Ancient hunter-gatherers living in what is now China may have been the first people in East Asia to process mustard and use complex tools, according to a new study by an international team of researchers.
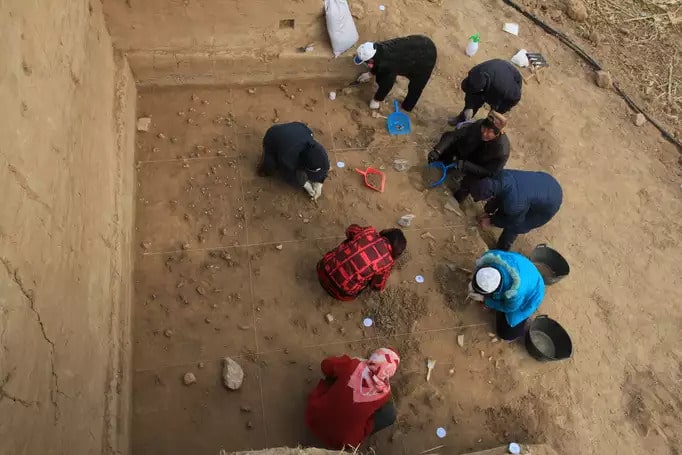
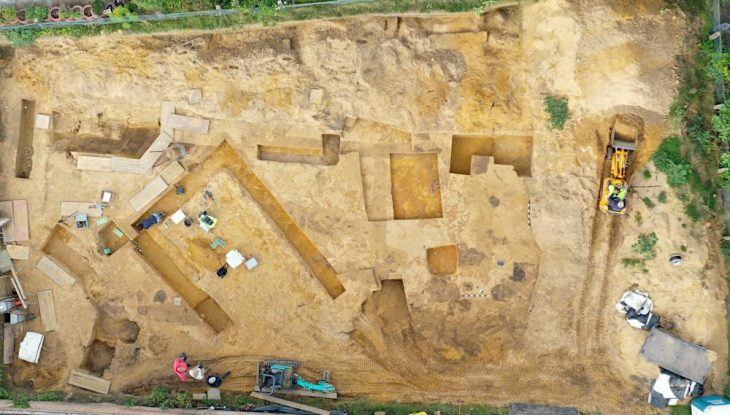
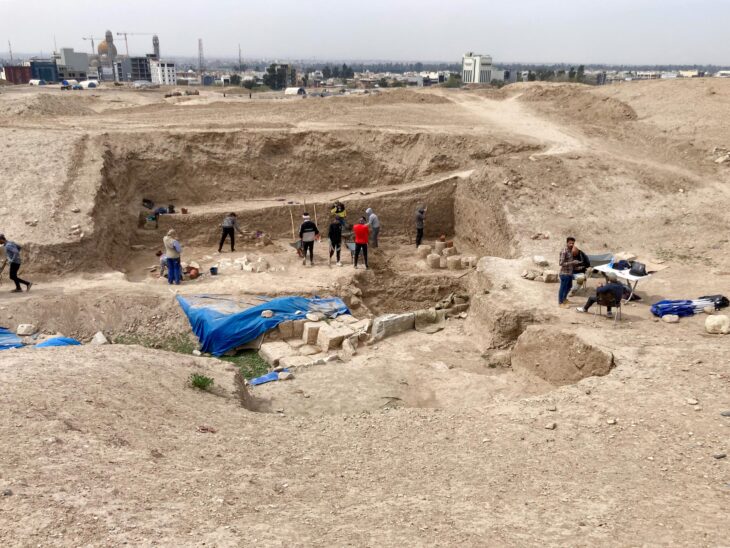
Archaeological excavations at the Xiamabei site in northern China’s Nihewan Basin reveal the existence of innovative behaviors and unique toolkits.
A new study describes with the earliest known evidence of ochre processing in Eastern Asia and a set of distinct blade-like stone tools, Xiamabei contains cultural expressions and features that are unique or exceedingly rare in northeastern Asia.
Describing their discovery in the journal Nature, researchers say that the recovered artifacts provide new insights into how human culture and technology spread across the globe as Homo sapiens populations expanded out of Africa.
Analysis by researchers from the University of Bordeaux, led by Francesco d’Errico, indicates that different types of ochre were brought to Xiamabei and processed through pounding and abrasion to produce powders of different color and consistency, the use of which impregnated the habitation floor. Ochre production at Xiamabei represents the earliest known example of this practice in Eastern Asia.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
40,000 years ago, the stone tools at Xiamabei reflect a distinct cultural adaption for northern China. Because little is known about stone tool industries in Eastern Asia until around 29,000 years ago, when micro blades became the dominant technique, the Xiamabei discoveries give important insights into toolmaking industries during the important transition era.
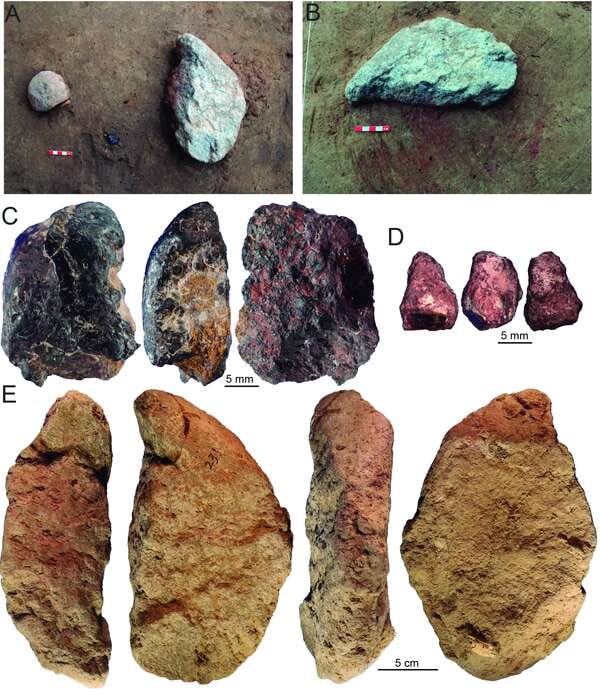
Researchers also discovered 382 tools significantly more complex than those found at any neighboring site. Produced using two different knapping techniques, these multipurpose implements are described as being “miniaturized,” with over half measuring less than 20 millimeters (0.8 inches).
Commenting on the significance of these findings, study author Dr Shixia Yang explained in a statement that “the ability of hominins to live in northern latitudes, with cold and highly seasonal environments, was likely facilitated by the evolution of culture in the form of economic, social and symbolic adaptations.”
“The finds at Xiamabei are helping us to understand these adaptations and their potential role in human migration.”
The researchers said that records from East Asia show that various adaptations took place when modern humans entered the region about 40,000 years ago. In their write-up, they explain that modern humans are believed to have arrived in the region around 40,000 years ago, although the nature of their interactions with other local hominins – such as Neanderthals and Denisovans – remains a mystery.
Given the unique nature of Xiamabei, the authors of the new paper argue that the archaeological record does not fit with the idea of continuous cultural innovation, or of a fully formed set of adaptations which enabled early humans to expand out of Africa and around the world.
“Our findings show that current evolutionary scenarios are too simple,” says Michael Petraglia of the Max Planck Institute in Jena, “and that modern human, and our culture, emerged through repeated but differing episodes of genetic and social exchanges over large geographic areas, rather than as a single, rapid dispersal wave across Asia.”
Cover Photo: © Fa-Gang Wang