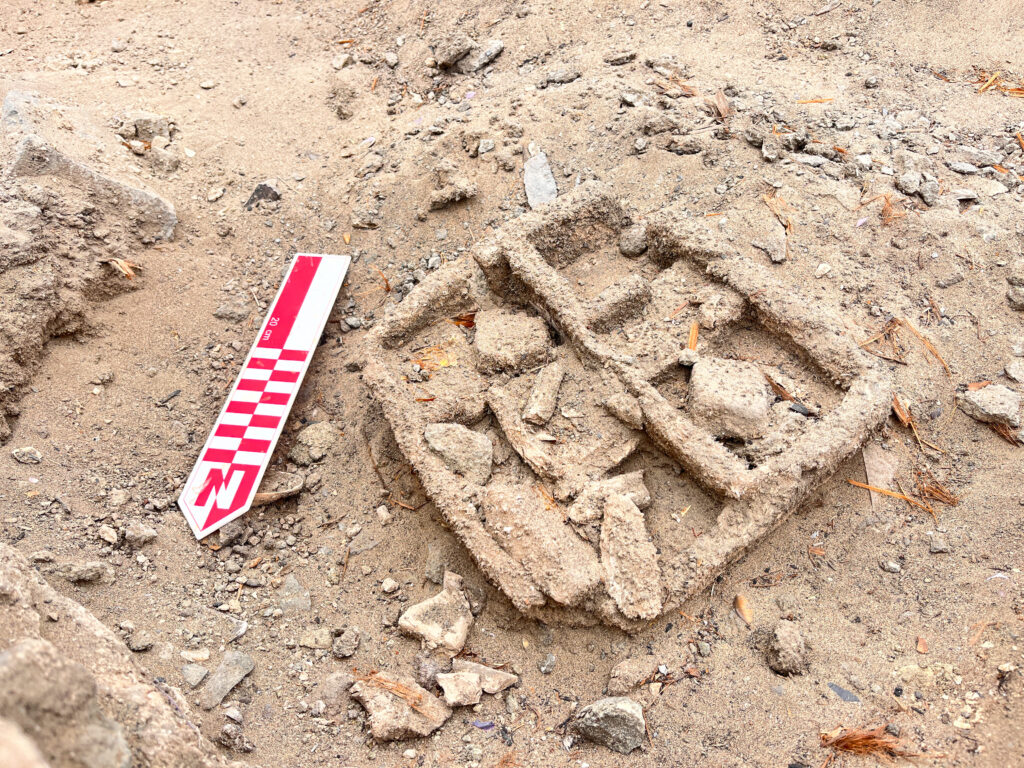

A Discovery of Global Significance
The newly uncovered frog sculpture not only enriches our knowledge of Vichama and Caral but also underscores the global importance of Peru’s archaeological heritage. As climate change and water scarcity remain pressing challenges today, the symbolism of frogs as bringers of rain and life carries a powerful resonance across millennia.
“This discovery reminds us that ancient societies faced environmental struggles much like our own,” noted Shady. “Their resilience and ability to embed these concerns into their cultural expressions make them a mirror for today’s world.”
For archaeologists and historians, the sculpture is a rare and invaluable artifact that adds a fresh dimension to the study of early Andean civilizations. It highlights the deep spiritual connection between people, nature, and survival—a bond that remains relevant in the present era.
Cover Image Credit: Peru’s Ministry of Culture